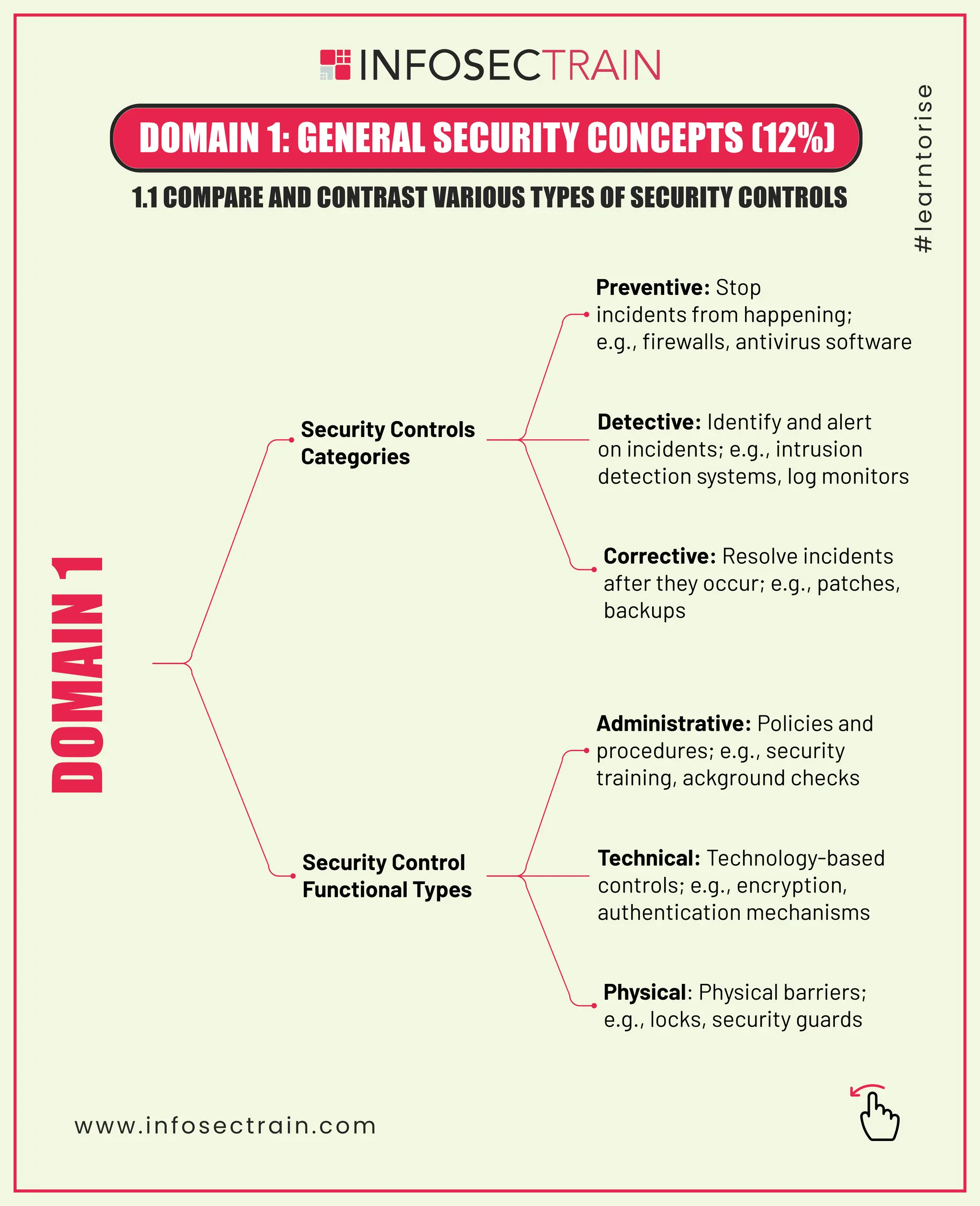
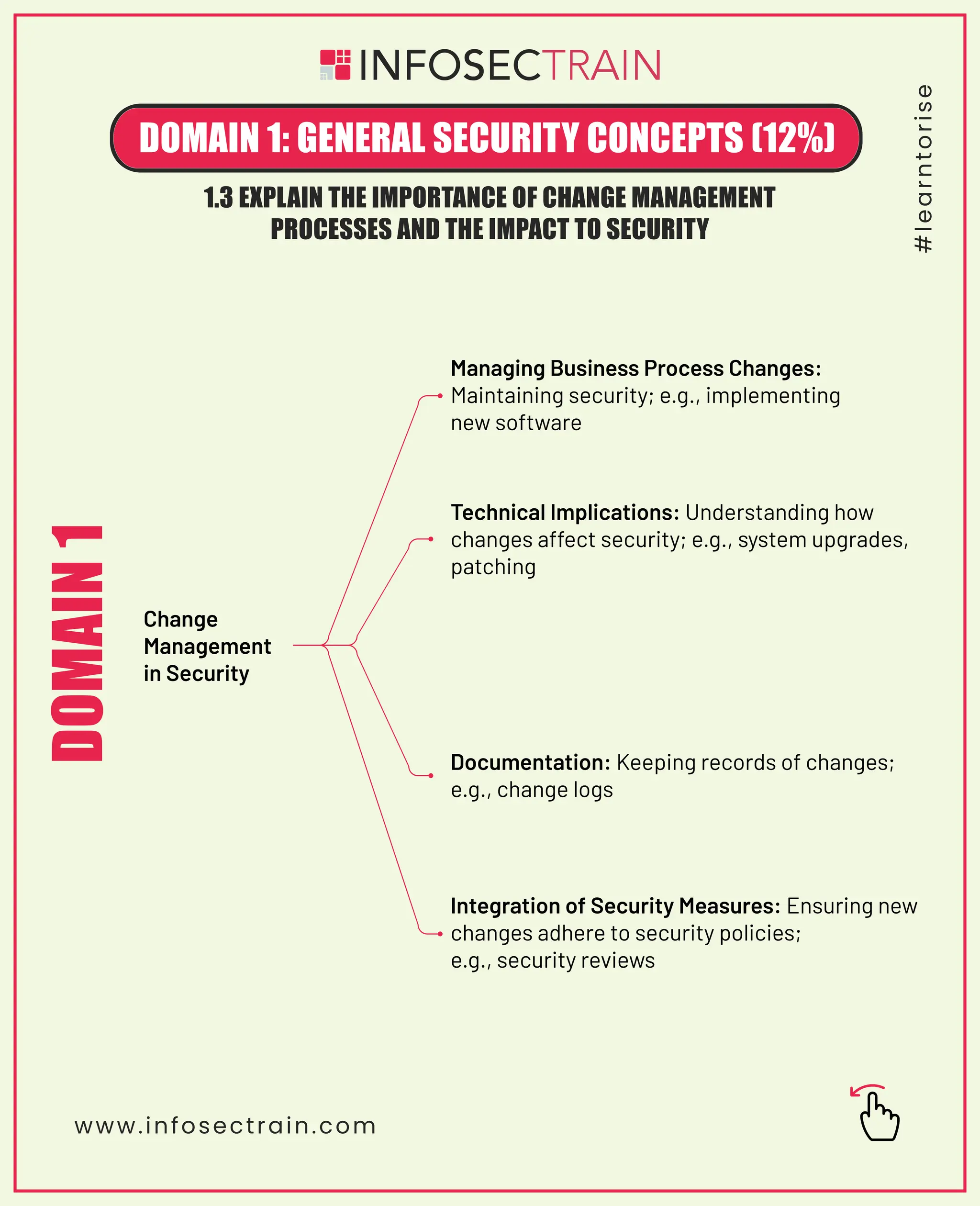
The document outlines various categories of security controls including preventive, corrective, detective, administrative, physical, and technical types. It covers fundamental security concepts such as confidentiality, integrity, availability, and the importance of change management and cryptographic solutions. Additionally, it highlights key principles like the zero trust model and the significance of managing business process changes to maintain security.