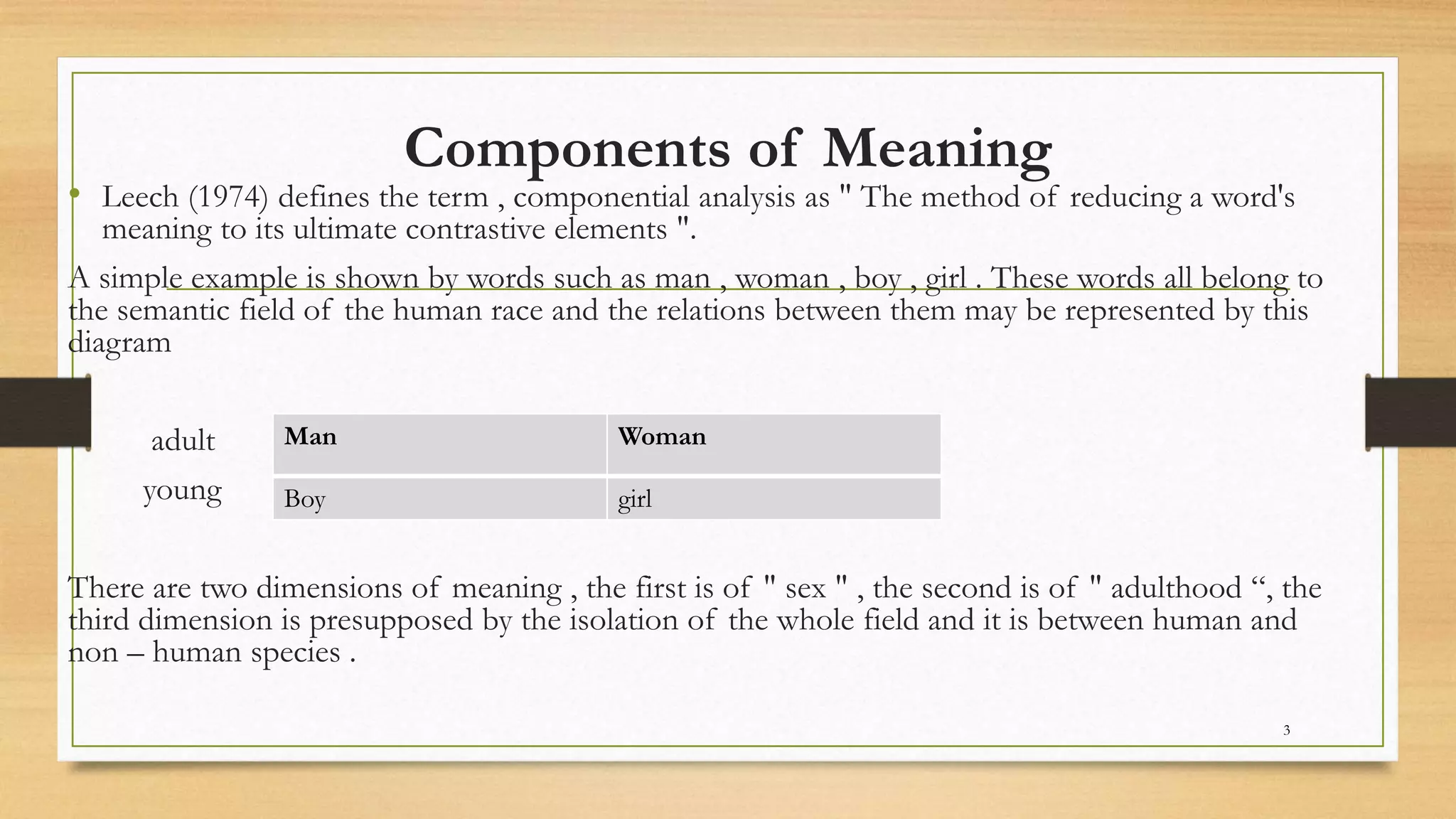
This document discusses componential analysis, which is a method proposed by structural semanticists to analyze word meanings. It breaks down a word's meaning into semantic features or components. Componential analysis provides insight into word meanings and relationships between related words. It analyzes dimensions like gender, age, etc. for related words. Plus and minus signs indicate whether a feature is present or absent in a word's meaning. Componential analysis has advantages like determining meaning acceptability and analyzing polysemy. However, it does not handle all semantic relations equally well.


![Components of Meaning cont.4
• Plus and minus signs are used to indicate whether a certain semantic feature is present
or absent in the meaning of a word, and these feature symbols are usually written in
capitalized letters.
• Man [+HUMAN,+ADULT,+MALE]
Woman[+HUMAN, +ADULT, -MALE]
• Boy[+HUMAN, -ADULT, +MALE]
• girl[+HUMAN,-ADULT,-MALE]
• By using such formulate , we can show the synonymy of two items , for example : adult
and grown up , can be given the same definitions + human , + adult although they differ
in stylistic meaning .
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/componentialanalysisofmeaning-221119083648-d25cc881/75/Componential-Analysis-of-Meaning-pptx-4-2048.jpg)
![Components of Meaning cont.5
• A brief illustration of the principles of componential analysis is as following:
we can take the terms siège, pouf, tabouret, chaise, fauteuil, and canapé
(a subfield of the field of furniture terms in French).
• The word which acts as a superordinate to the field under consideration is
siège, ‘seating equipment with legs.’ If we use the dimensions s1 ‘for seating,’
s2 ‘for one person,’ s3 ‘with legs,’ s4 ‘with back,’ s5 ‘with armrests,’ s6 ‘of
rigid material,’ then chaise ‘chair’ can be componentially defined as [+ s1, +
s2, + s3, + s4, − s5, + s6], and canapé ‘sofa’ as [+ s1, − s2, + s3, + s4, +
s5, + s6], and so on.
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/componentialanalysisofmeaning-221119083648-d25cc881/75/Componential-Analysis-of-Meaning-pptx-5-2048.jpg)








