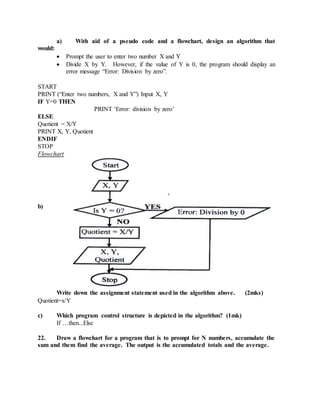
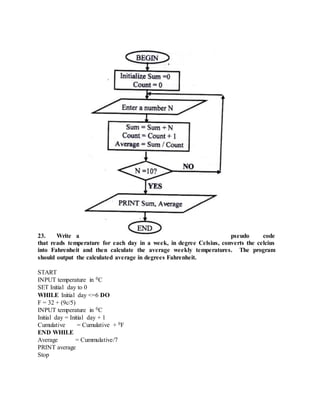
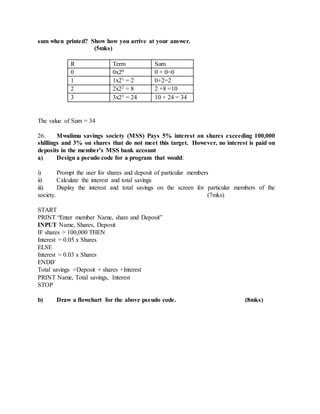
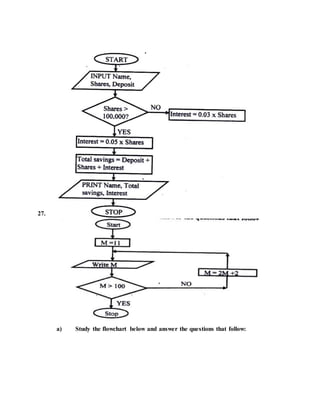
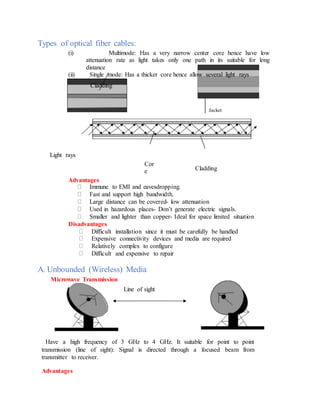
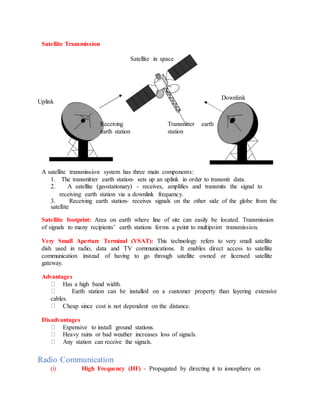
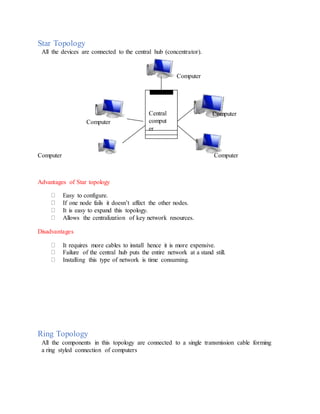
This document provides an overview of key topics in computer education, including:
- The importance of equal access to education and how technology can help address disparities.
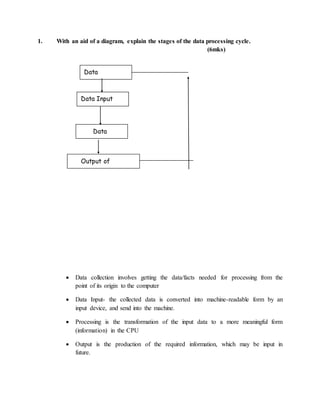
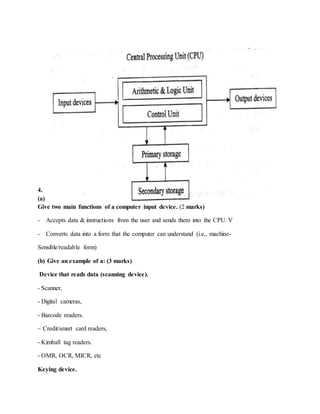
- An introduction to the parts of a computer, including input/output devices and the central processing unit.
- Classifications of computers by size, purpose, and functionality.
- The development of computers from first to fifth generation and how the technology has advanced.
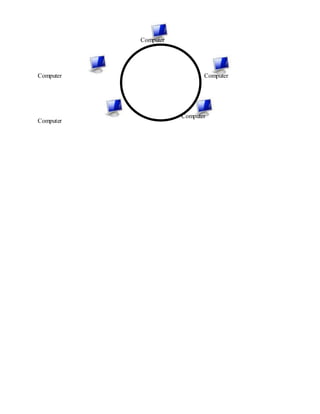
- Common areas where computers are used, such as offices, education, communication, and more.
- Safety precautions that should be followed when working in a computer laboratory.



























































































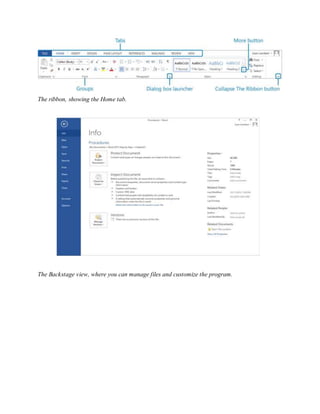
































































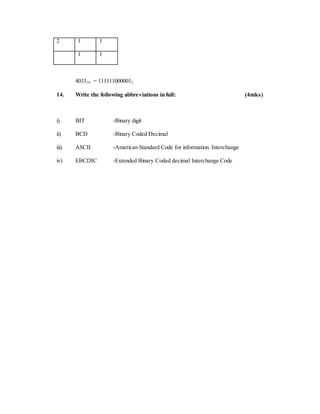
![2 1 0
1 1
410 = 1002
Step 2: Add binary notations
1002
112 +
1112 1112
3 Rem
2 1 1
1 1
310 = 112
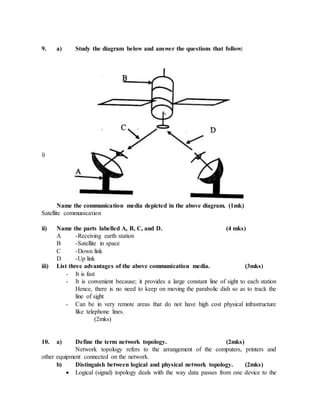
d) Convert 101000000011111112 to its Hexadecimal equivalent. (2mks)
20
23
22
21
20
23
22
21
20
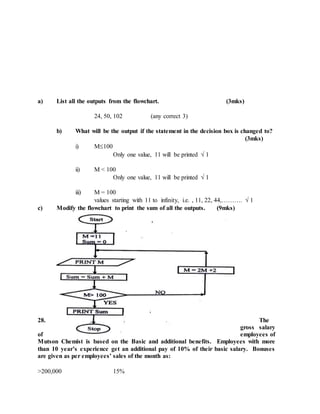
23
2+21
20+
23
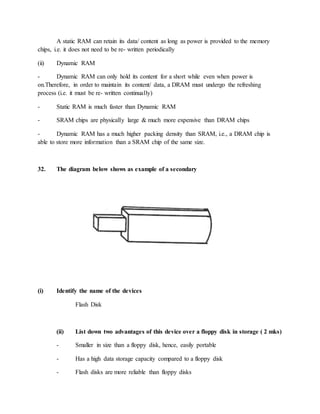
22
21
20
1 0100 0000 0111 1111
= [1] + [4] + [0] + [4+2+1] +[8+4+2+1]
=[1] +[4] +[0] +[7] +[15]
= 1407F16
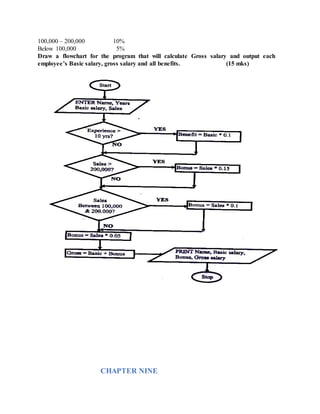
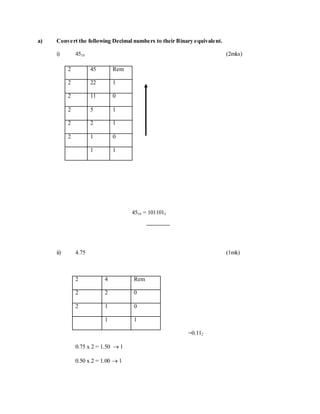
7. a) State one use ofhexadecimal notation in a computer. (1mk)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/completecomputerstudiesnotes-220524064854-4cf50f26/85/COMPLETE-COMPUTER-STUDIES-NOTES-doc-163-320.jpg)
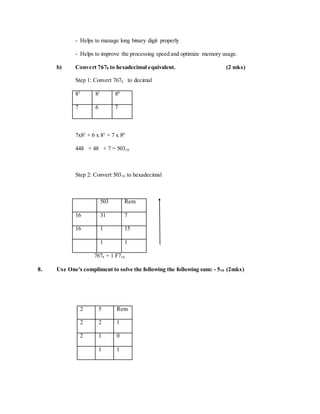
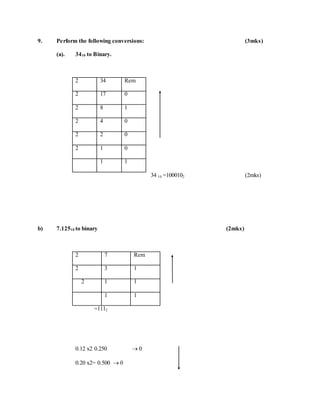
![0.500x2=1.000 1
= 0.0012
= 111.0012 (1mk)
c) 1011012 to a base 10 number.
25
24
23
22
21
20
1 0 1 1 0 1
= (1x25
) + (1x23
) + (1x22
) + (1x20
)
=32 + 8 + 4+ 1
=4510
d) 10.112 to decimal (2mks)
= (1x21
) + (0x20
) (1x2-1
) + (1x2-2
) 1
= 2 + 0 ½ + ¼
= 2. {0.5 + 0.25} = 2.7510 1 (3mks)
e) 20.216 to decimal (2mks)
161
161
160
7 0 2
= [2x161
] + [ 0x160
] [2x (1/16)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/completecomputerstudiesnotes-220524064854-4cf50f26/85/COMPLETE-COMPUTER-STUDIES-NOTES-doc-166-320.jpg)
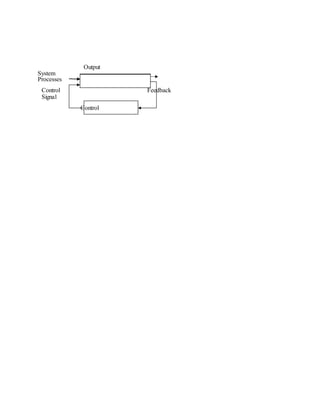
![=32. [0.125]
= 32.12310
f) 7AB16 to decimal (2mks)
162
161
160
7 A B
= [7x162
] + [10x 161
] + [11x160
]
=1792 + 160 +11 = 196310
g) 0.111011.0102 to Octal (2mks)
22
21
20
21
20
21
000 1 1 1 0 1 1 . 0 1 0
= {4 + 2+ 1} {2+1} {2 +1} {2}
=73.28
10. Convert 57.410 to its Octal equivalent (2mks)
8 57 Rem
8 7 1
8 7 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/completecomputerstudiesnotes-220524064854-4cf50f26/85/COMPLETE-COMPUTER-STUDIES-NOTES-doc-167-320.jpg)

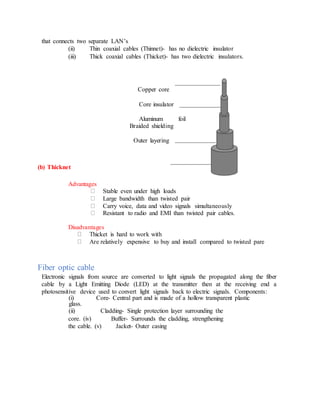
![00001000
11111011 +
(1)00000011 =1000000112 (2mks)
12. Convert 7AE16 to a decimal number. (2mks)
Step 1
162+
161
160
7 A E
=[7x162
] + [12x161
] + [1x160
]
= 3840 + 192 +1 = 403310
Step 2
2 4033 Rem
2 2016 1
2 1008 0
2 504 0
2 252 0
2 126 0
2 63 0
2 31 1
2 15 1
2 7 1
2 3 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/completecomputerstudiesnotes-220524064854-4cf50f26/85/COMPLETE-COMPUTER-STUDIES-NOTES-doc-169-320.jpg)