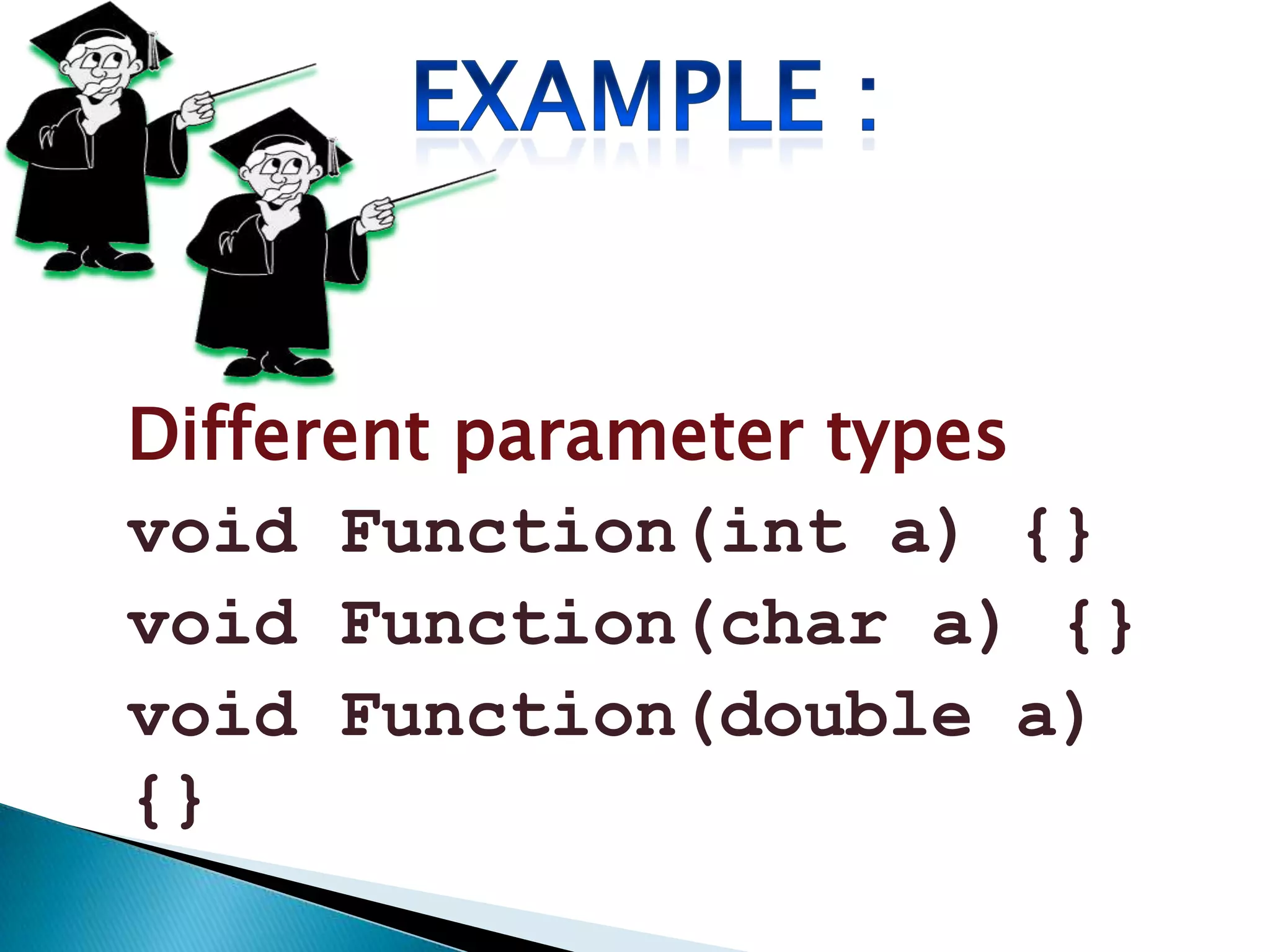
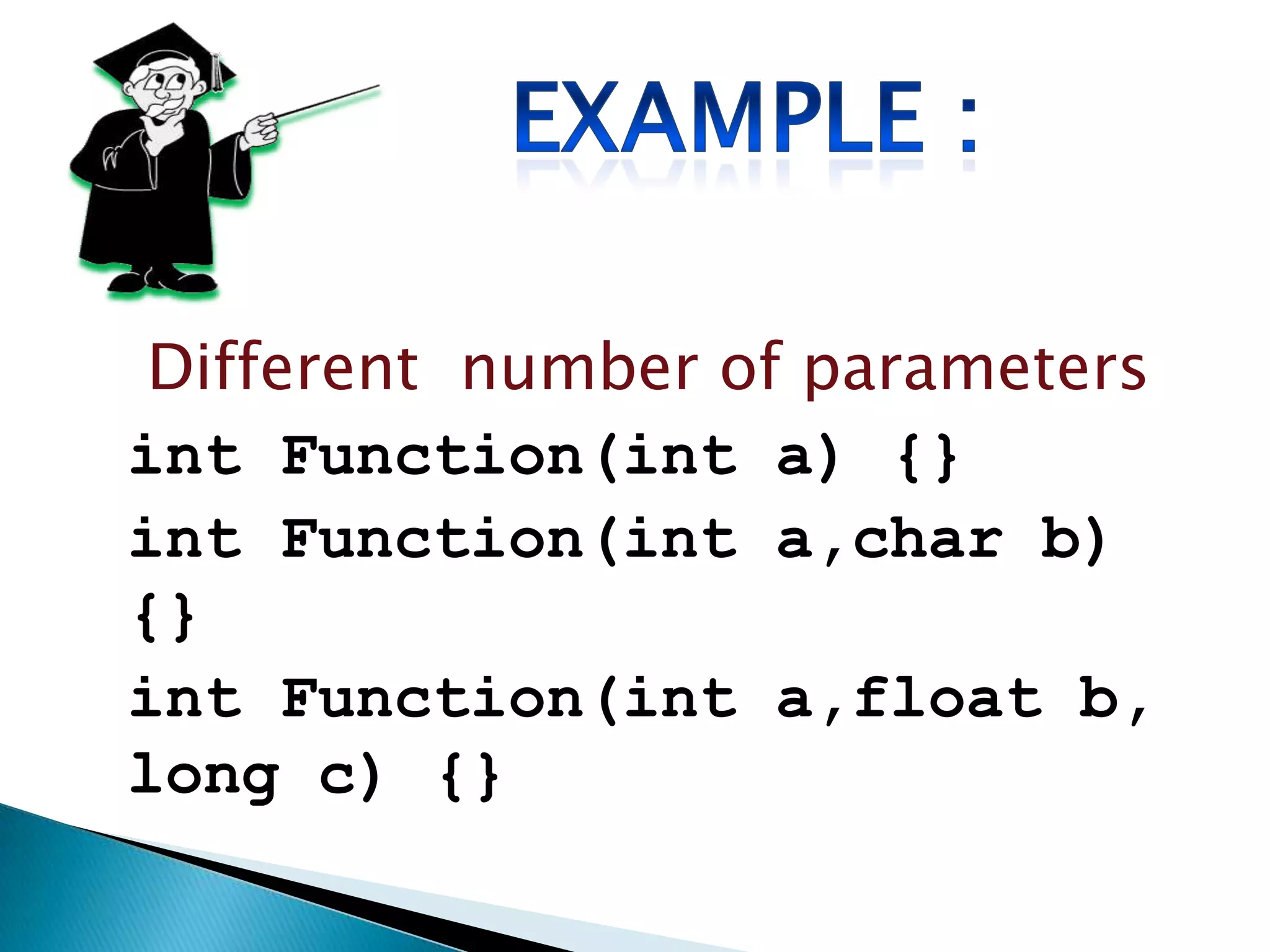
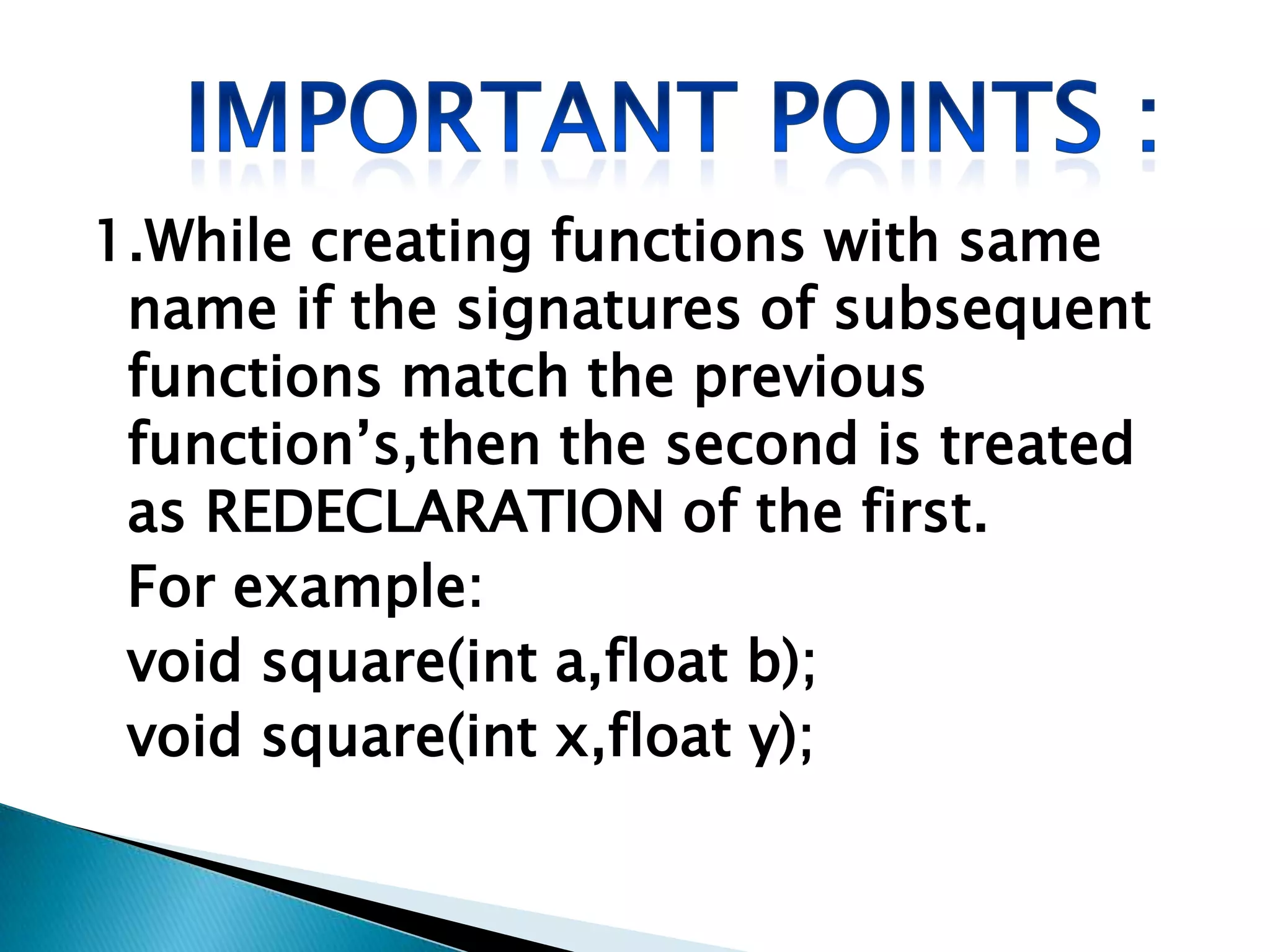
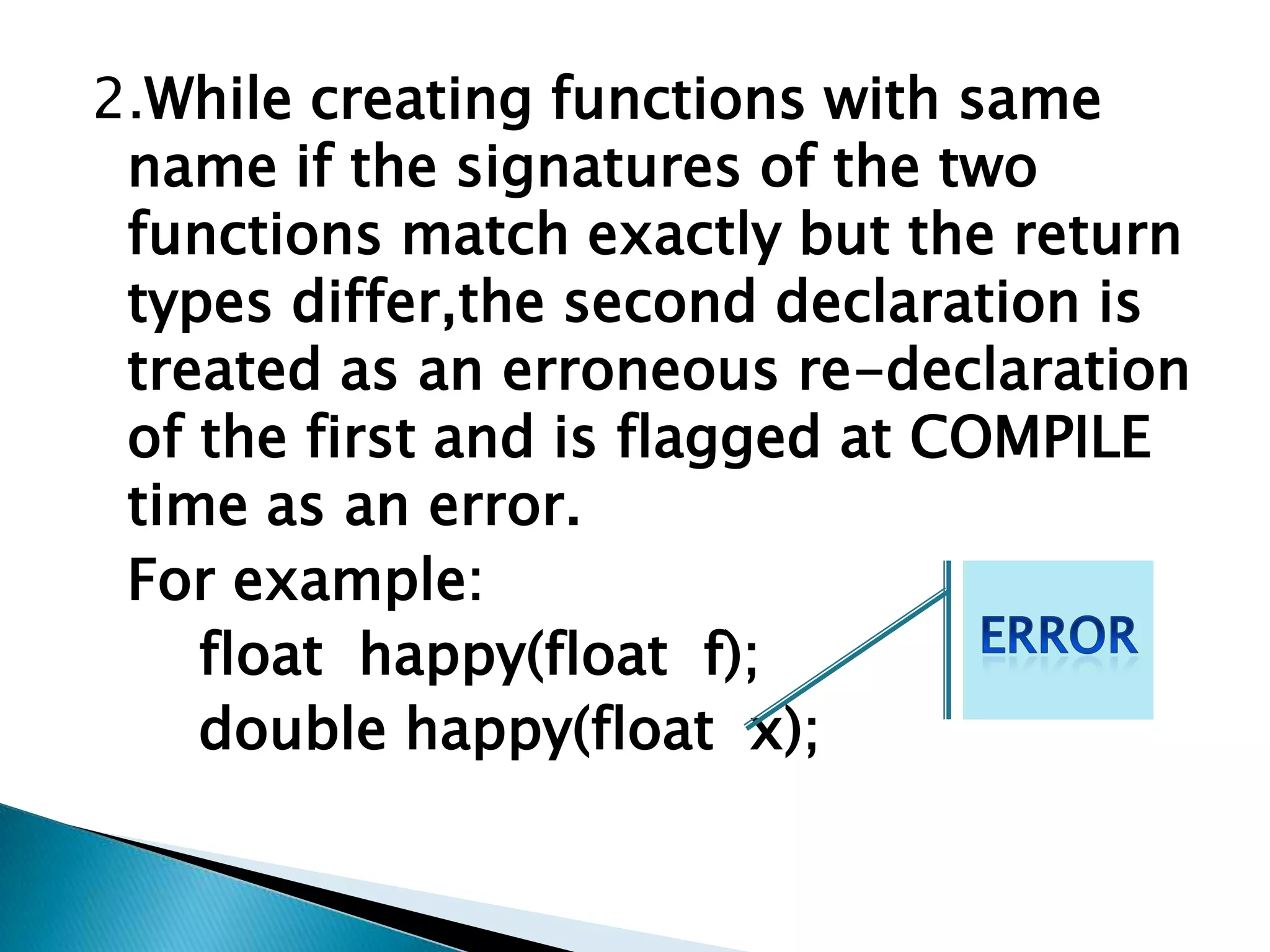
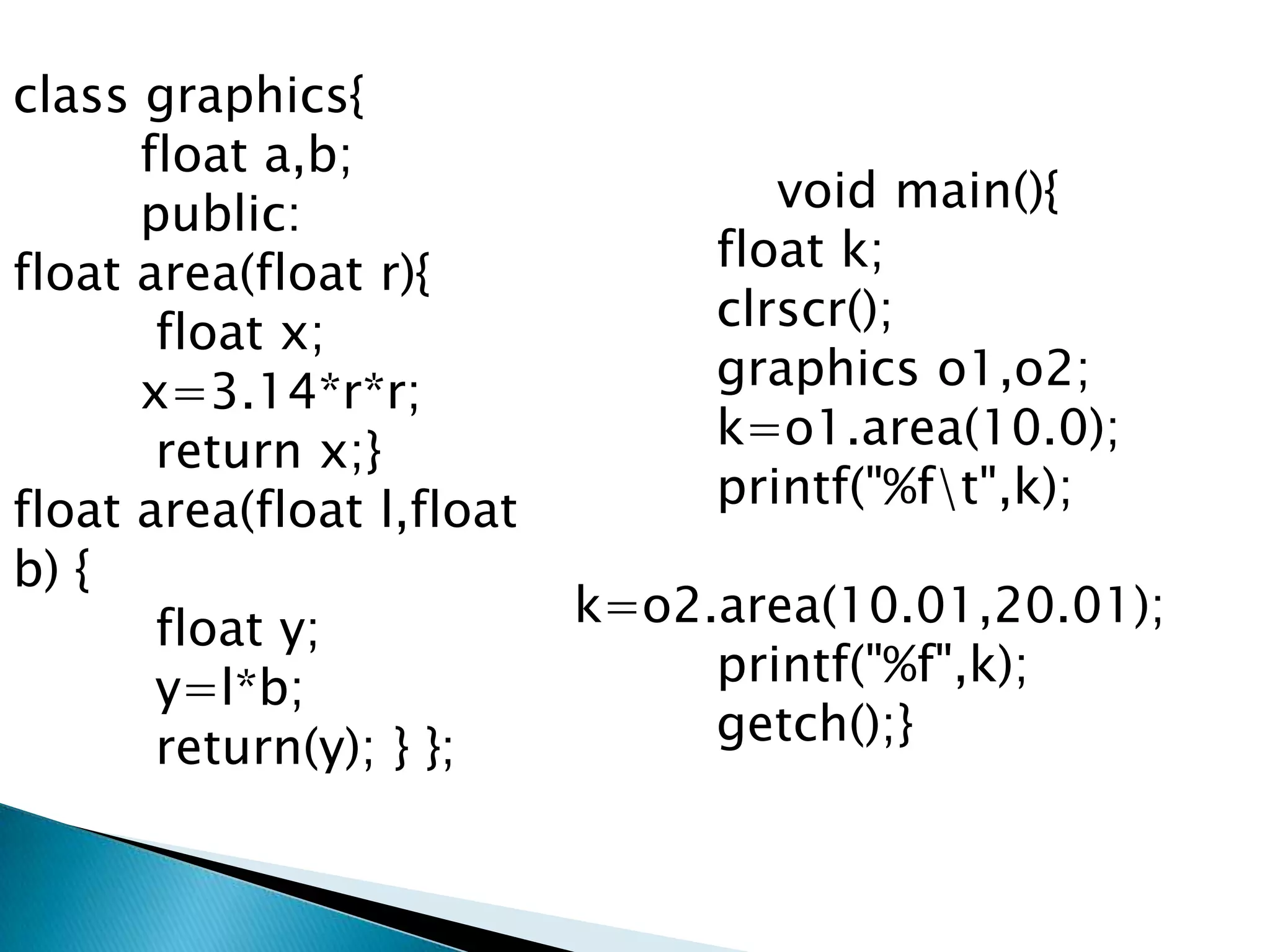
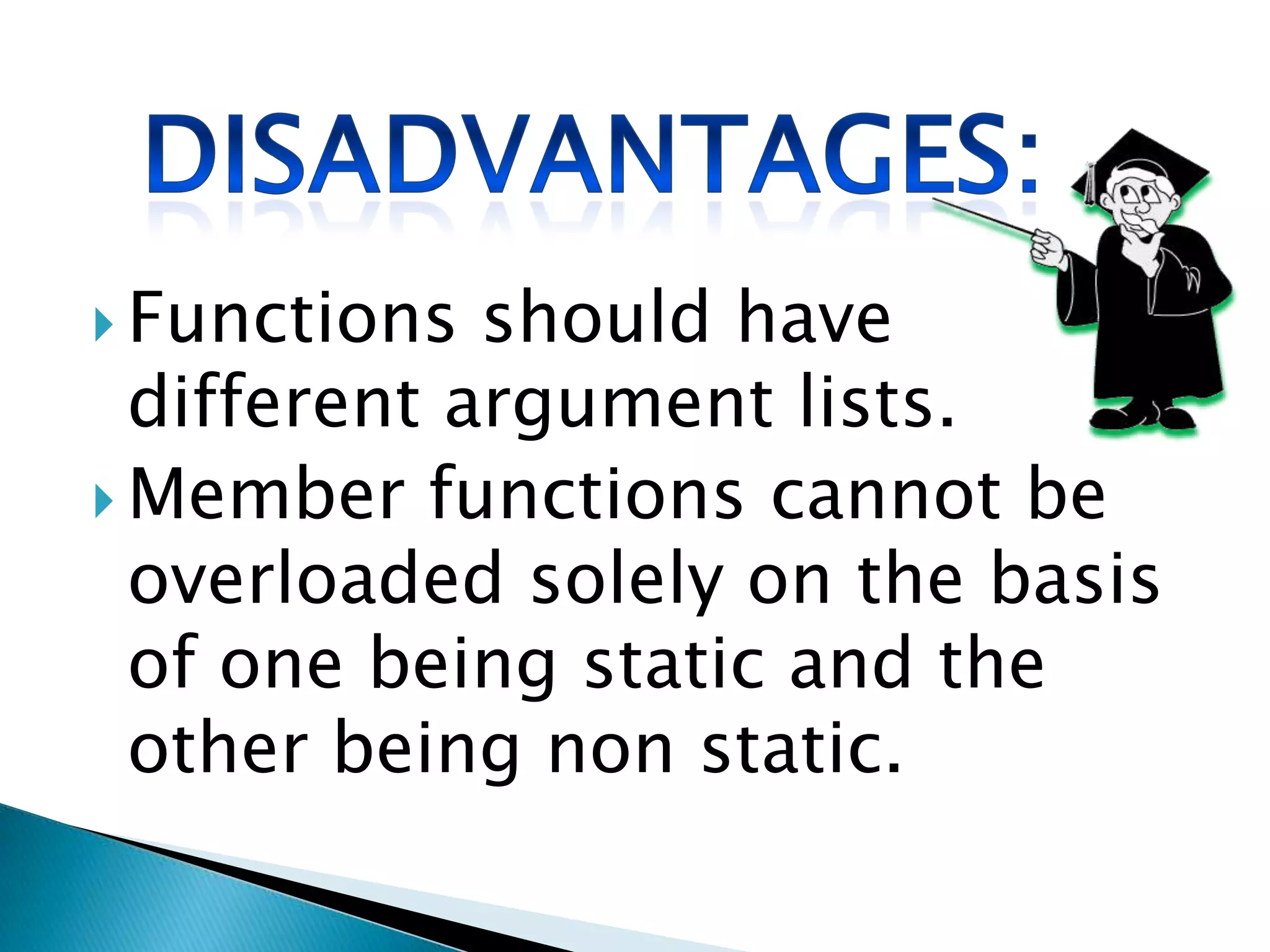
Polymorphism allows an entity to take on multiple forms. In C++, polymorphism is implemented through overloaded functions, overloaded operators, and virtual functions. Function overloading allows functions to have the same name but different parameters, either by type or number of arguments. Overloaded functions must have the same name but different signatures to distinguish them. Classes can contain overloaded member functions.