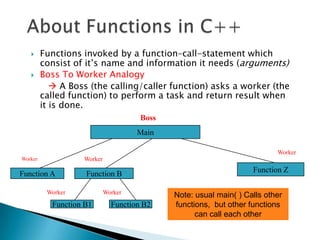
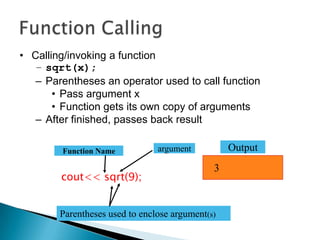
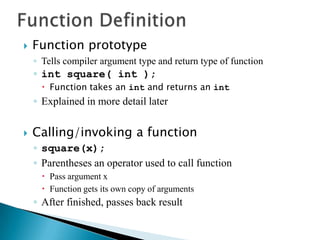
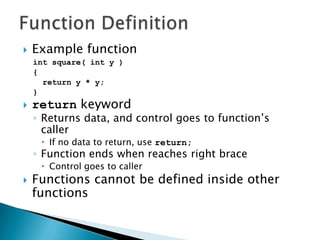
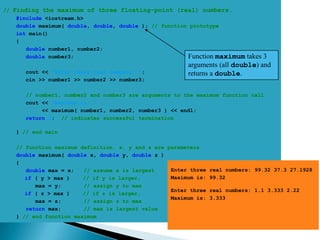
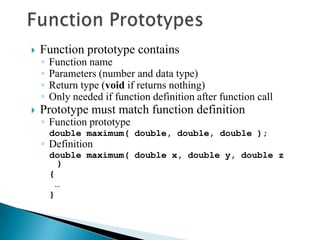
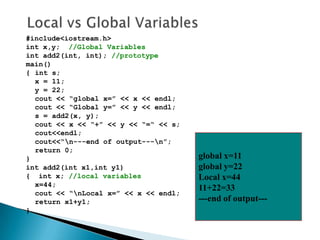
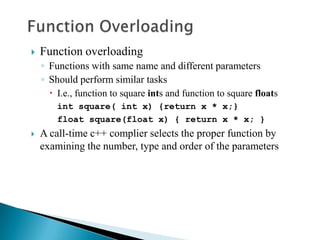
The document contains information about Tarandeep Kaur, including her name, section, and roll number. It then lists and describes various topics related to functions in C++, including definition of functions, function calling, function prototypes, void functions, local vs global variables, function overloading, and recursion. Examples are provided to illustrate function calling, passing arguments, return values, and differences between call by value and call by reference.