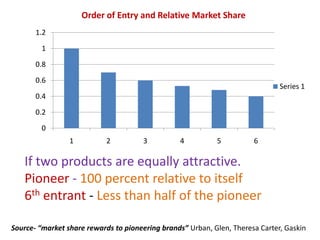
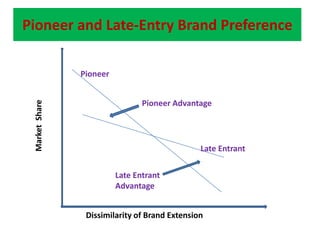
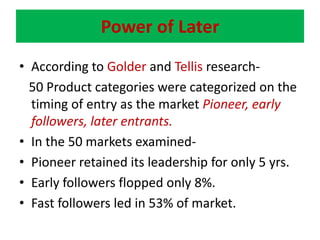
This document discusses competitive brand strategies for pioneers and late entrants. It notes that pioneers have advantages like preference formation, category association, awareness and recall, and preemptive positioning that allow them to gain a large initial market share, often over half. However, late entrants can also succeed through strategies like fast following the pioneer in a better way, differentiation, or redefining what buyers know about the established brand. Research showed that pioneers typically only retained leadership for 5 years, while early and fast followers often succeeded in leading the market over the long run in over half of cases examined.