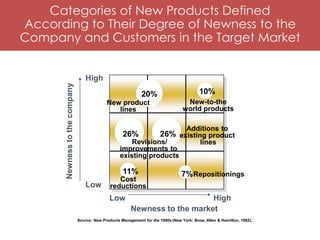
The document discusses marketing strategies during the introduction stage of a new product. It outlines six key strategies: 1) Attracting customers through advertising, PR, and publicity; 2) Inducing customers to try the product through samples and pricing incentives; 3) Engaging in customer education; 4) Strengthening distribution channel relationships; 5) Building availability through trade promotion; 6) Setting pricing objectives to balance investment and market realities. It also categorizes new products based on their newness and discusses advantages of pioneering vs following strategies.
![][Welcome to
Marketing Strategy
Marketing Strategies During The
Introduction Stage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/161125ppt5-161201072317/75/5-2-mlc-introduction-stage-1-2048.jpg)