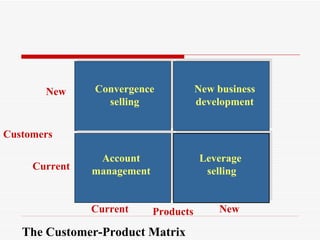
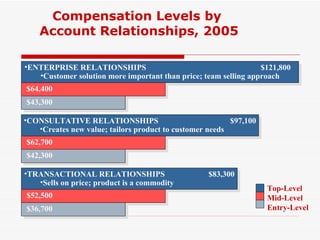
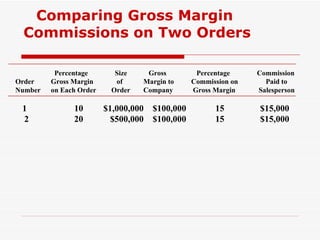
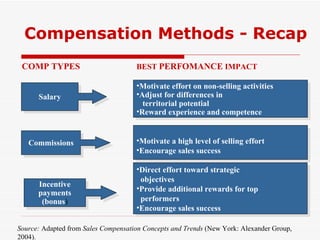
The document discusses various methods for compensating salespeople, including straight salary, straight commission, and combination plans involving salary plus bonuses or commissions. It provides details on the benefits and drawbacks of different compensation types and explores trends toward using incentive payments and customer satisfaction metrics in determining compensation. Sample compensation levels from industry surveys are presented for various sales roles.