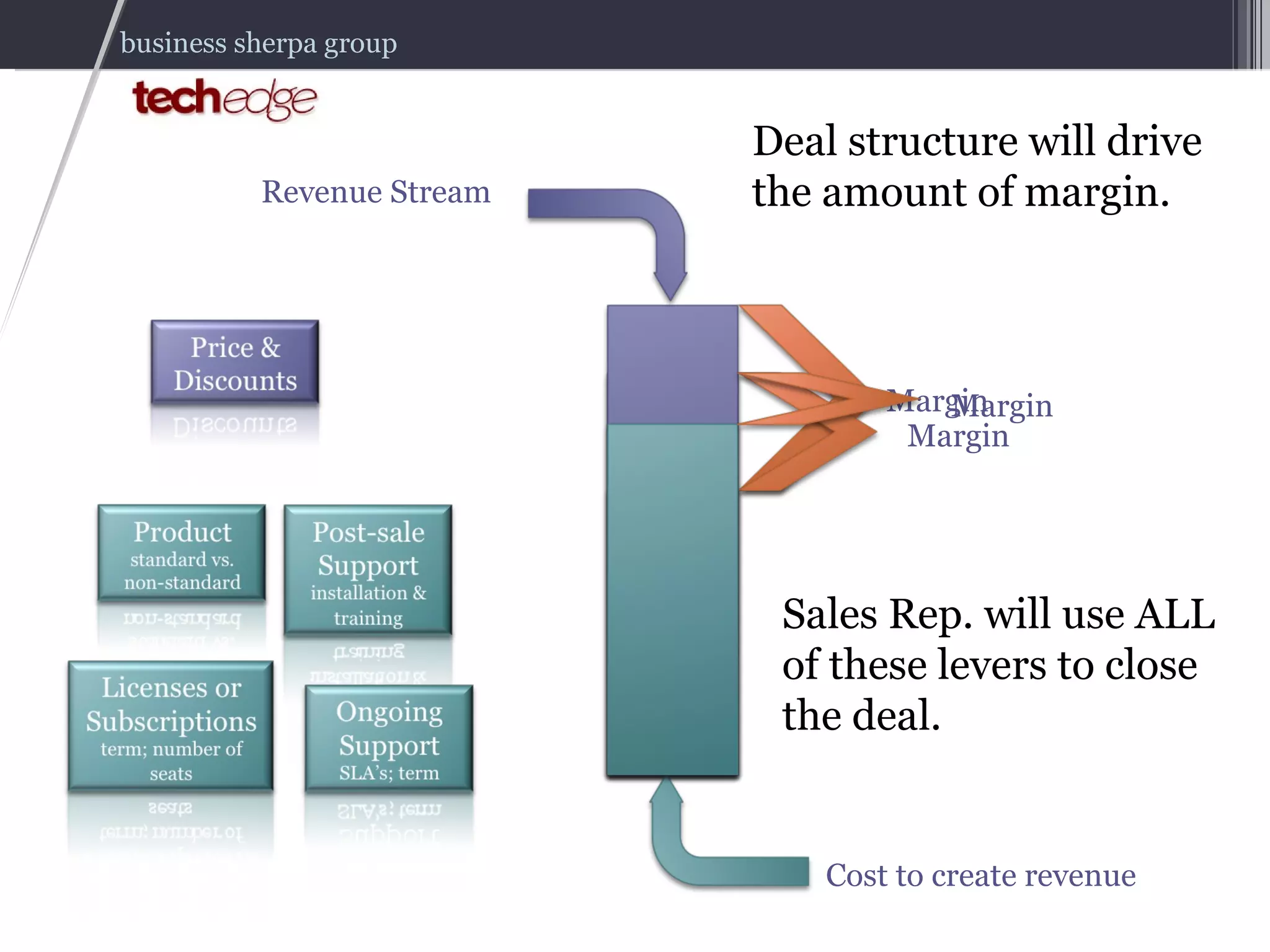
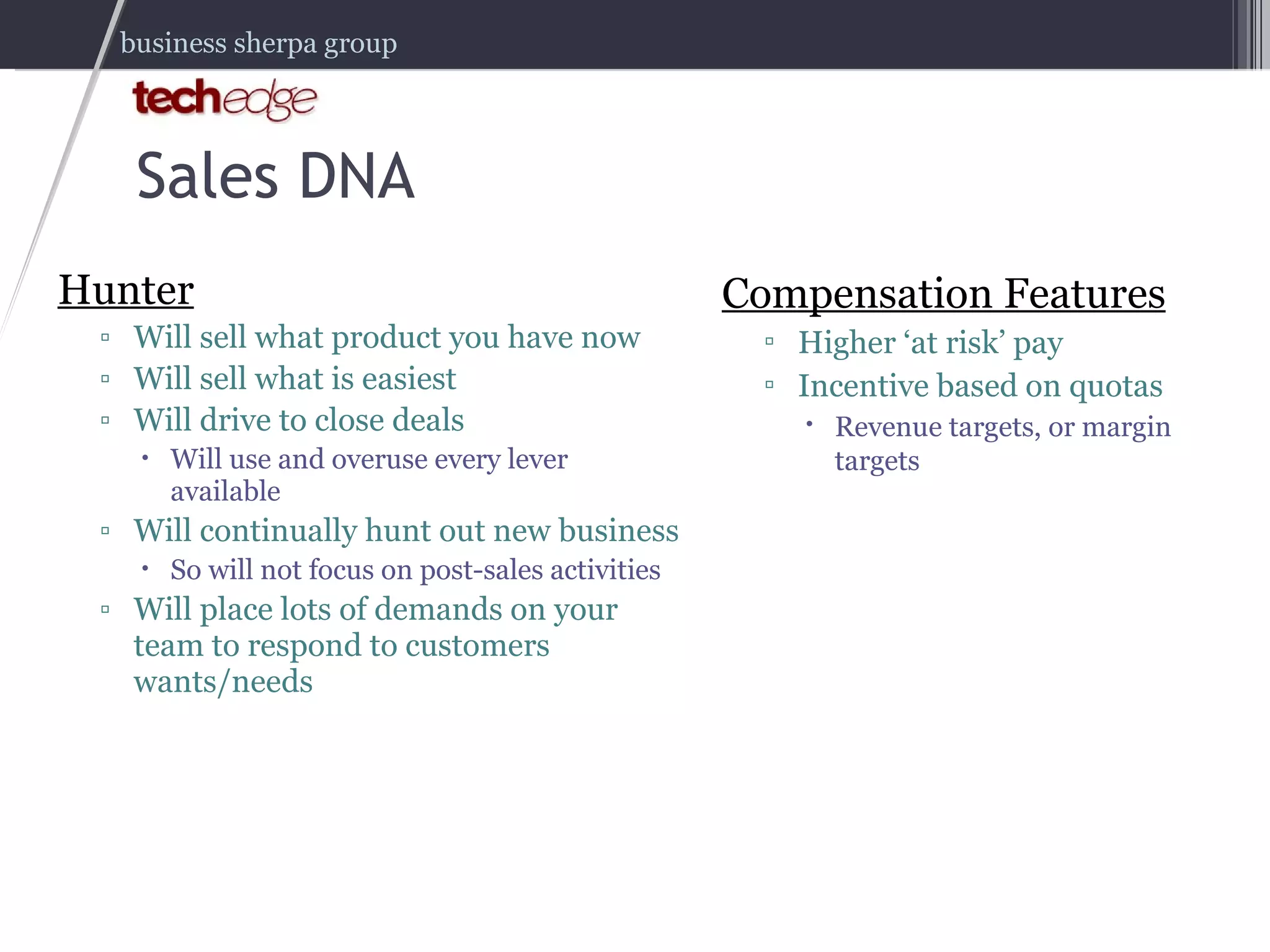
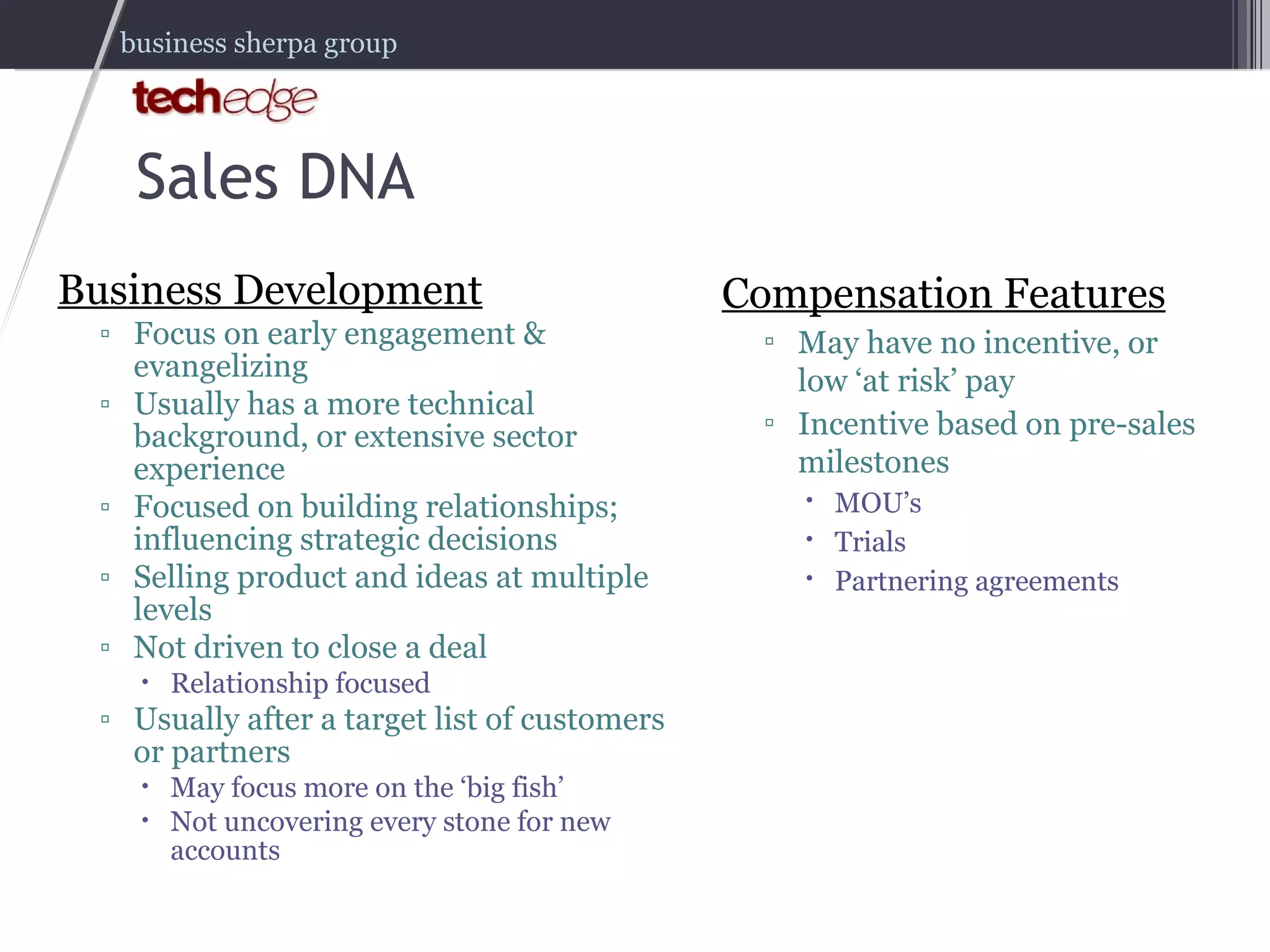
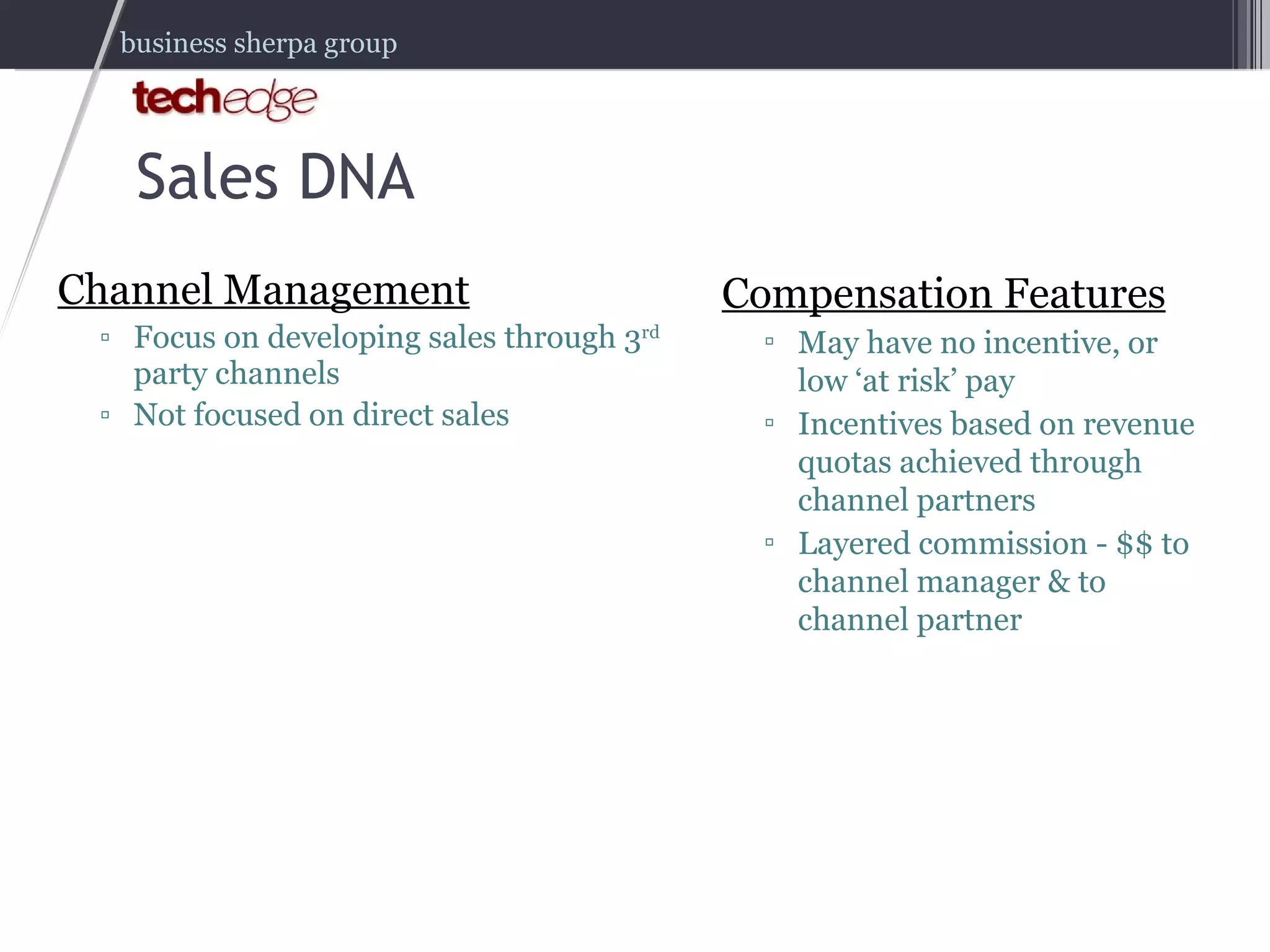
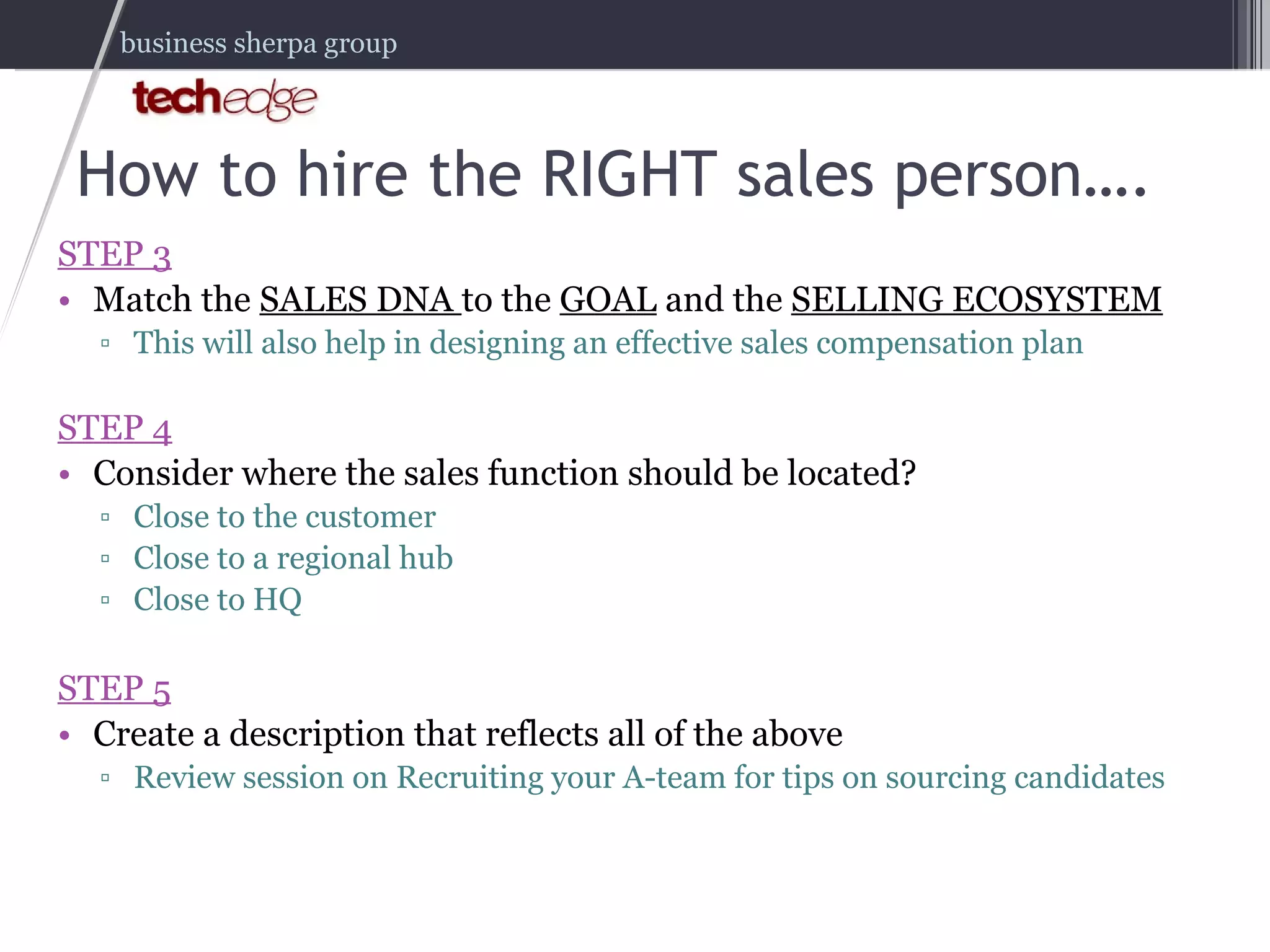
The document outlines strategies for effectively managing and compensating sales teams to boost business revenue. It emphasizes the importance of aligning sales DNA with business goals and the selling ecosystem, as well as creating comprehensive sales compensation plans. It also highlights key lessons learned from real-world experiences in hiring and managing sales professionals.