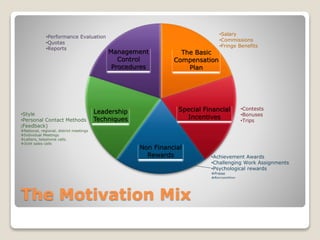
The document provides an overview of motivation and evaluation in sales management, detailing various compensation plans including salary, commission, and bonuses, along with their advantages and disadvantages. It discusses leadership techniques and nonfinancial rewards aimed at motivating sales personnel and the importance of performance evaluation. Additionally, it highlights common communication issues within sales management and provides quizzes on effective communication principles.