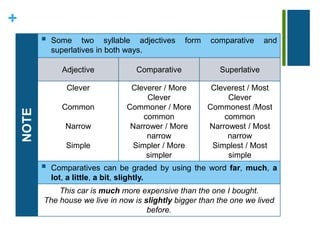
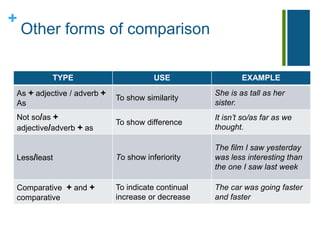
This document discusses the rules for forming comparatives and superlatives in English. It explains that the comparative form uses "than" to compare two objects or people, while the superlative shows which thing has a quality above others. It provides spelling rules for forming comparatives and superlatives depending on the adjective's syllable length and ending. Irregular forms like "good/better/best" are also covered. The document concludes with other forms of comparison like "as," "not so/as," and "less/least."