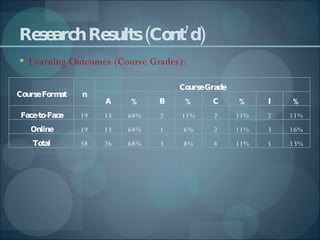
The document outlines two studies: a comparative study examining learner satisfaction and outcomes in online versus face-to-face learning environments, and a non-comparative study evaluating metacognitive knowledge development supported by the Knowcat system. The comparative study involved 38 students, revealing higher satisfaction and better perceptions of interaction and support among face-to-face learners, while the non-comparative study showed that collaboration via Knowcat enhanced students' metacognitive awareness. Both studies utilized specific evaluation instruments, but only quantitative analysis was performed in the first study, and qualitative insights were limited in the second.