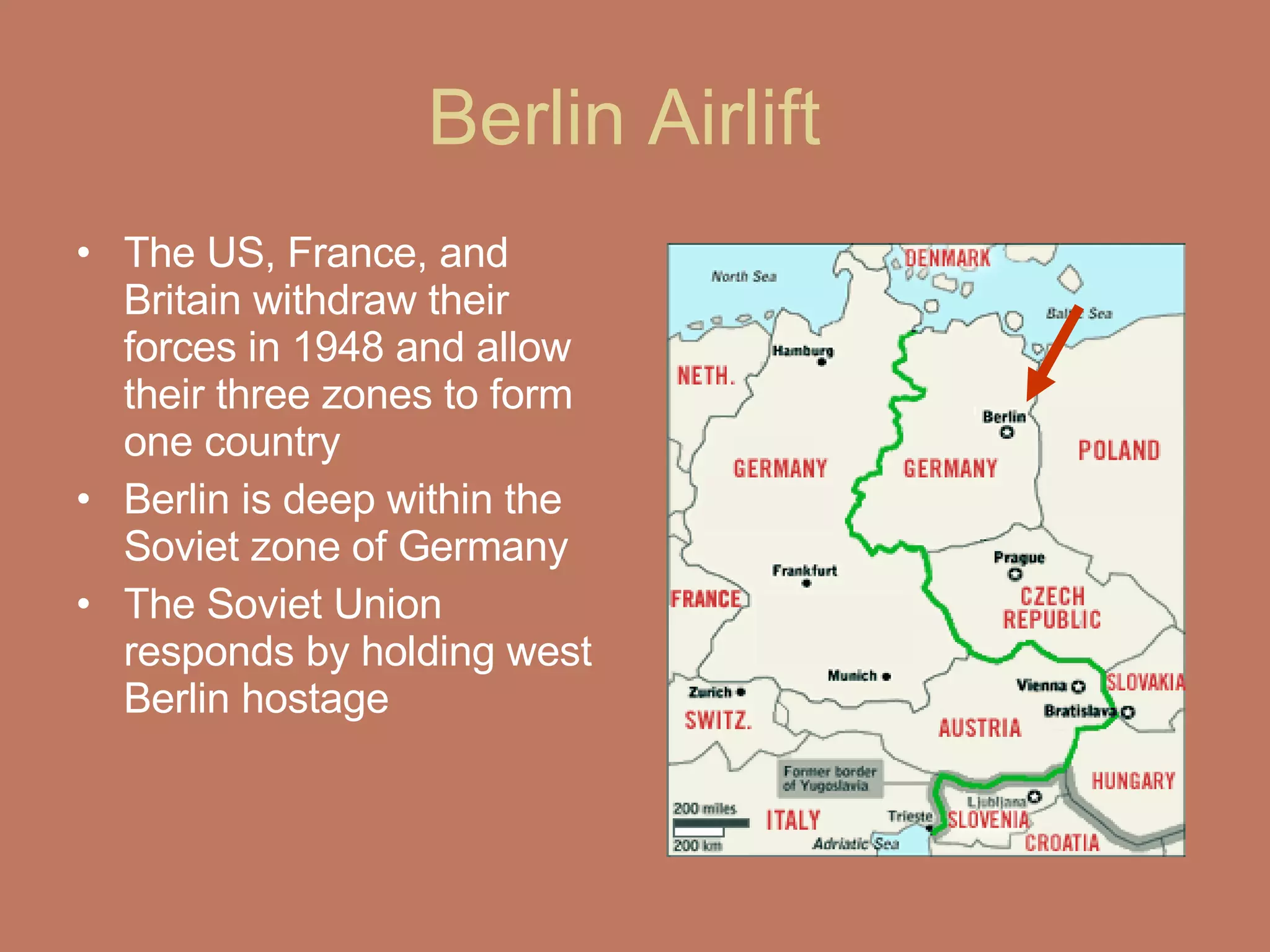
1) The document discusses the origins and escalation of tensions between the US/Western allies and the Soviet Union following World War II, including the Berlin Blockade and Airlift and the formation of opposing military alliances like NATO and the Warsaw Pact.
2) It also covers the development of nuclear weapons by both sides and the beginning of a dangerous arms race, as well as conflicts in areas like China and Korea as the Cold War spread globally.
3) Events in China are discussed in depth, including Mao Zedong's rise to power amid civil war, his radical reforms based on Marxism, and later disastrous social campaigns like the Great Leap Forward and Cultural Revolution.