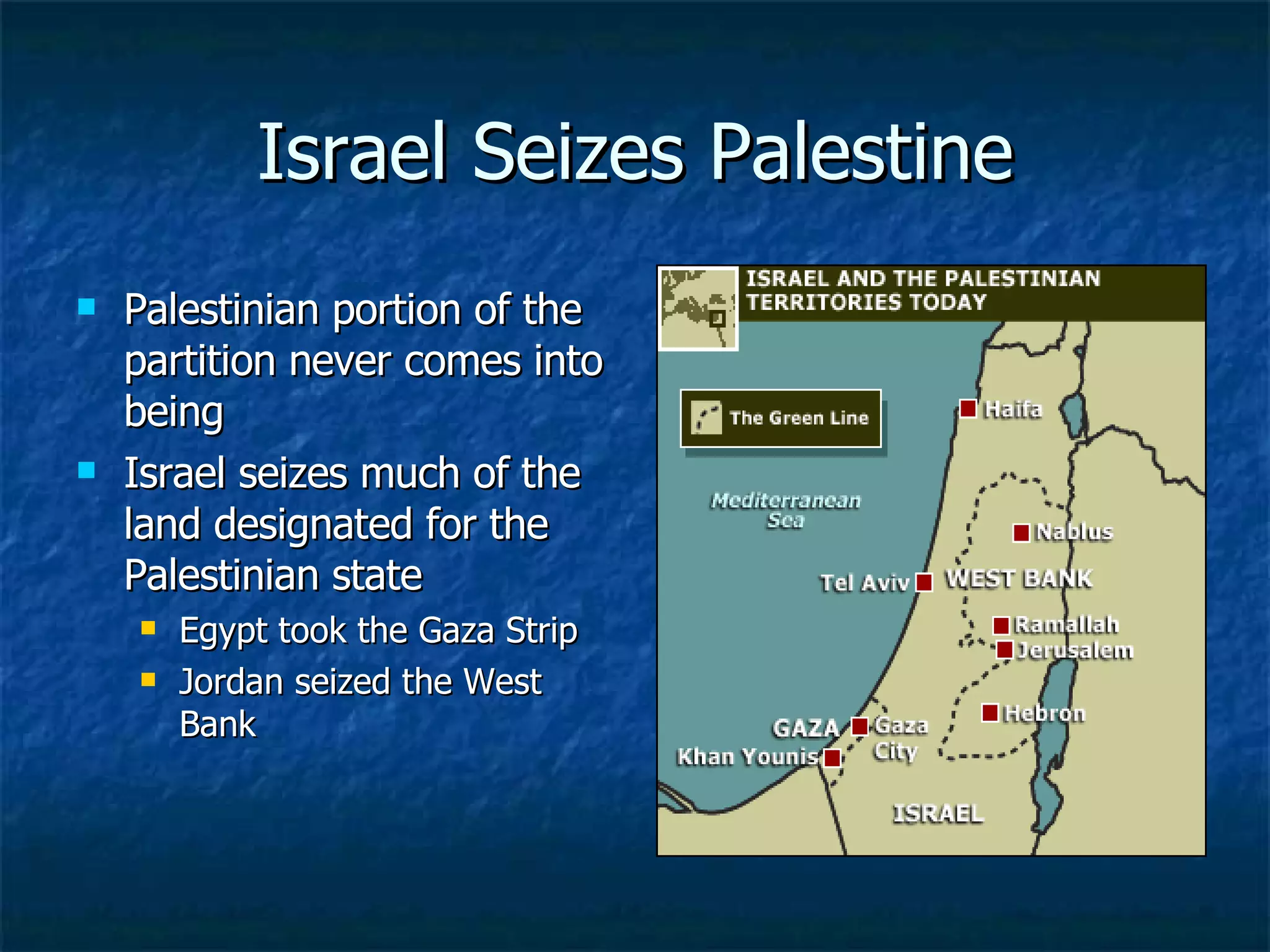
The document provides background information on several topics related to post-World War 2 geopolitics, including the formation of Israel, Palestinian statehood, and ongoing conflicts between Israel and its Arab neighbors. It discusses the British mandate over Palestine after WWI, the UN partition plan that created Israel in 1948, and subsequent wars like the Six Day War of 1967 and Yom Kippur War of 1973. It also outlines diplomatic efforts like the Camp David Accords and Oslo Accords that sought peace agreements.