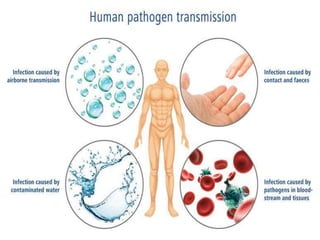
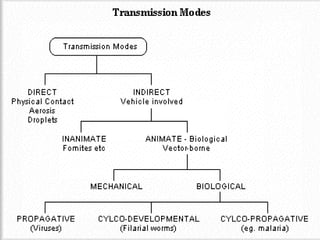
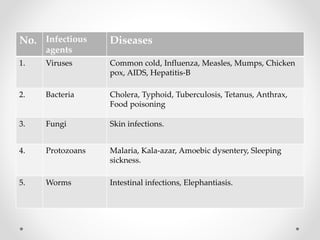
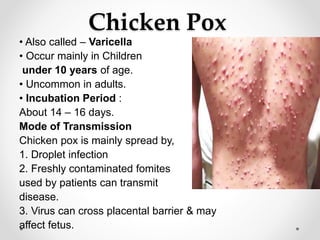
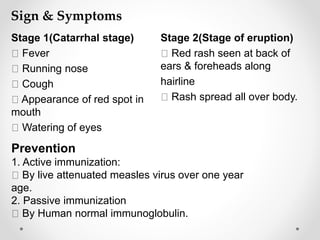
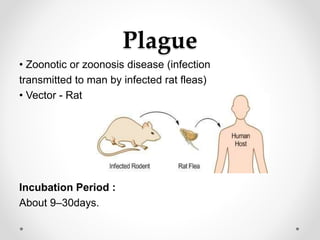
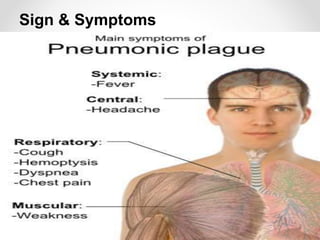
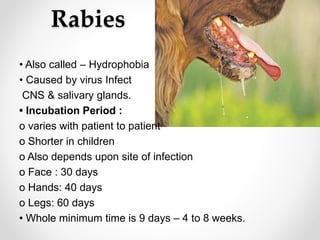
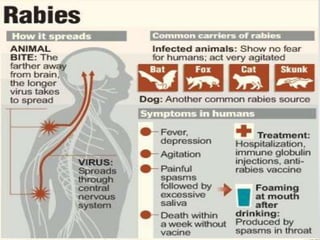
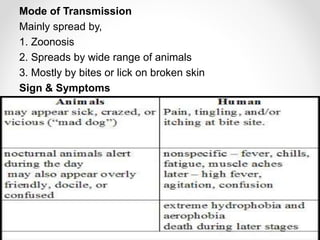
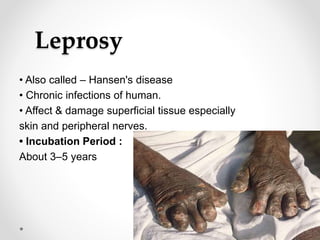
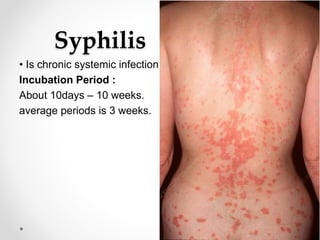
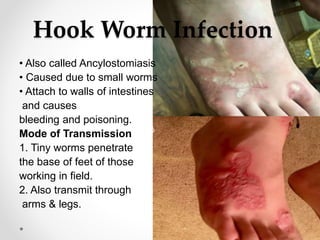
Communicable diseases are infections that can be transmitted from person to person, caused by various pathogens including viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoans, and worms. Common types include respiratory infections like tuberculosis and influenza, sexually transmitted diseases like AIDS and syphilis, and intestinal infections such as cholera and typhoid fever. Prevention methods vary by disease but generally include vaccination, good hygiene practices, and awareness initiatives.