The document discusses various topics related to communication including:
- The four main functions of communication as knowledge management, decision making, coordinating work, and fulfilling relational needs.
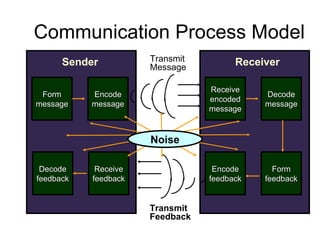
- Models of the communication process and potential barriers like perceptions, filtering, language, ambiguity and information overload.
- Components of effective listening as outlined in the HURIER model.
- Causes and solutions to information overload including using gatekeepers and queuing messages.
- Factors that influence preferences for oral vs. written communication depending on message clarity.