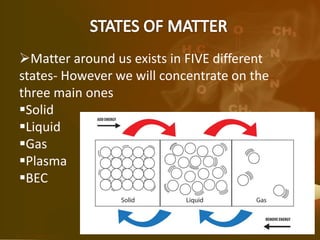
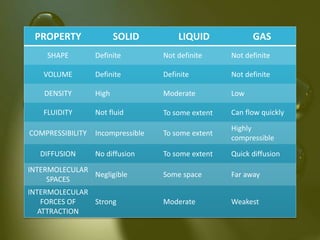
Matter is defined as anything that has mass, occupies space, and can be perceived through the senses, consisting of atoms which can be of various types. Particles of matter have specific properties such as the presence of space between them, continuous movement, and the ability to attract each other, which are demonstrated through various proofs. Matter exists in five states—solid, liquid, gas, plasma, and Bose-Einstein condensate—and can change states due to temperature variations.