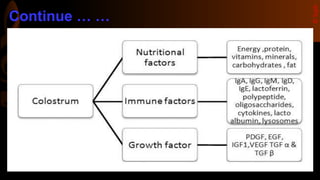
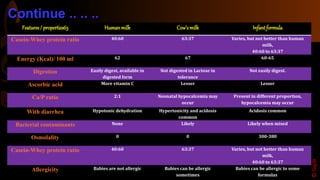
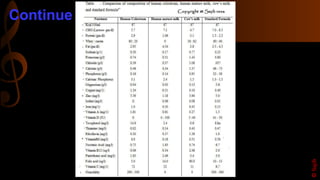
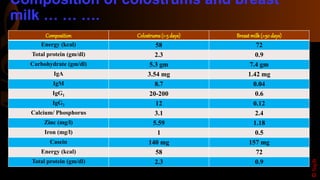
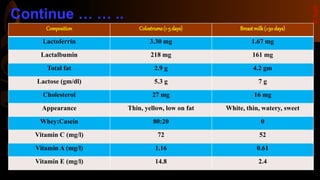
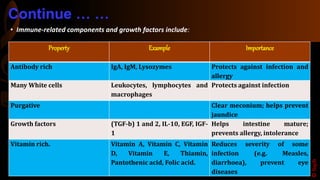
Colostrum is the first milk produced after birth and is particularly rich in immunoglobulins, antimicrobial peptides, and growth factors that are important for the nutrition, growth, and development of newborn infants as well as providing passive immunity. It lasts for 2-4 days after lactation begins. Colostrum contains higher amounts of proteins, vitamins, minerals, and antibodies compared to mature breastmilk and helps protect newborns from infections. The antibodies and growth factors in colostrum act as a first vaccination for newborns by providing passive protection against bacteria, viruses, and diseases.