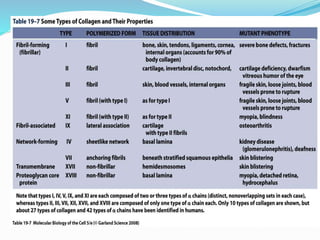
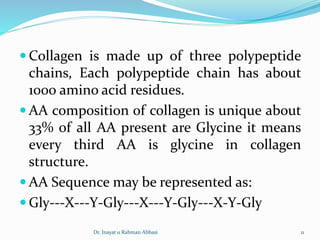
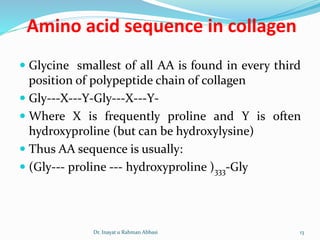
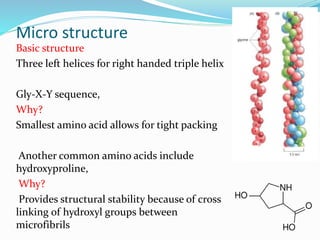
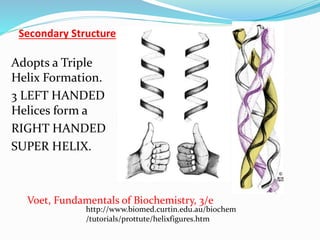
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body and provides structure and strength. It forms triple helix structures that incorporate glycine residues which allow for tight packing. There are many types of collagen that are important for tissues like bone, cartilage, tendons and skin. Collagen synthesis involves post-translational modifications like hydroxylation and glycosylation before forming mature triple helix structures that are cross-linked. Abnormalities in collagen synthesis and structure can lead to diseases like osteogenesis imperfecta, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, and scurvy caused by vitamin C deficiency which is required for hydroxylation.