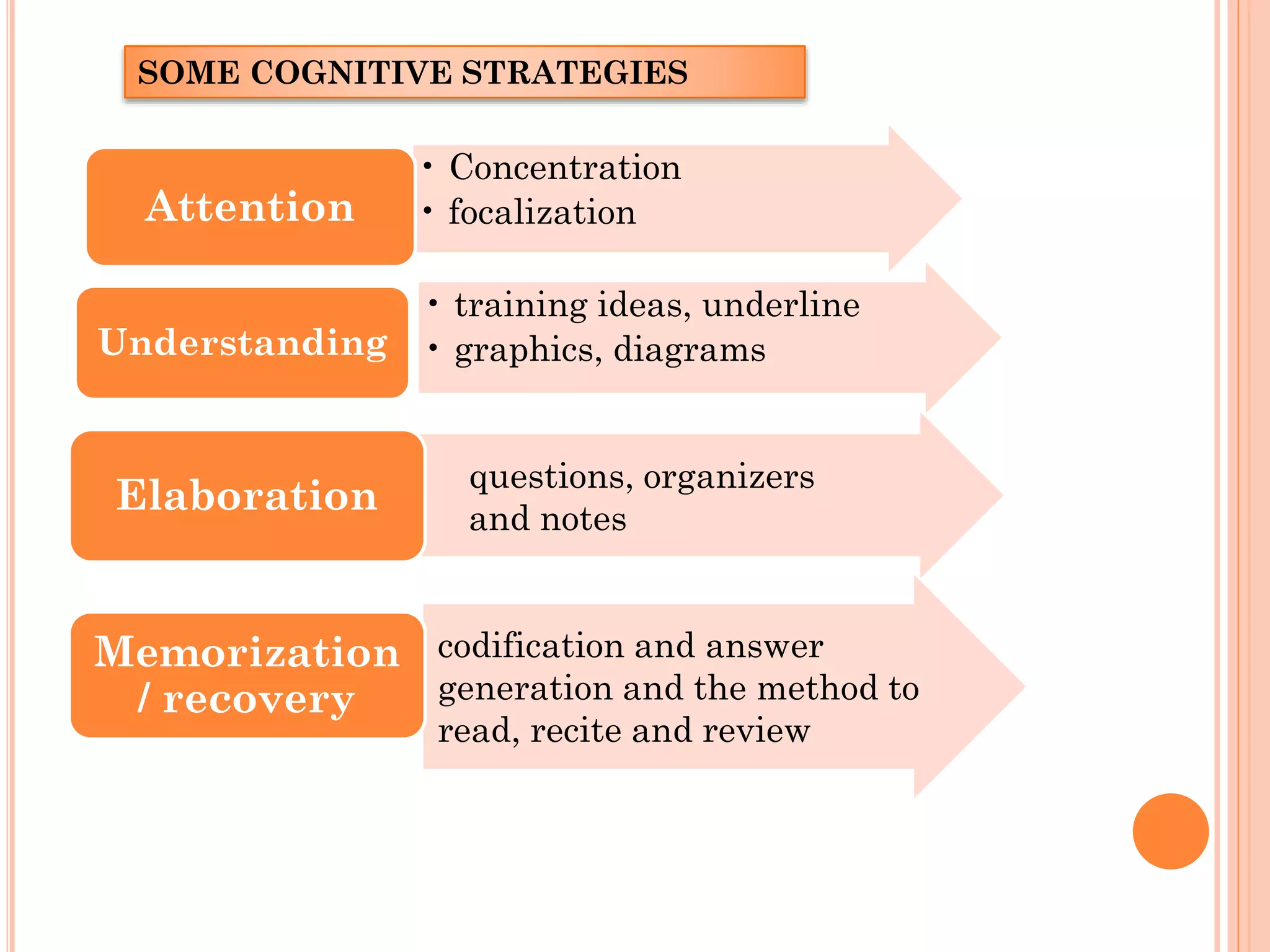
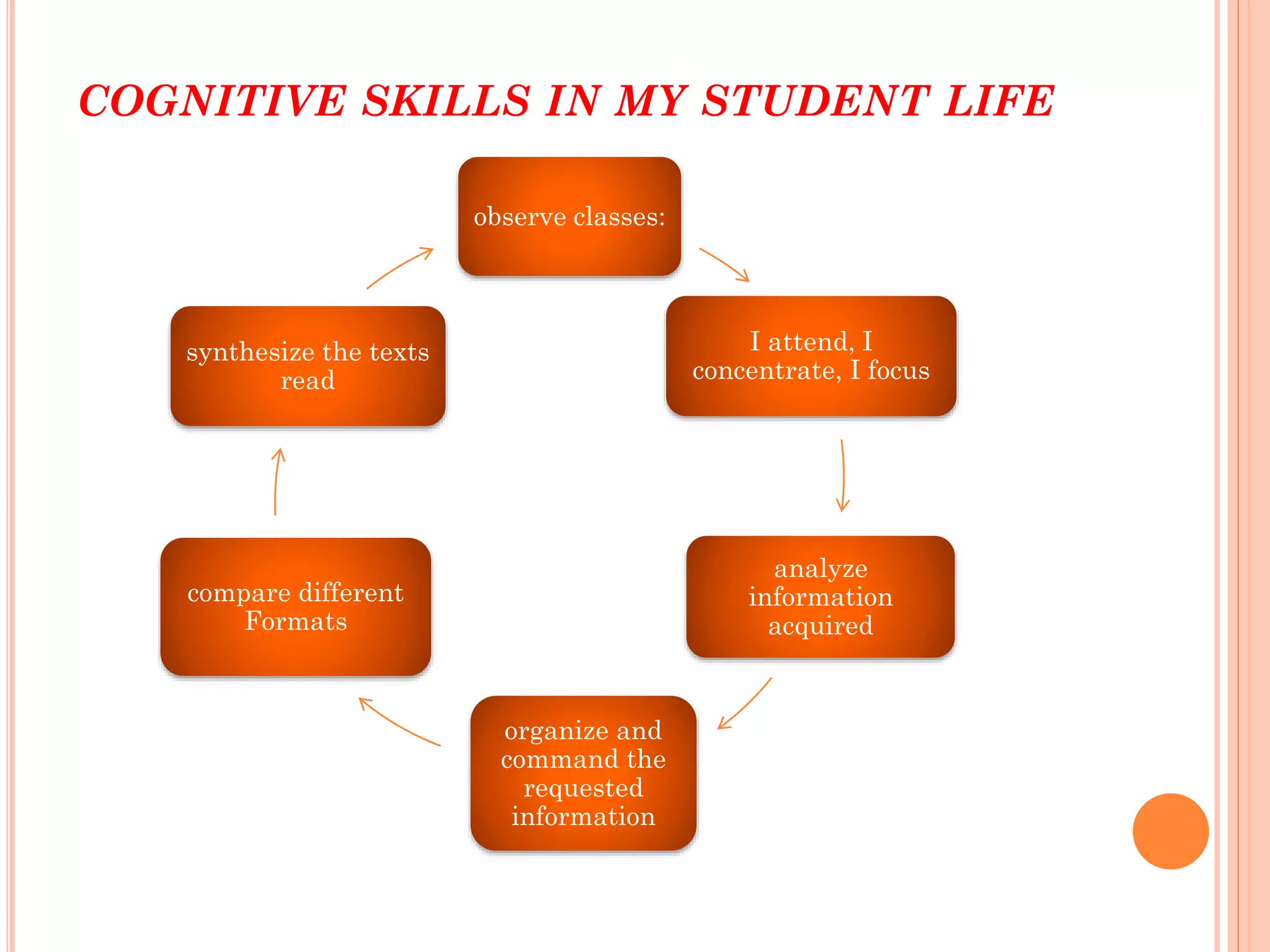
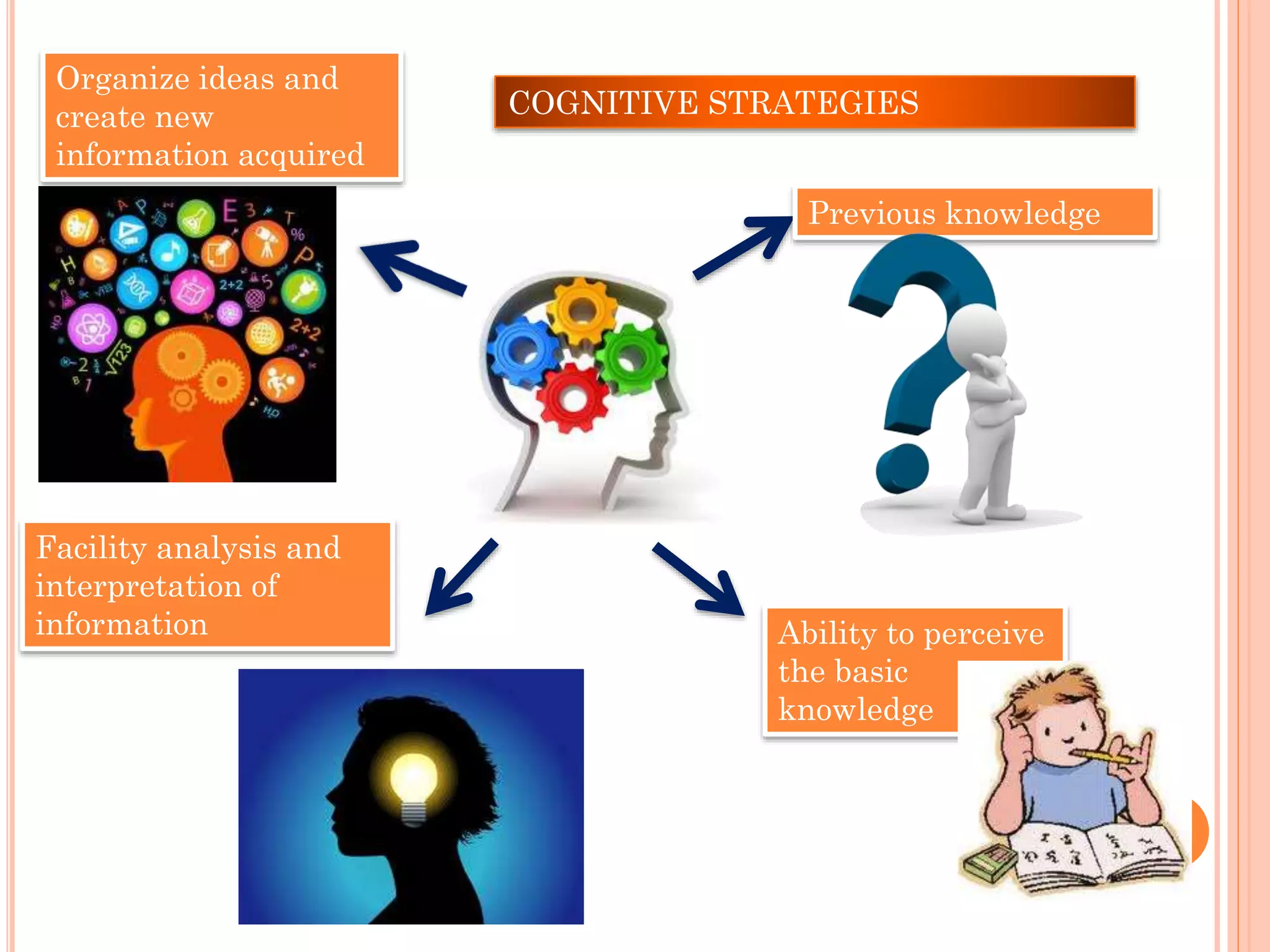
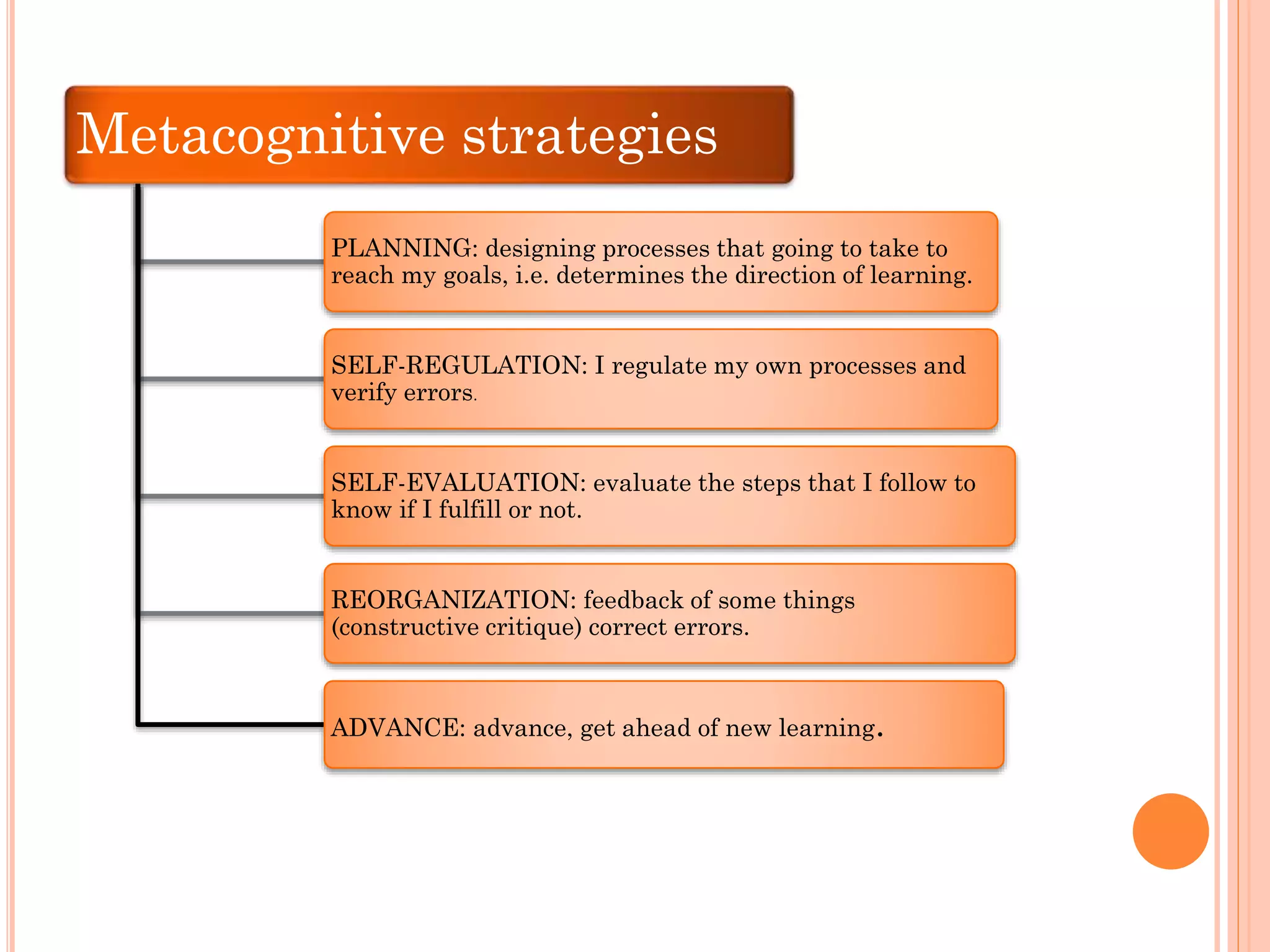
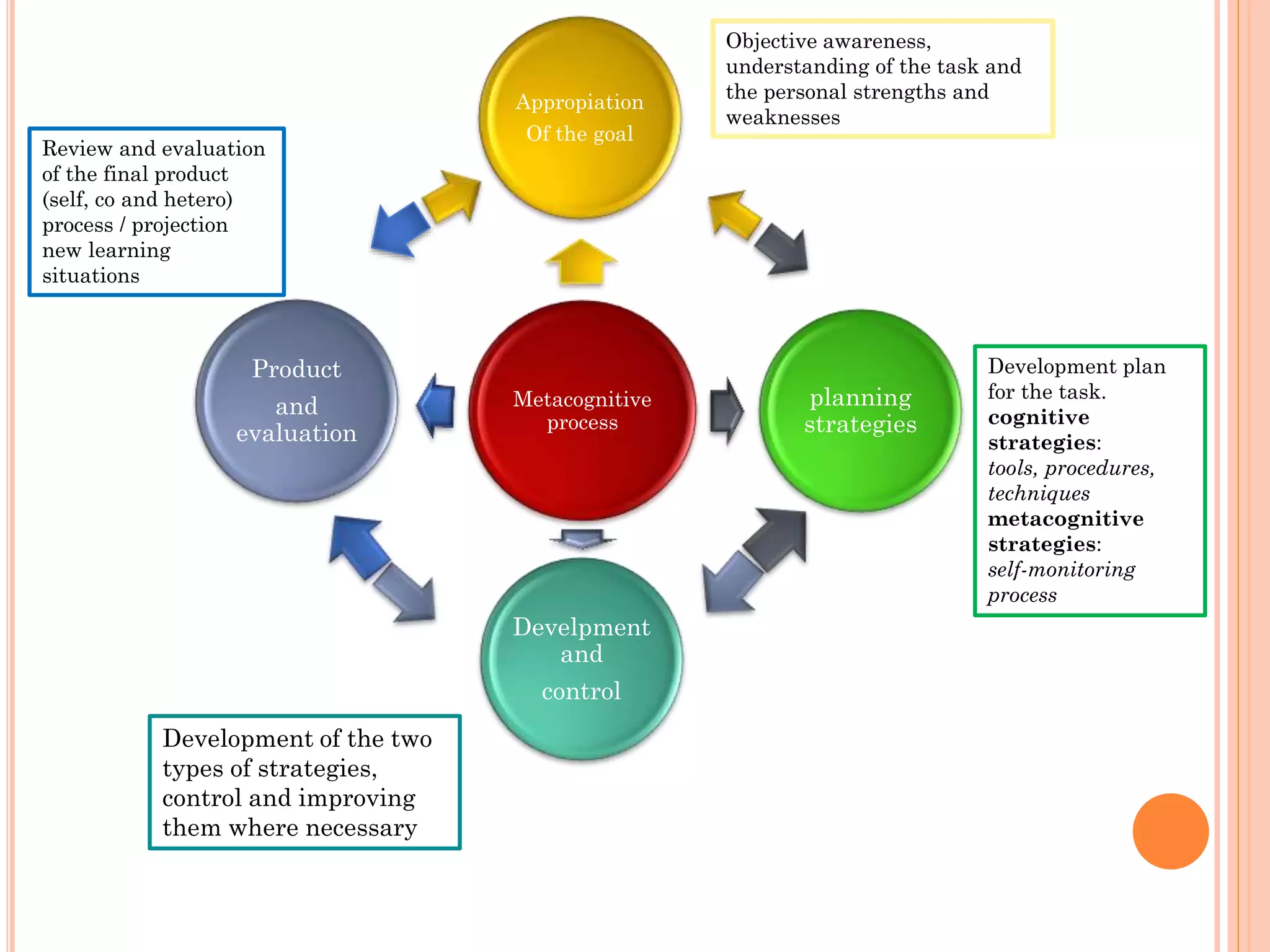
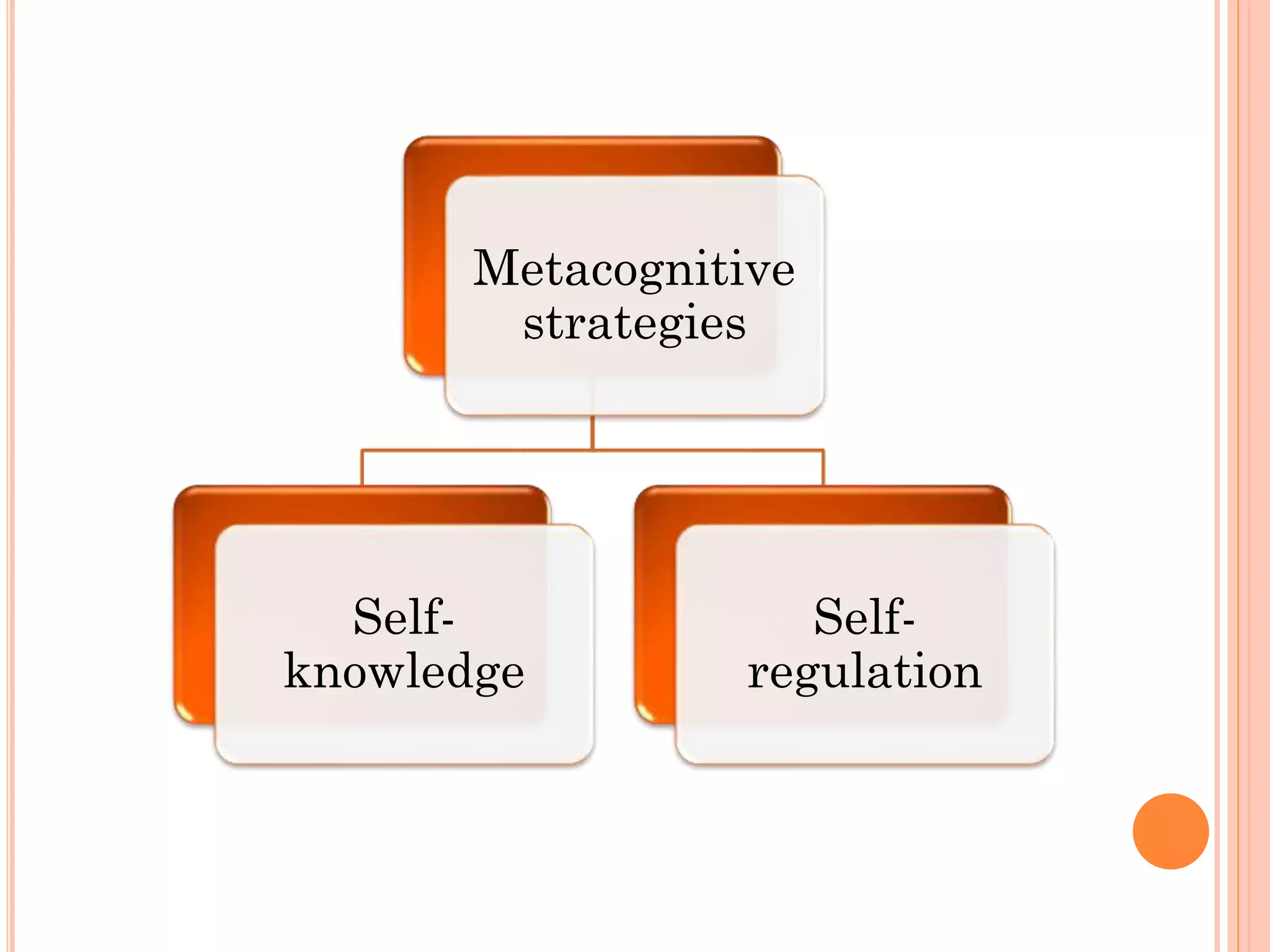
The document discusses cognitive and metacognitive strategies. It defines cognitive strategies as processes that directly operate on collecting, analyzing, understanding, and storing information. Some examples of cognitive strategies mentioned are concentration, attention, understanding, elaboration, and memorization. Metacognitive strategies are defined as mental activities used to process information and give it meaning. They help analyze and control cognitive processes. Metacognitive strategies discussed include planning, self-regulation, self-evaluation, and reorganization. The document stresses that metacognitive strategies require self-knowledge and appropriate resources to promote significant learning.