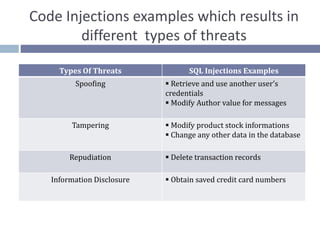
This document discusses code injection and SQL injection. It defines code injection as a technique used to attack data-driven applications by inserting malicious SQL statements. It describes different types of threats from SQL injection like spoofing, tampering, and information disclosure. It provides examples of how SQL injection can happen through authentication bypass and dropping tables. It recommends input validation, least privileges, prepared statements, and output encoding to prevent SQL injection vulnerabilities.