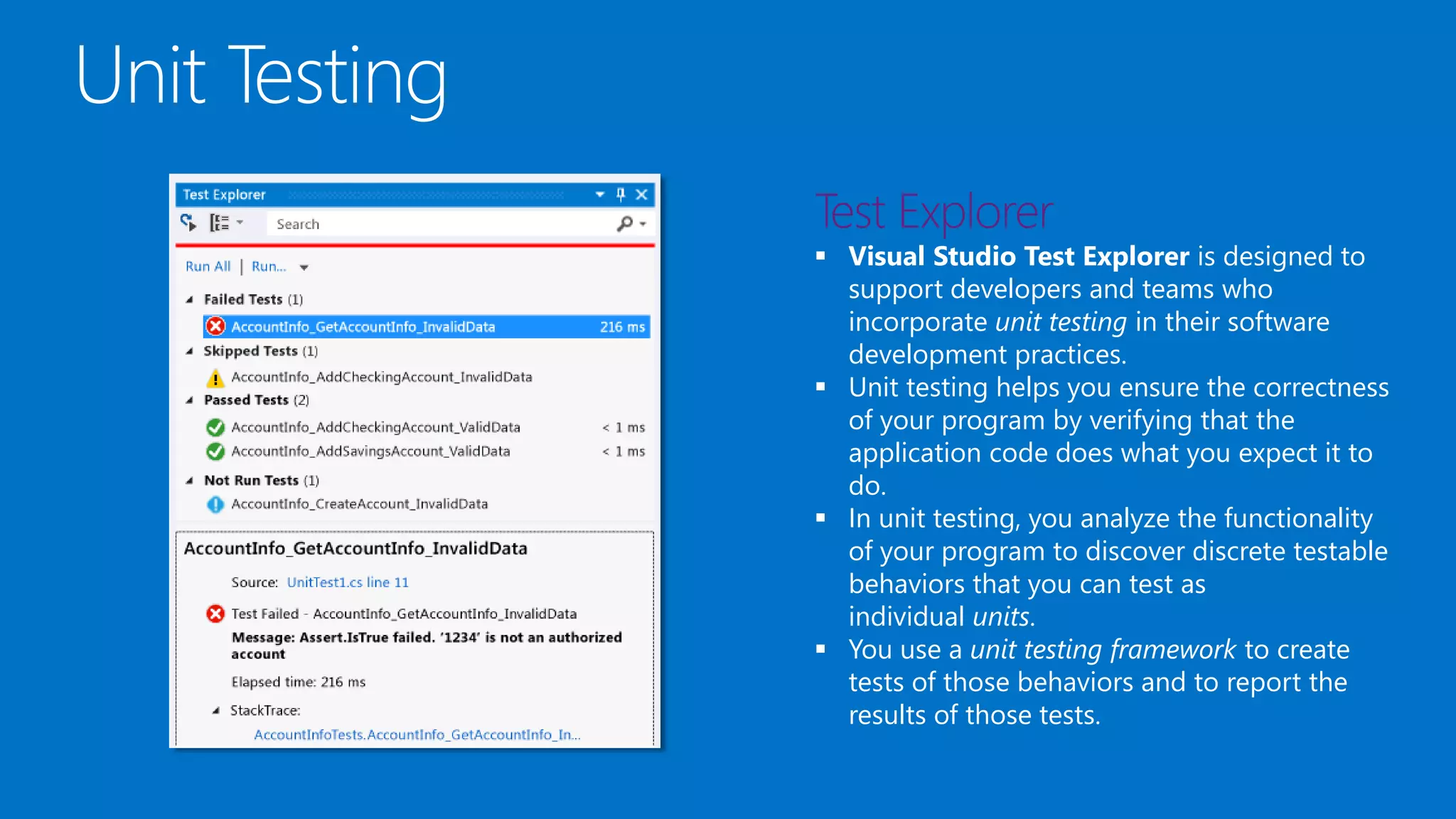
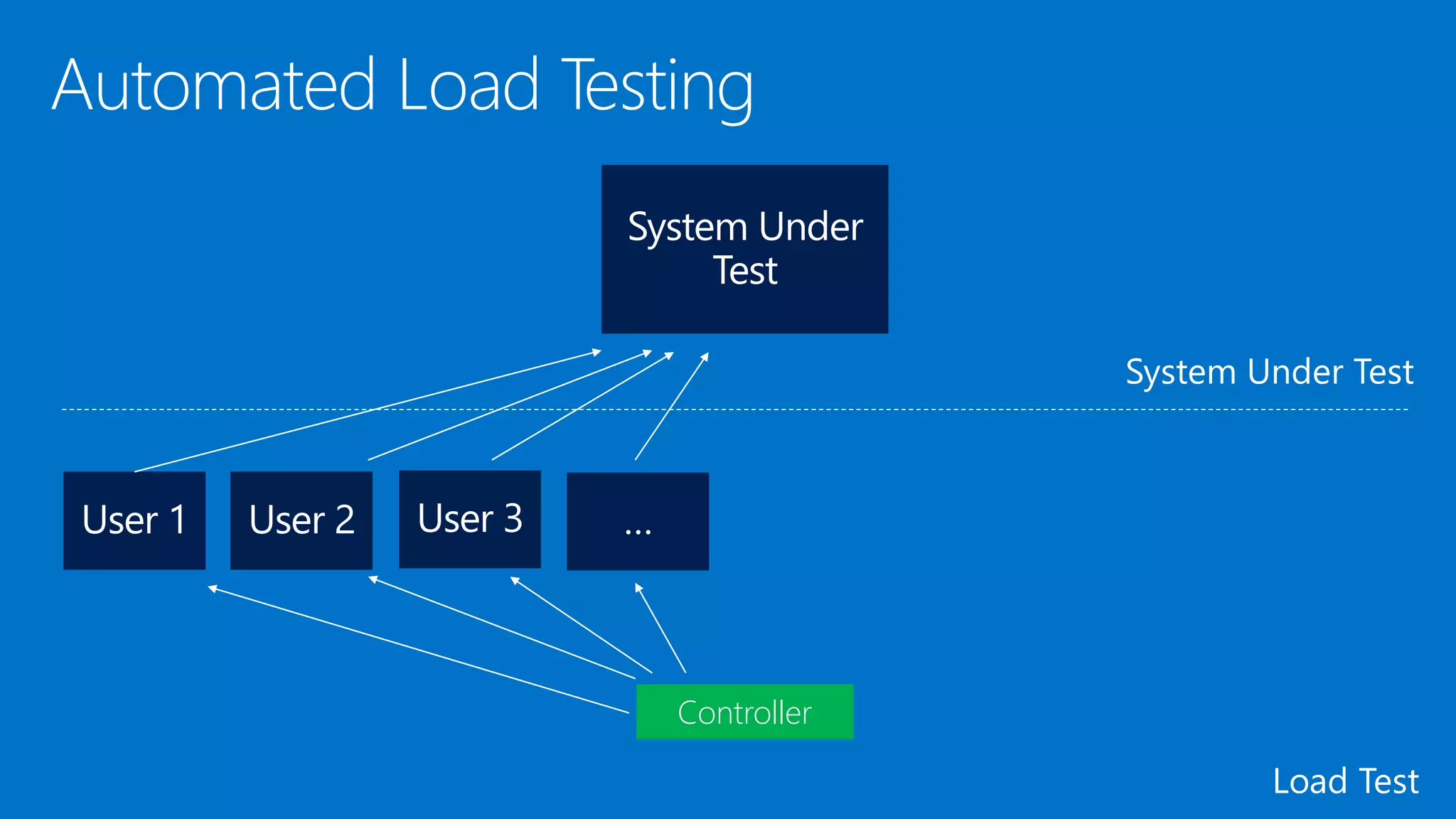
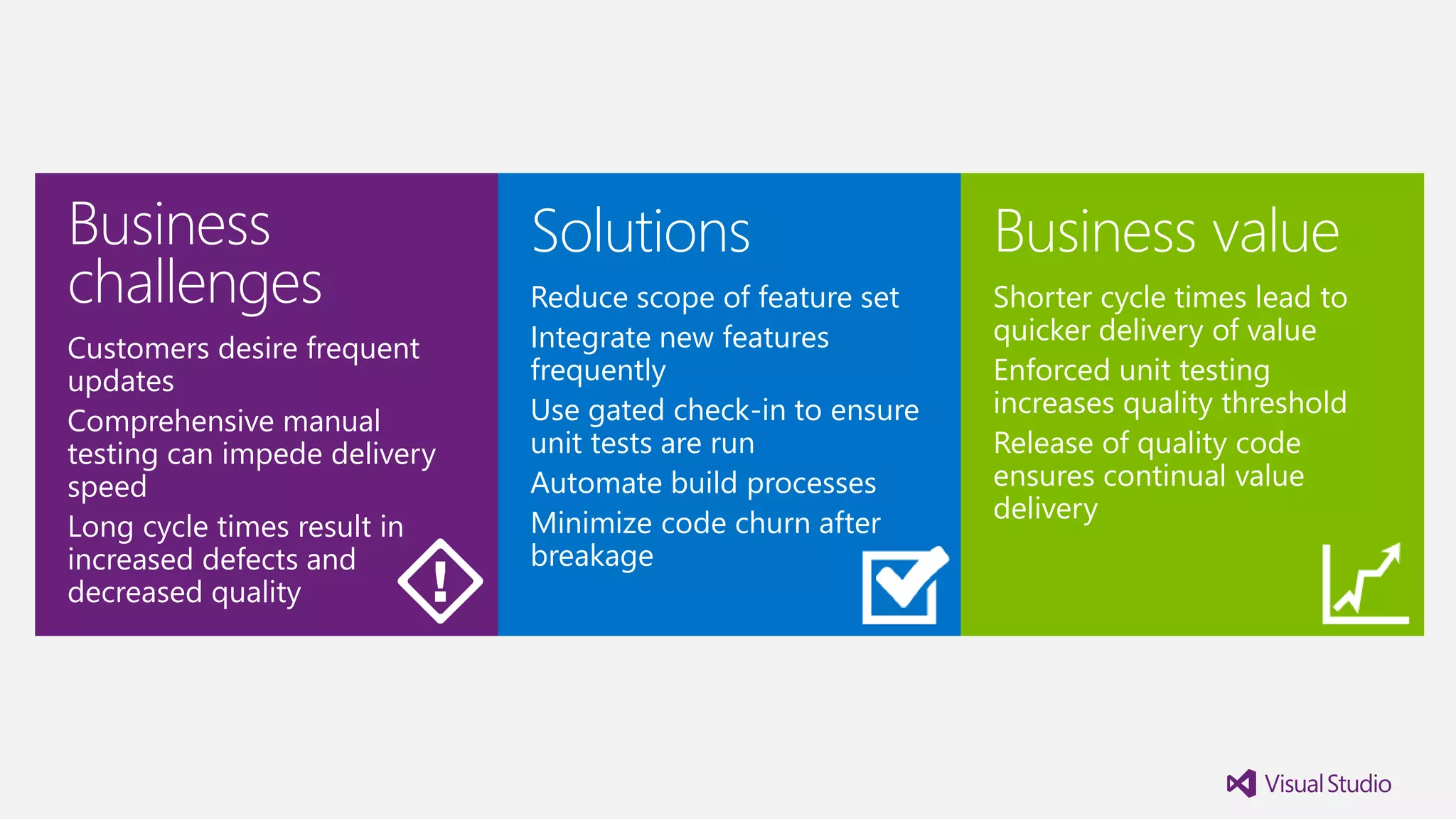
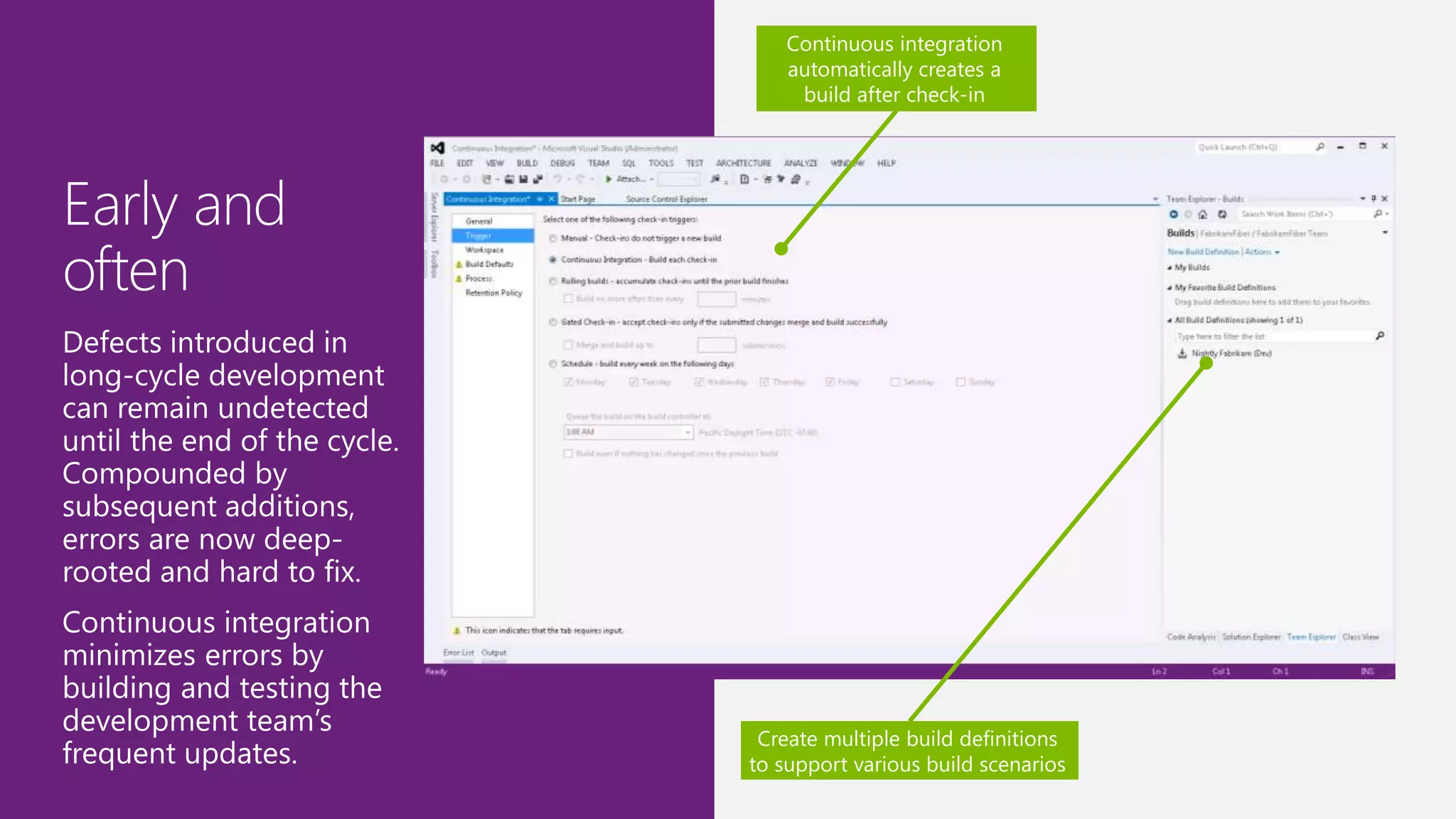
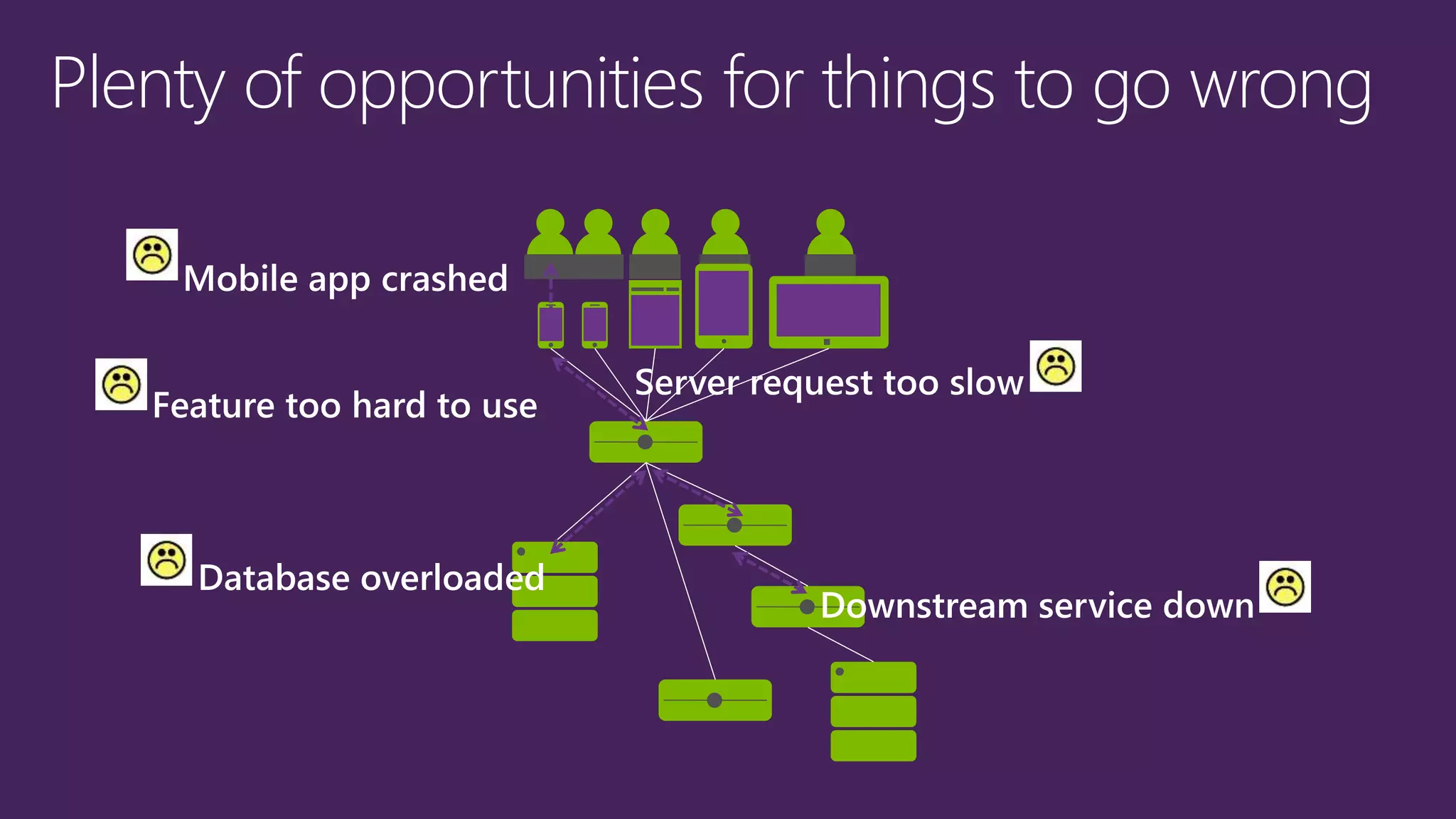
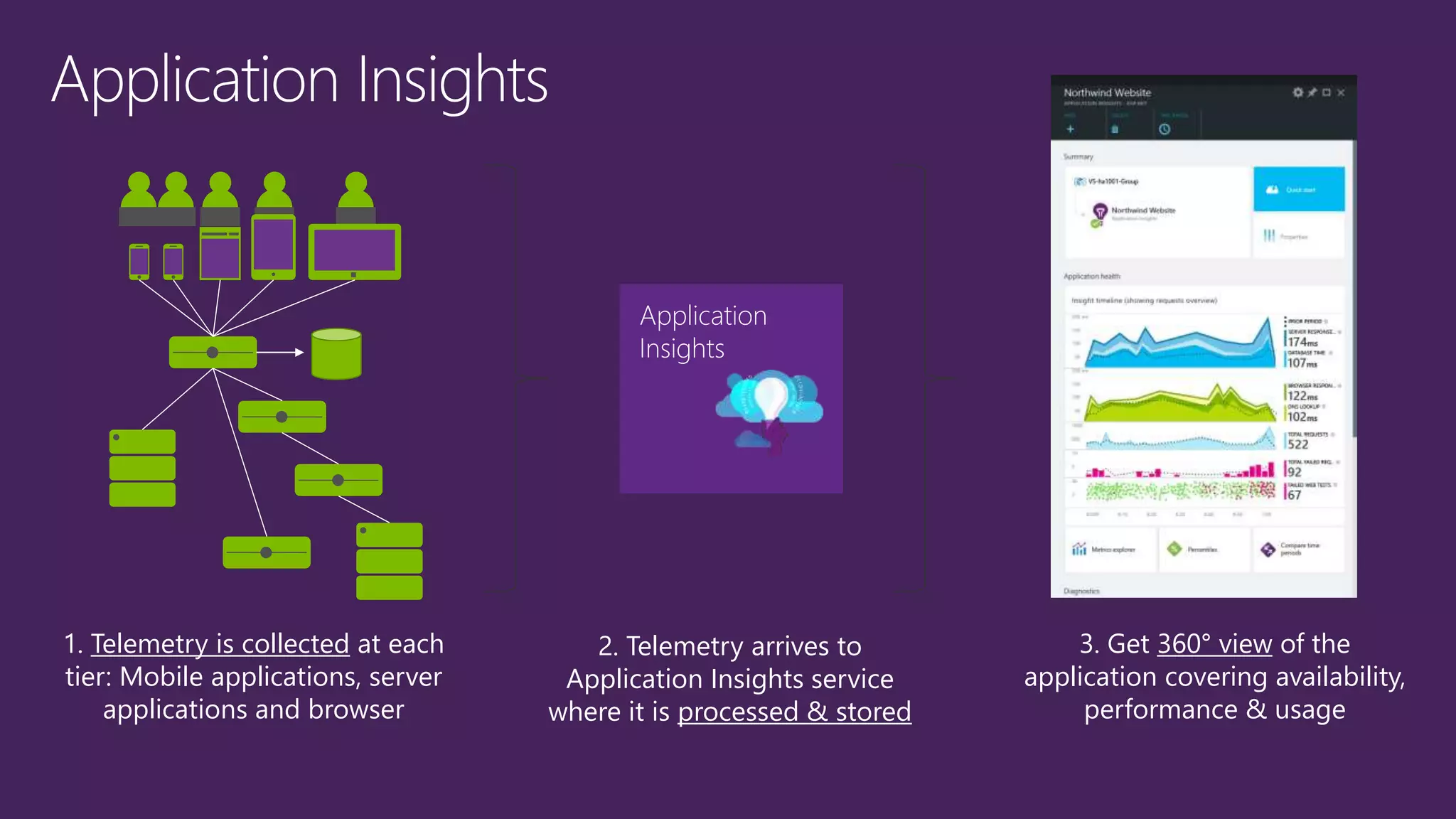
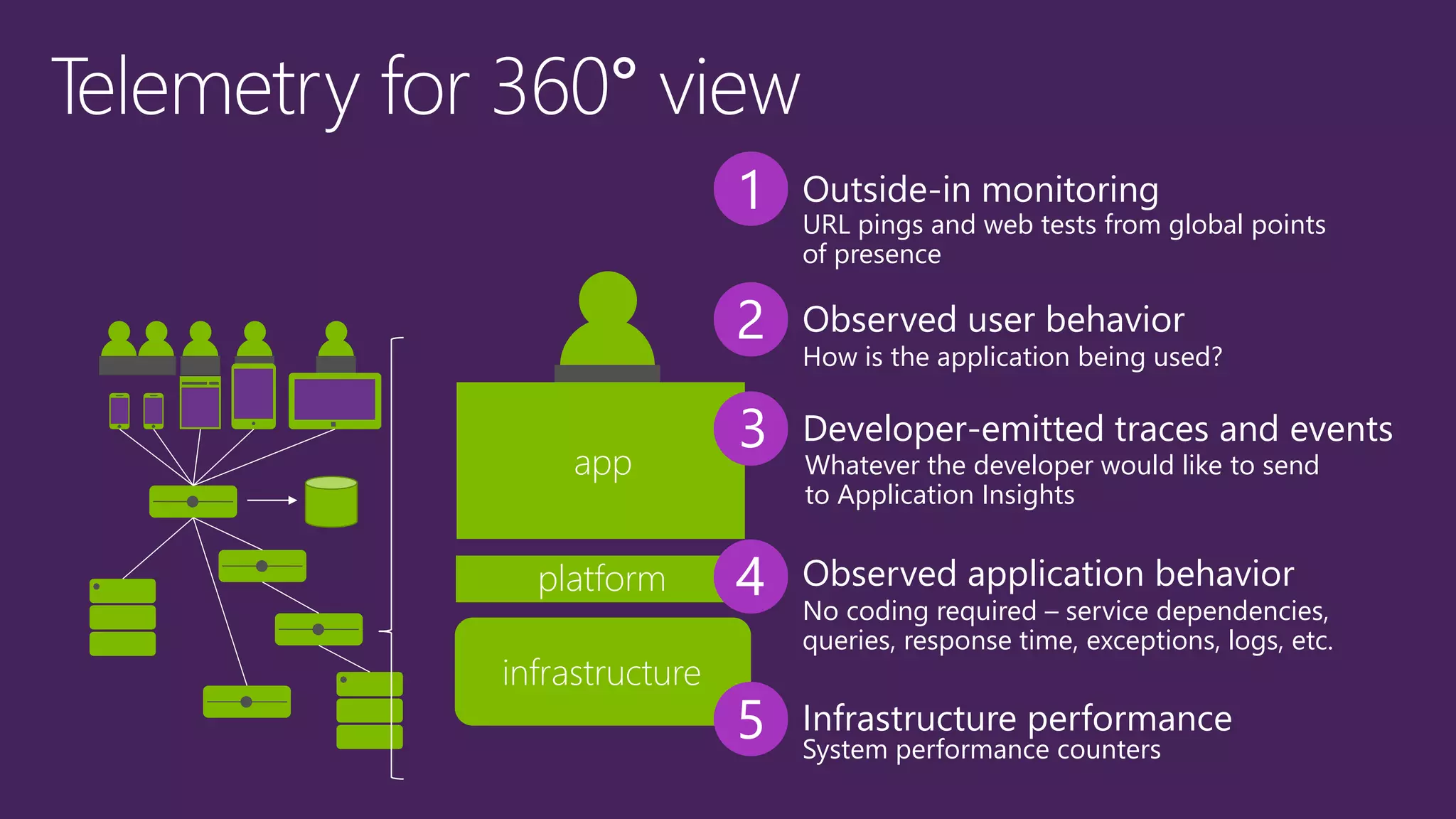
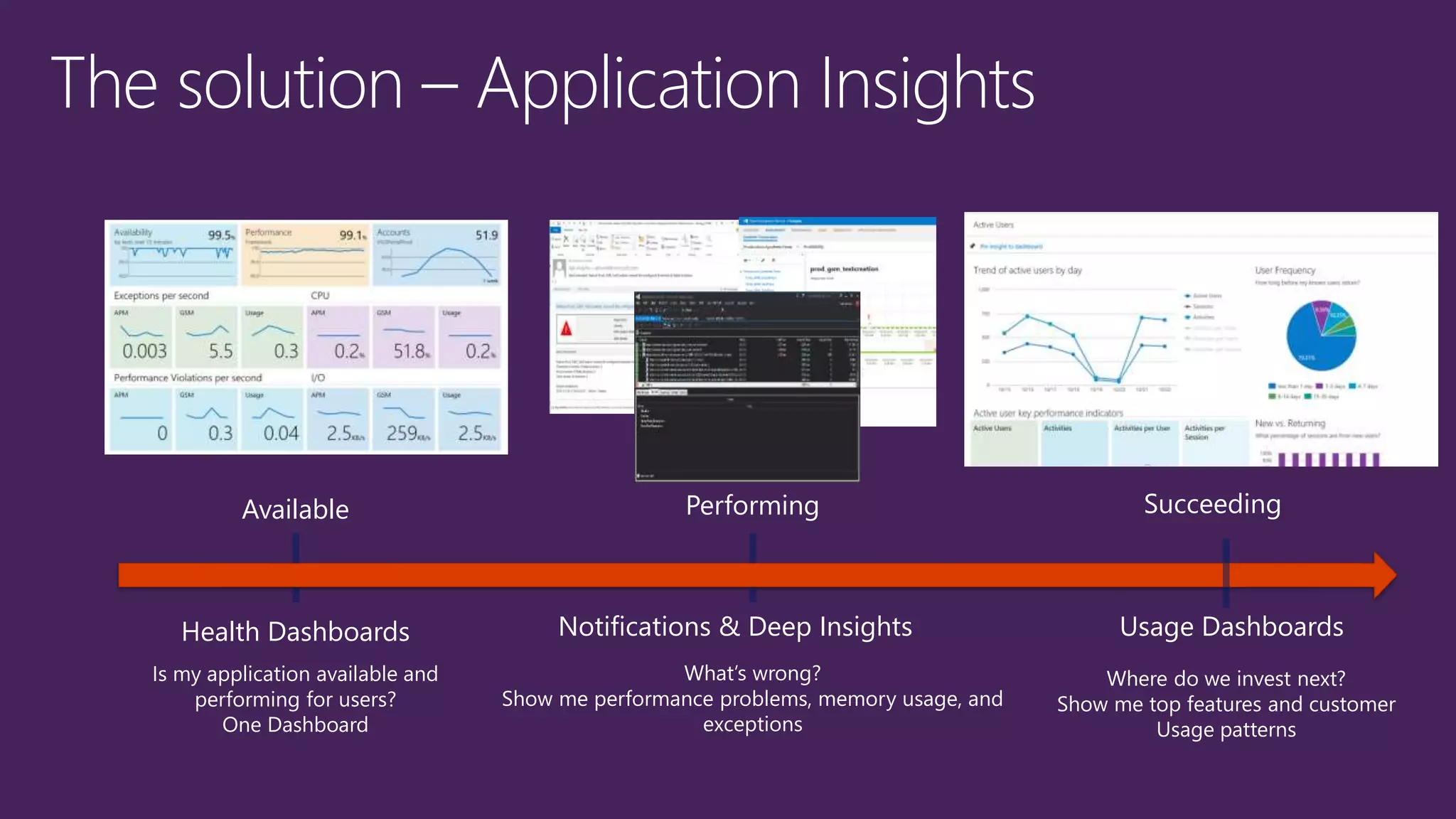
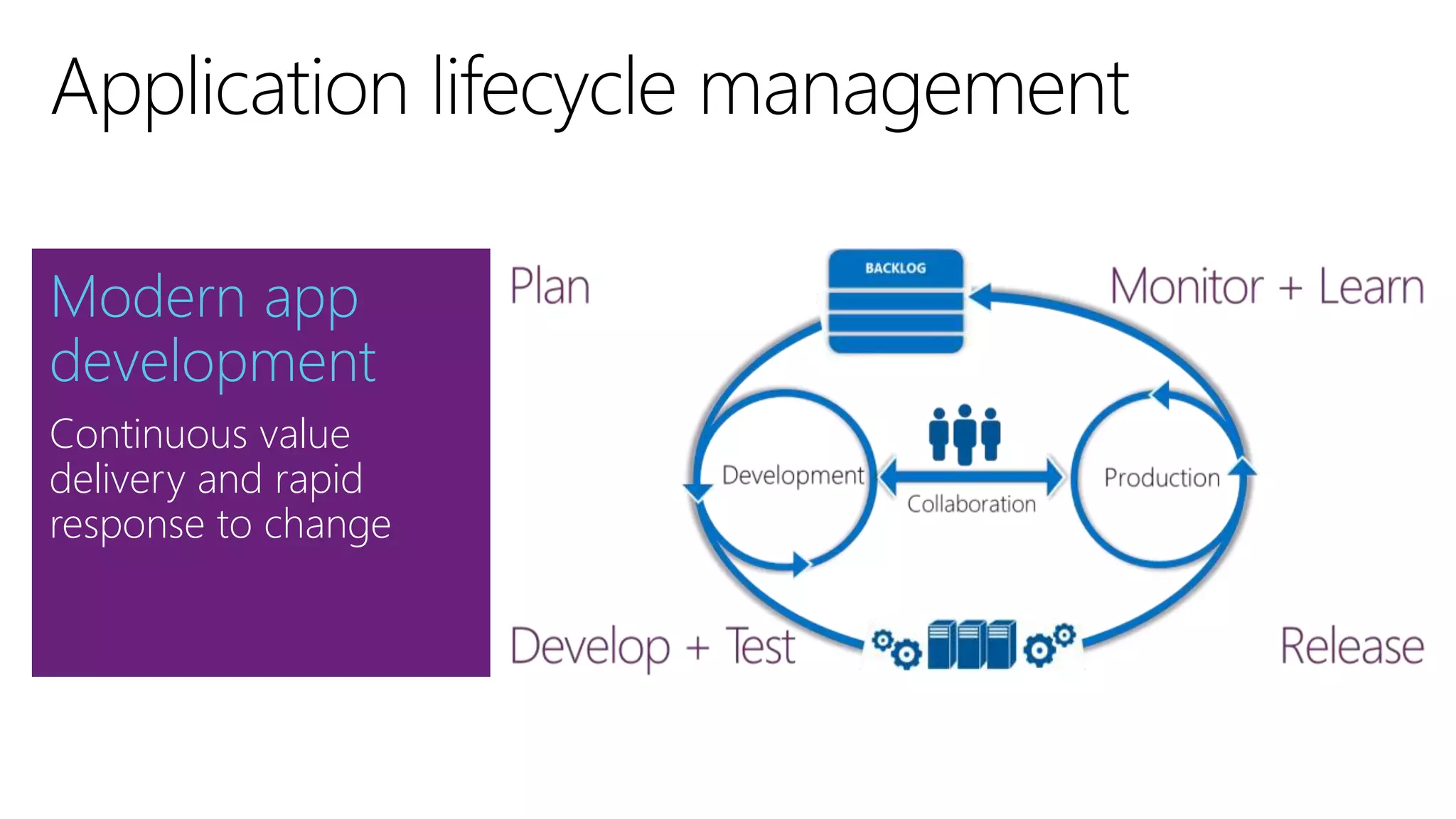
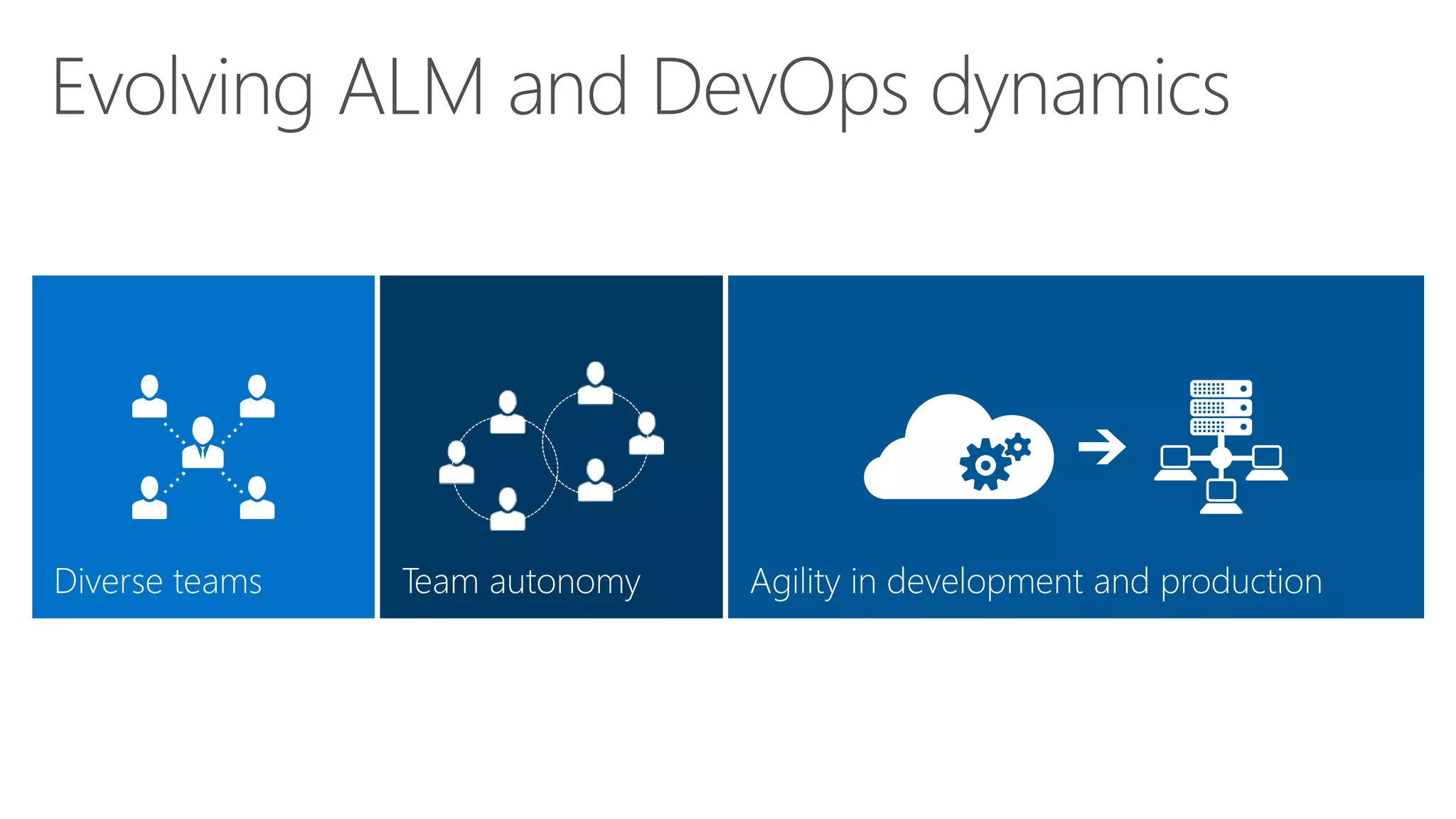
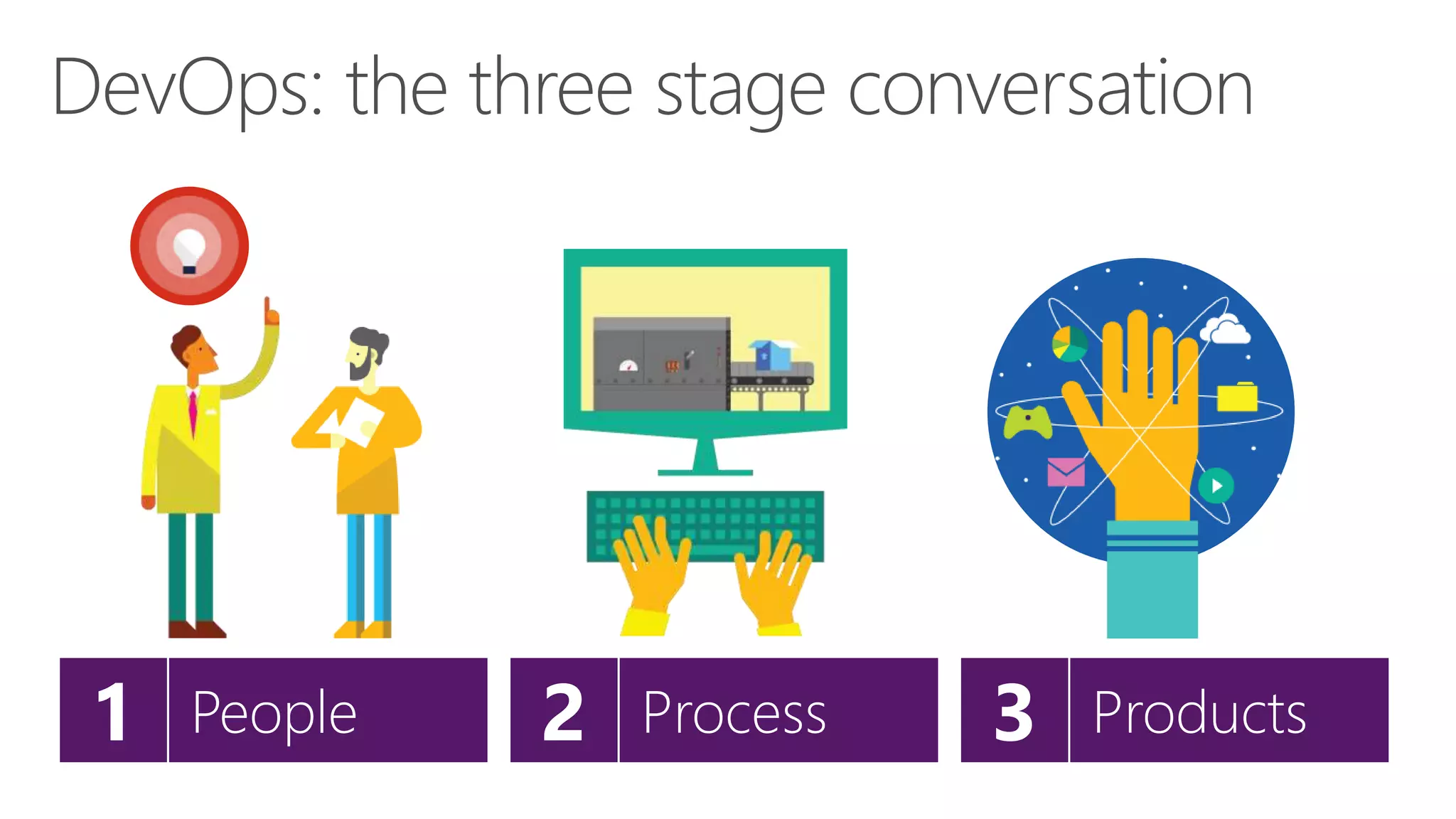
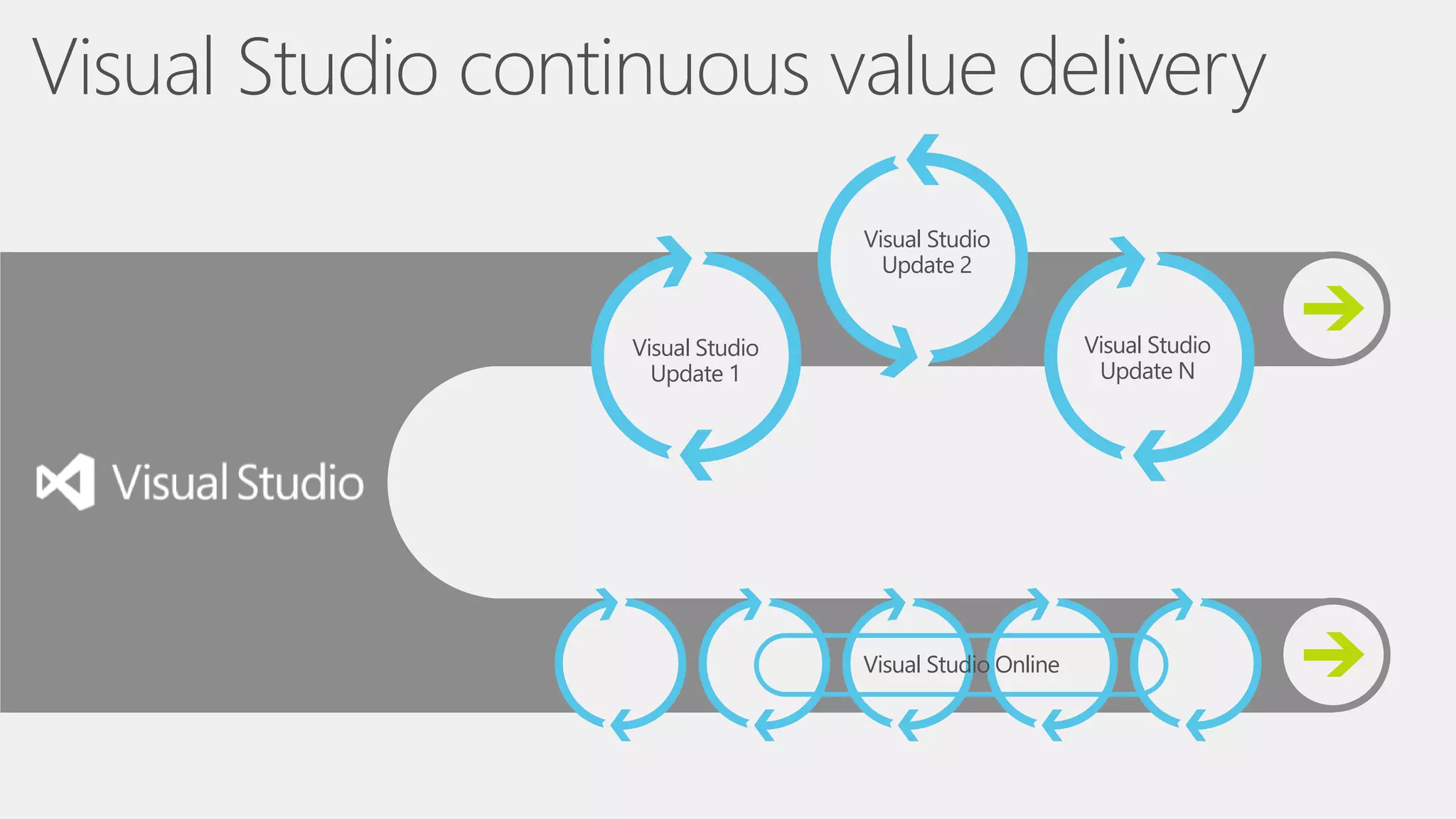
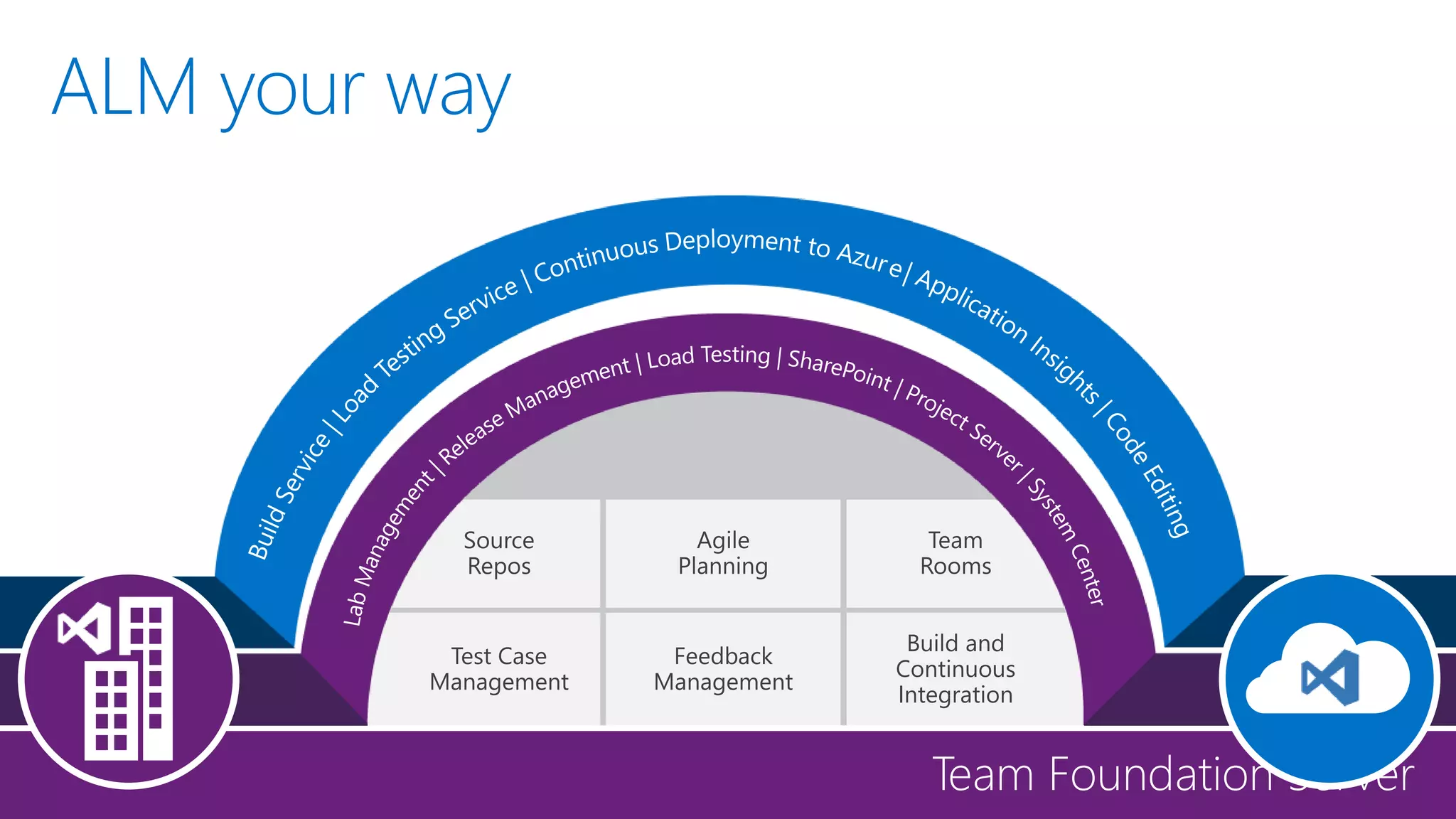
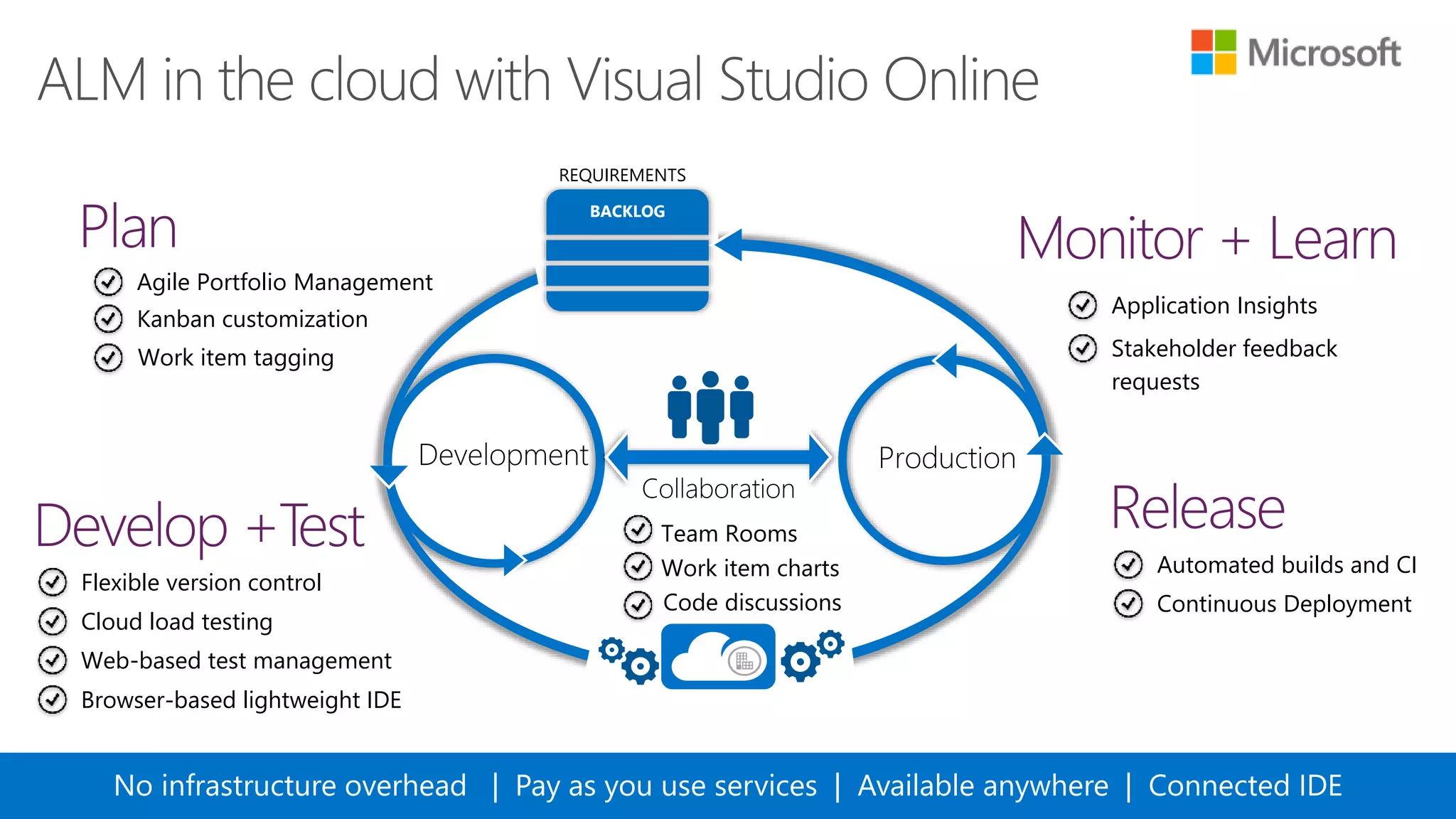
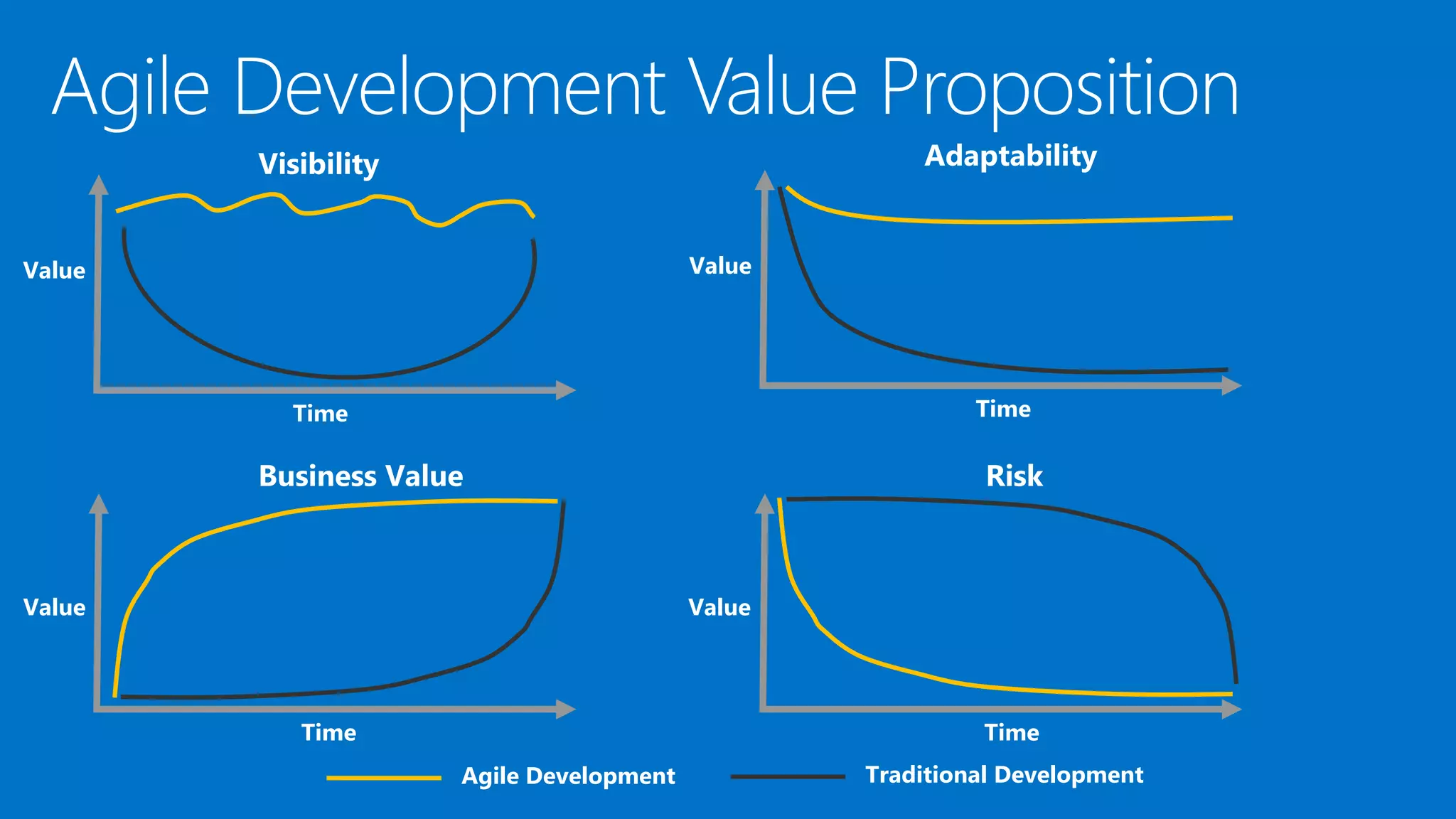
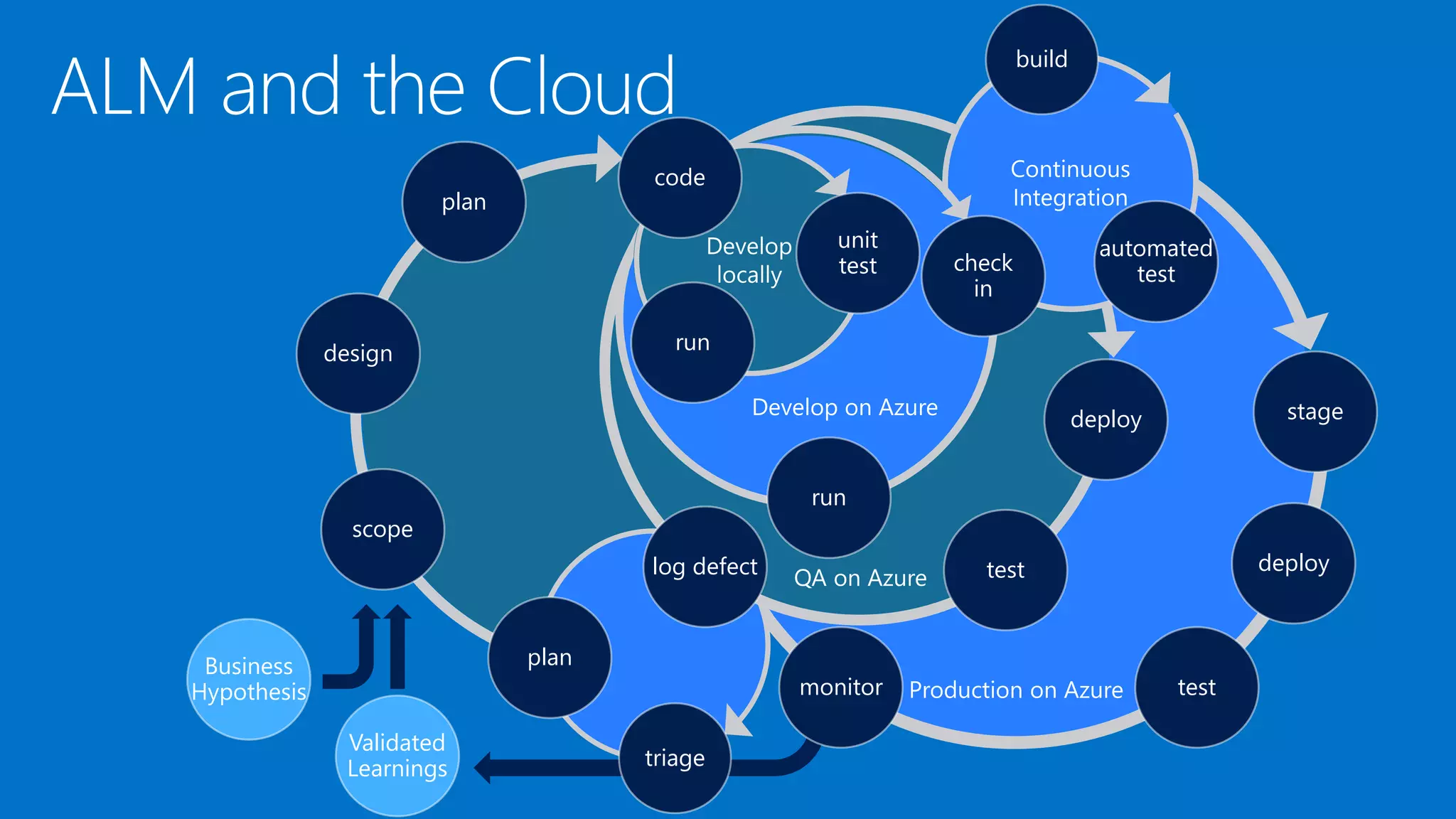
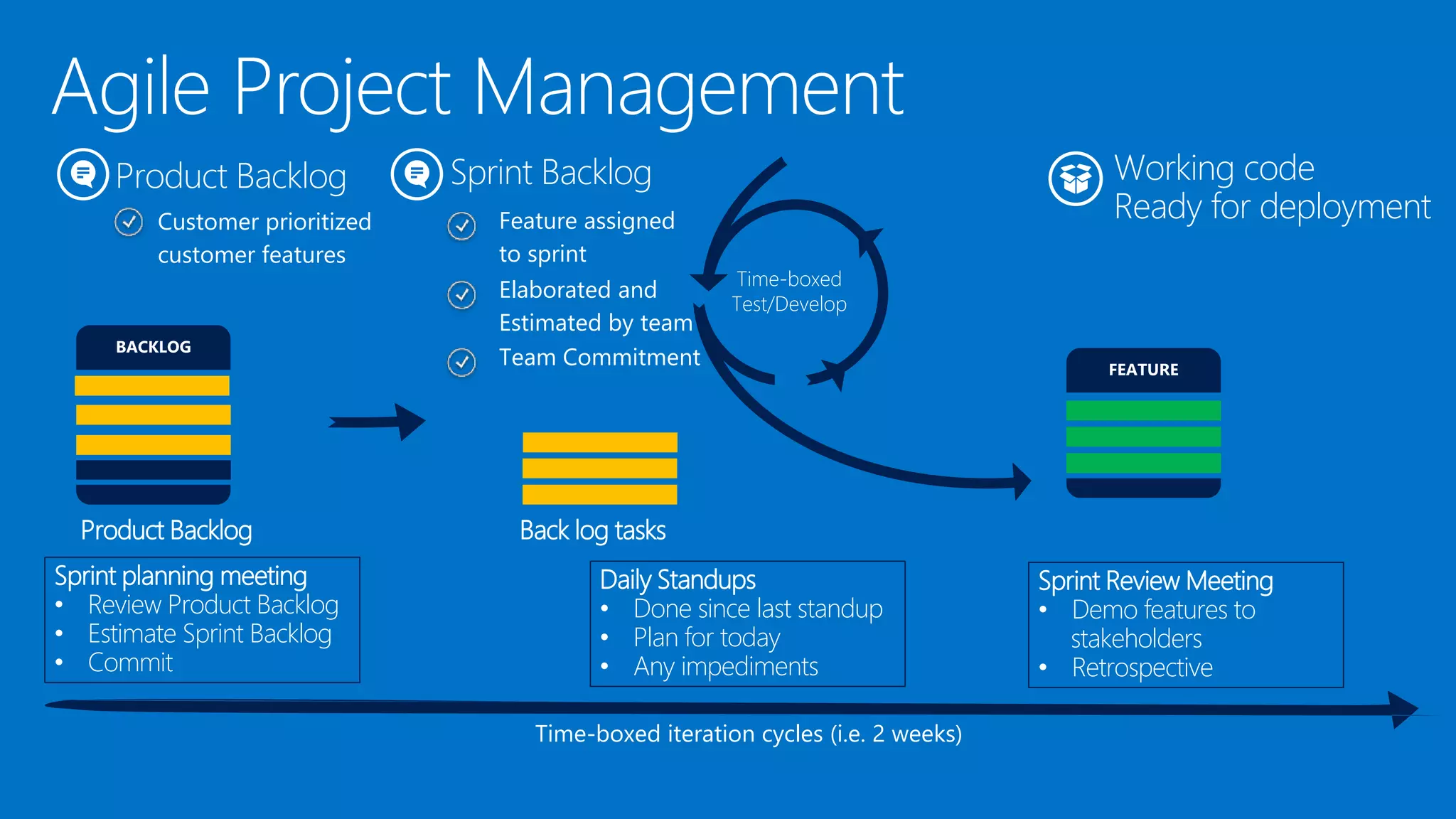
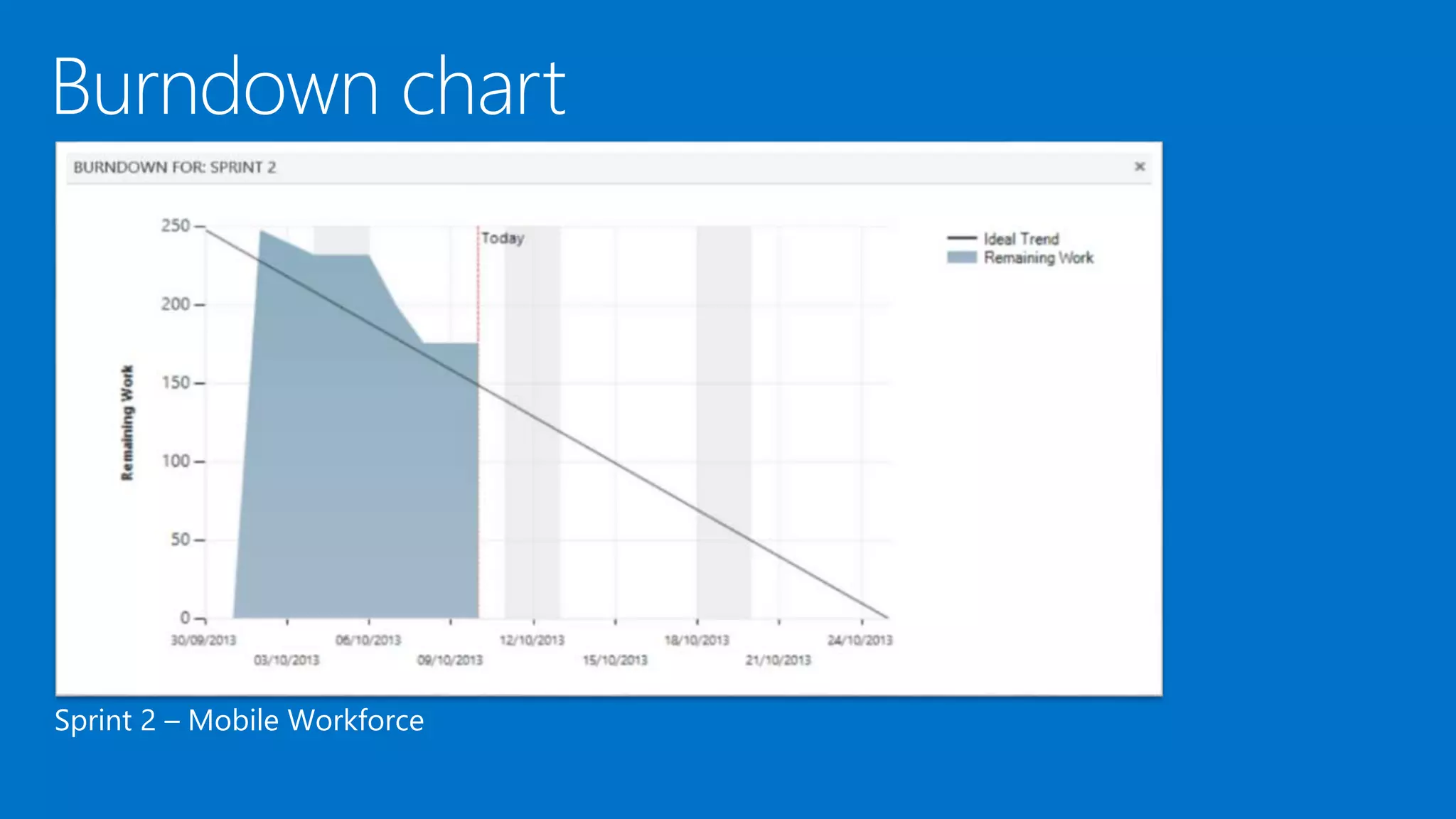
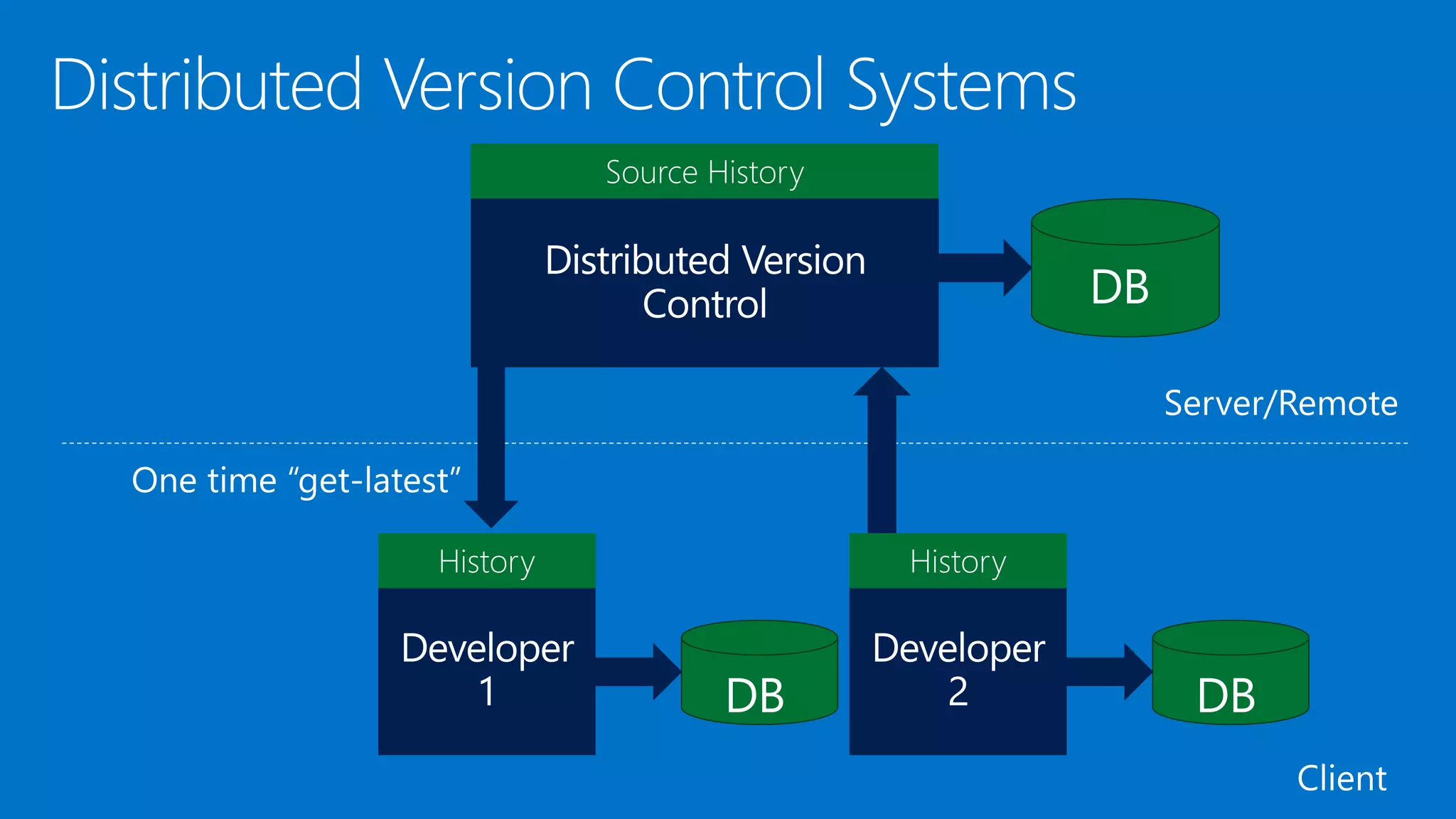
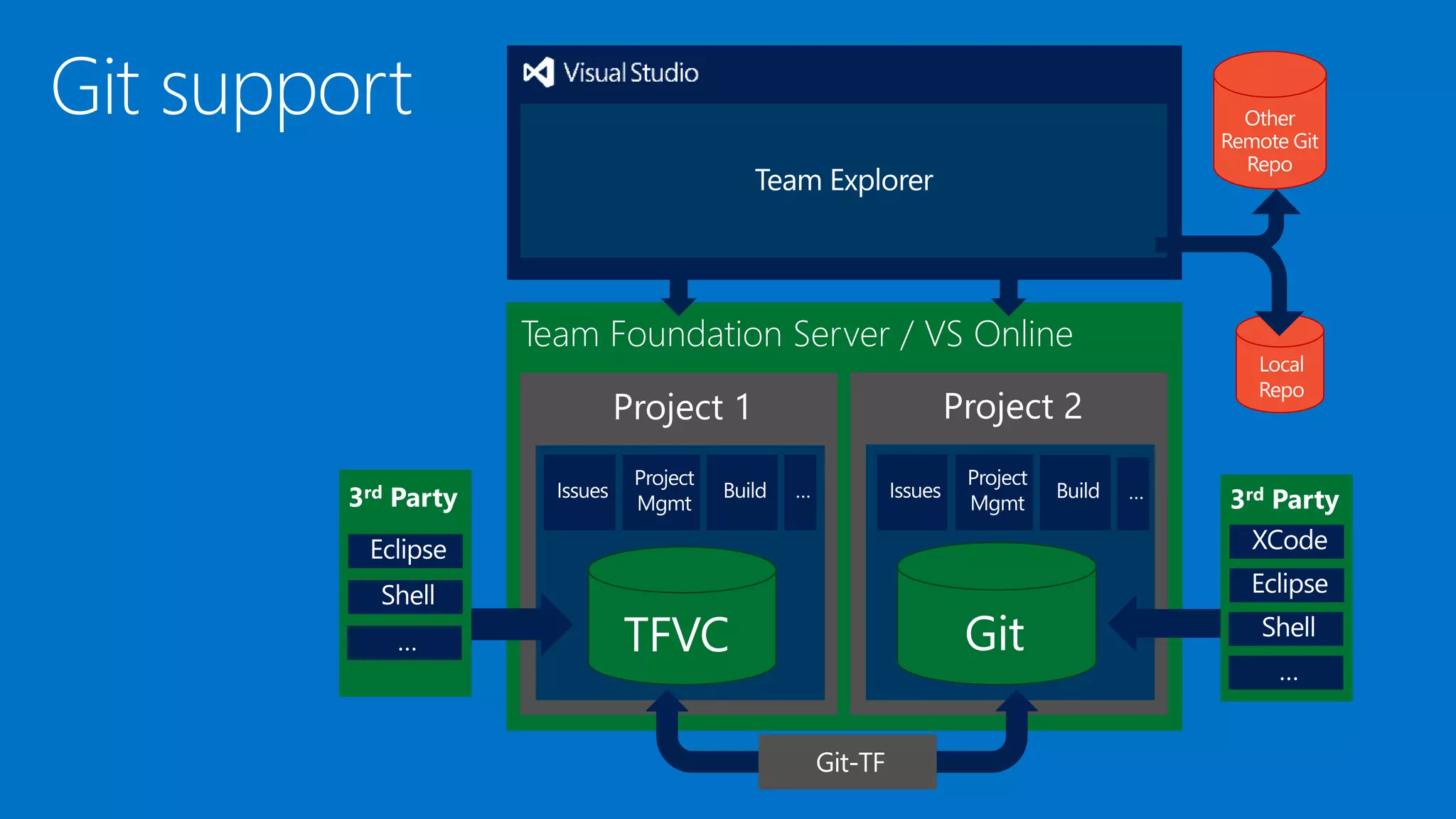
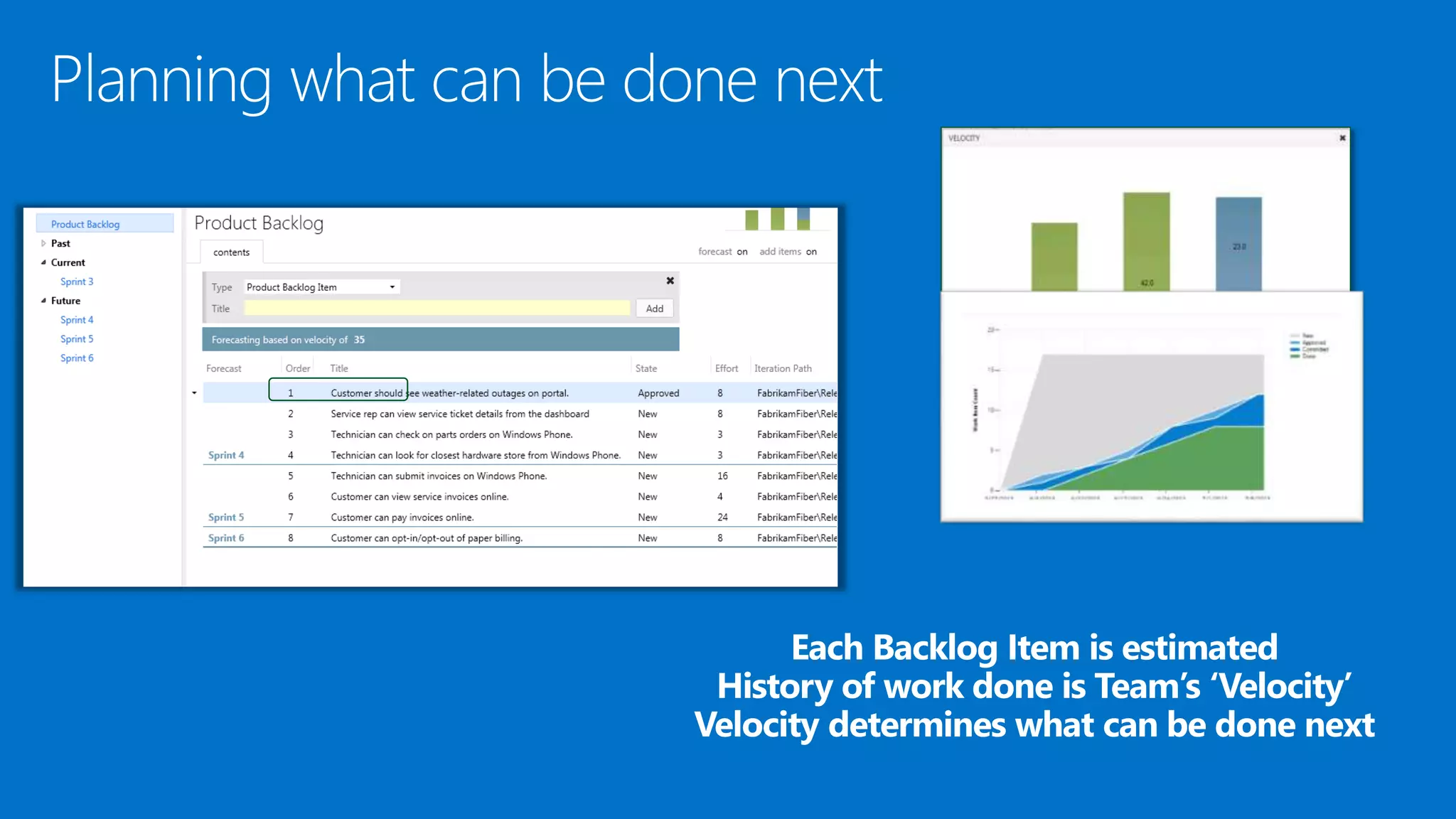
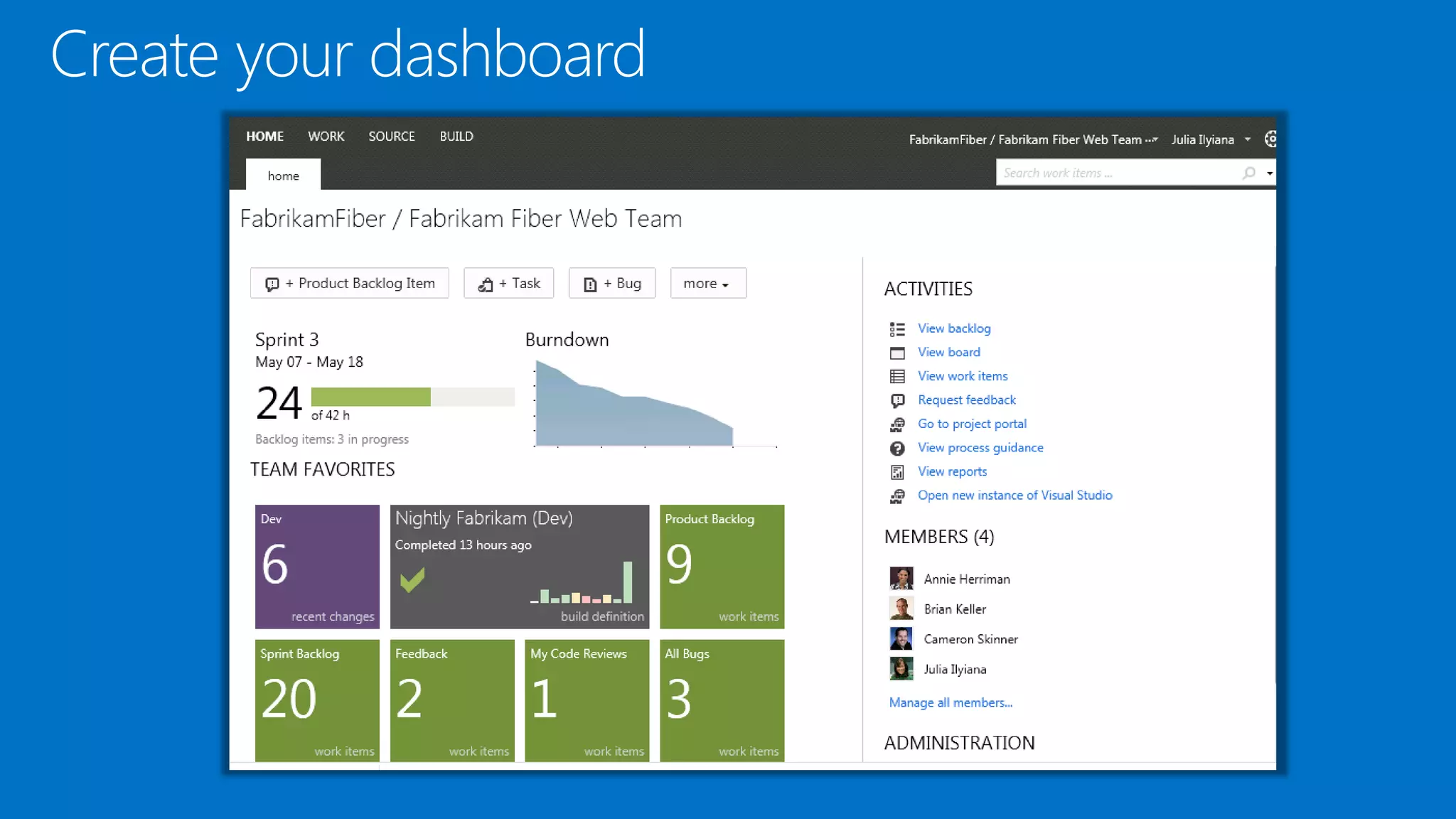
The document outlines modern app development practices focused on continuous value delivery, rapid response to change, and agile methodologies. It covers tools and techniques for project management, version control, unit testing, and monitoring applications using Visual Studio and Azure services. Key benefits emphasized include shorter cycle times, enhanced quality through automated testing, and improved user experience through application insights.

















![ TDD is a robust way of designing software
components (“units”) interactively so that
their behavior is specified through unit
tests.
Whenever you are tempted to type
something into a print statement or a
debugger expression, write it as a test
instead.
Manual or automated testing is much
better for finding bugs.
Automated integration tests are much
better for detecting regression (things that
used to work but have unexpectedly stopped
working).
[TestMethod]
public void Debit_WithValidAmount_UpdatesBalance()
{
// arrange
double beginningBalance = 11.99;
double debitAmount = 4.55;
double expected = 7.44;
BankAccount account =
new BankAccount("Mr. X", beginningBalance);
// act
account.Debit(debitAmount);
// assert
double actual = account.Balance;
Assert.AreEqual(expected, actual, 0.001,
"Account not debited correctly");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codeinthecloudcompletedeck-141218082326-conversion-gate02/75/Code-in-the-Cloud-December-8th-2014-39-2048.jpg)