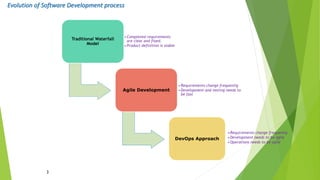
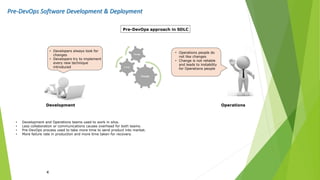
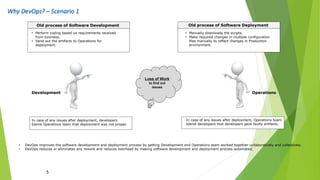
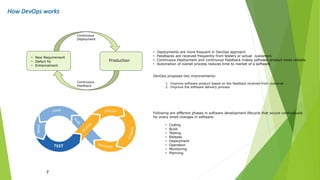
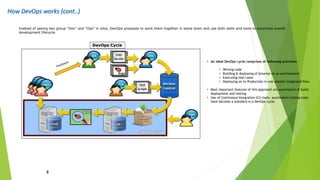
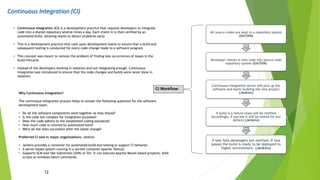
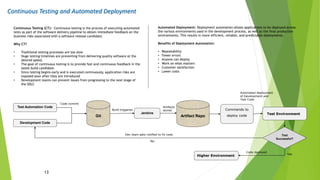
The document outlines DevOps as a software development approach that combines development and operations to enhance software delivery through continuous practices like development, testing, integration, deployment, and monitoring. It emphasizes collaboration between teams, automation, and the importance of continuous feedback to improve product quality, reduce failure rates, and increase efficiency. Additionally, it discusses the evolution of software development processes and the critical role of various tools and practices such as continuous integration and deployment in achieving successful DevOps implementation.