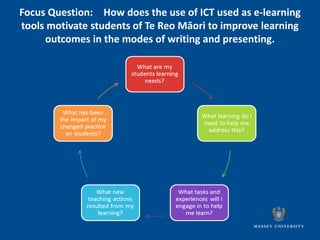
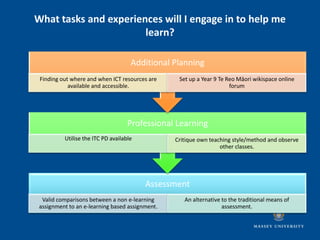
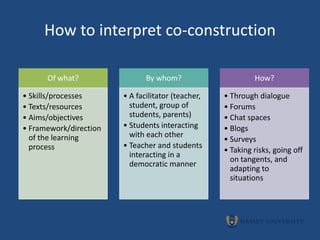
The document outlines indicators of success for Māori students enjoying education, including a case study on a Te Reo Māori class project that utilized ICT tools to motivate students and improve learning outcomes. It discusses establishing a culture of co-construction between teachers and students through sharing responsibility, creating common understandings, and reflecting together on classroom experiences. The document poses questions to consider implementing these ideas to develop thriving learning communities.