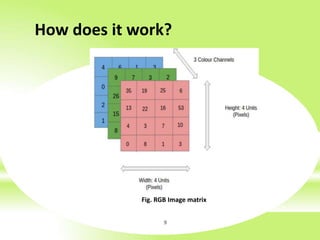
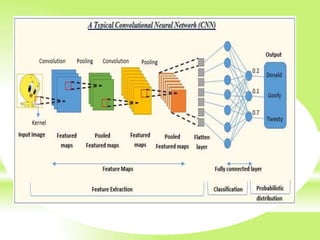
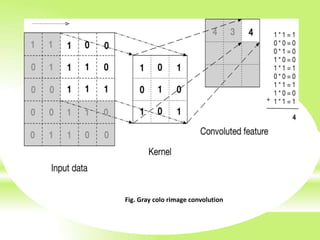
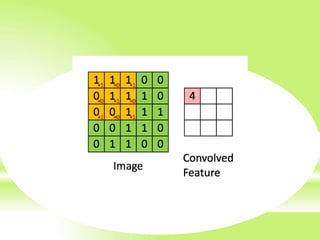
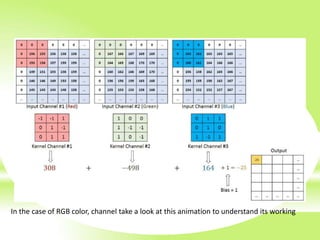
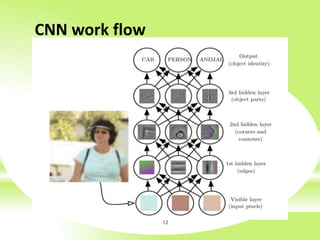
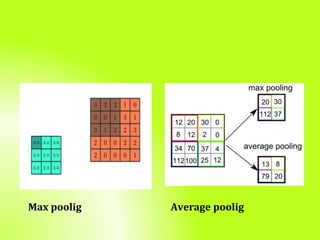
The document is a technical presentation on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), detailing their background, operation, and features. It discusses the advantages and drawbacks of CNNs, such as their effectiveness in pattern recognition and the high resource requirements for training. Additionally, it covers various applications of CNNs in fields like healthcare, automotive, and social media.