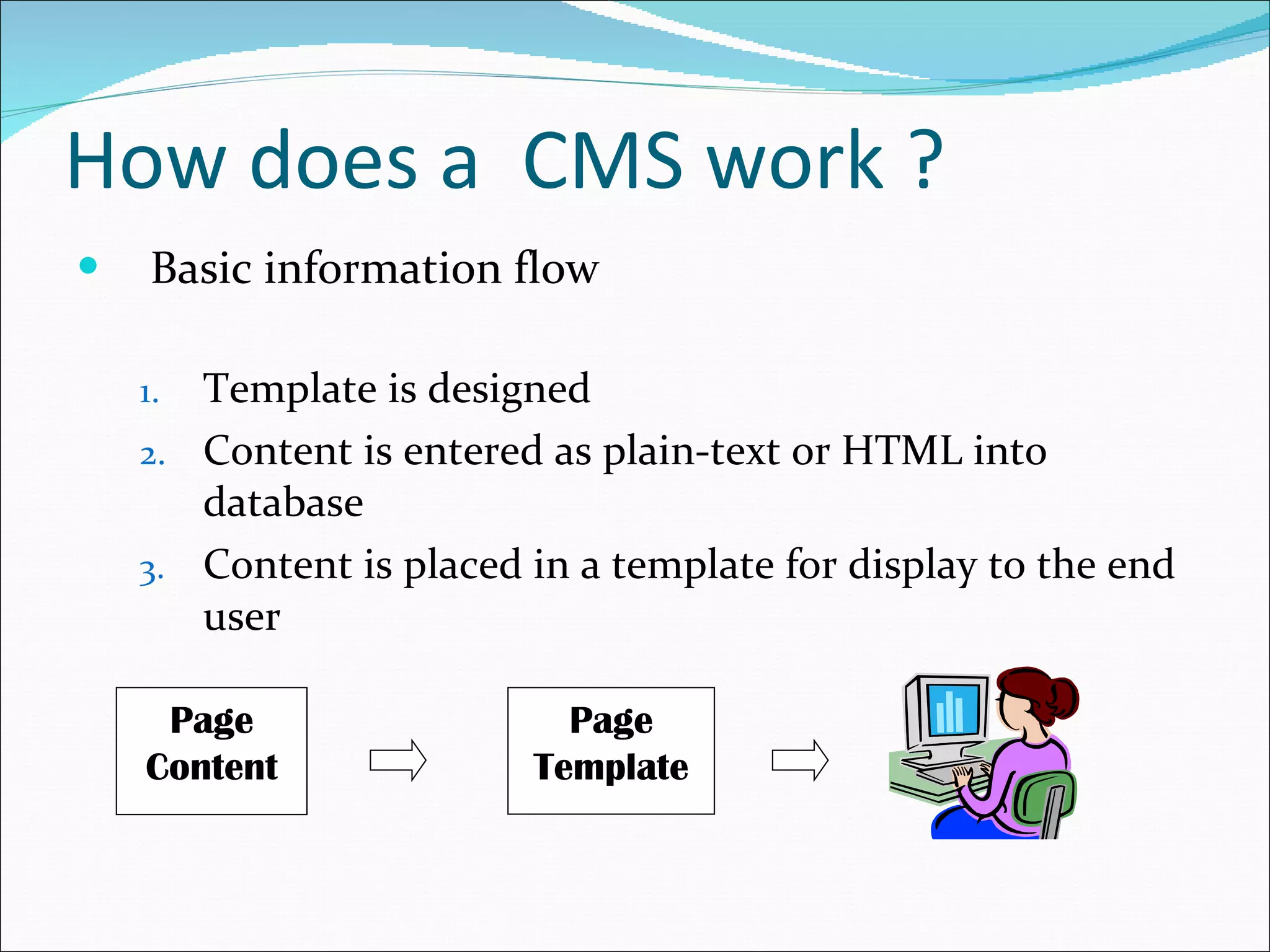
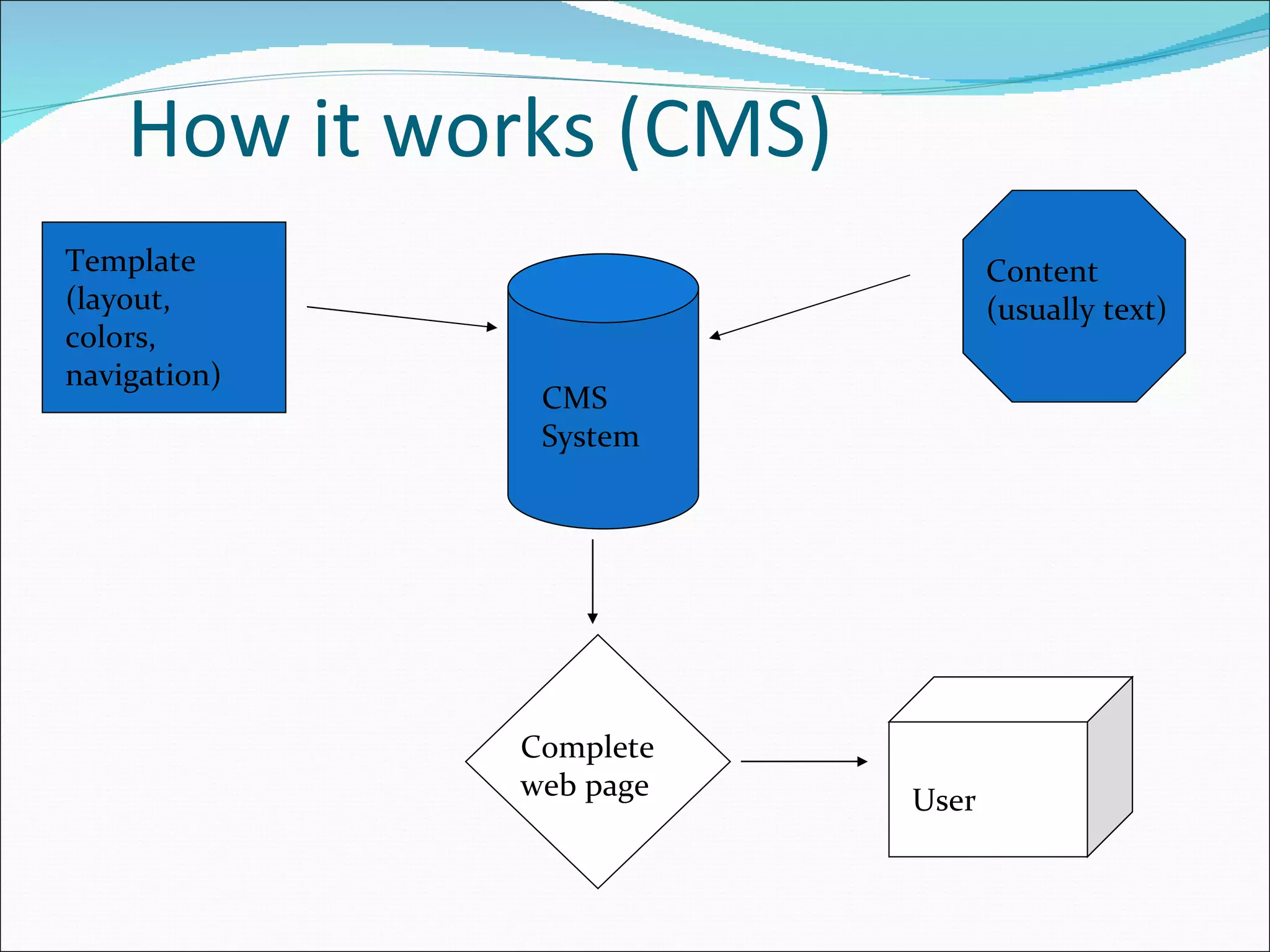
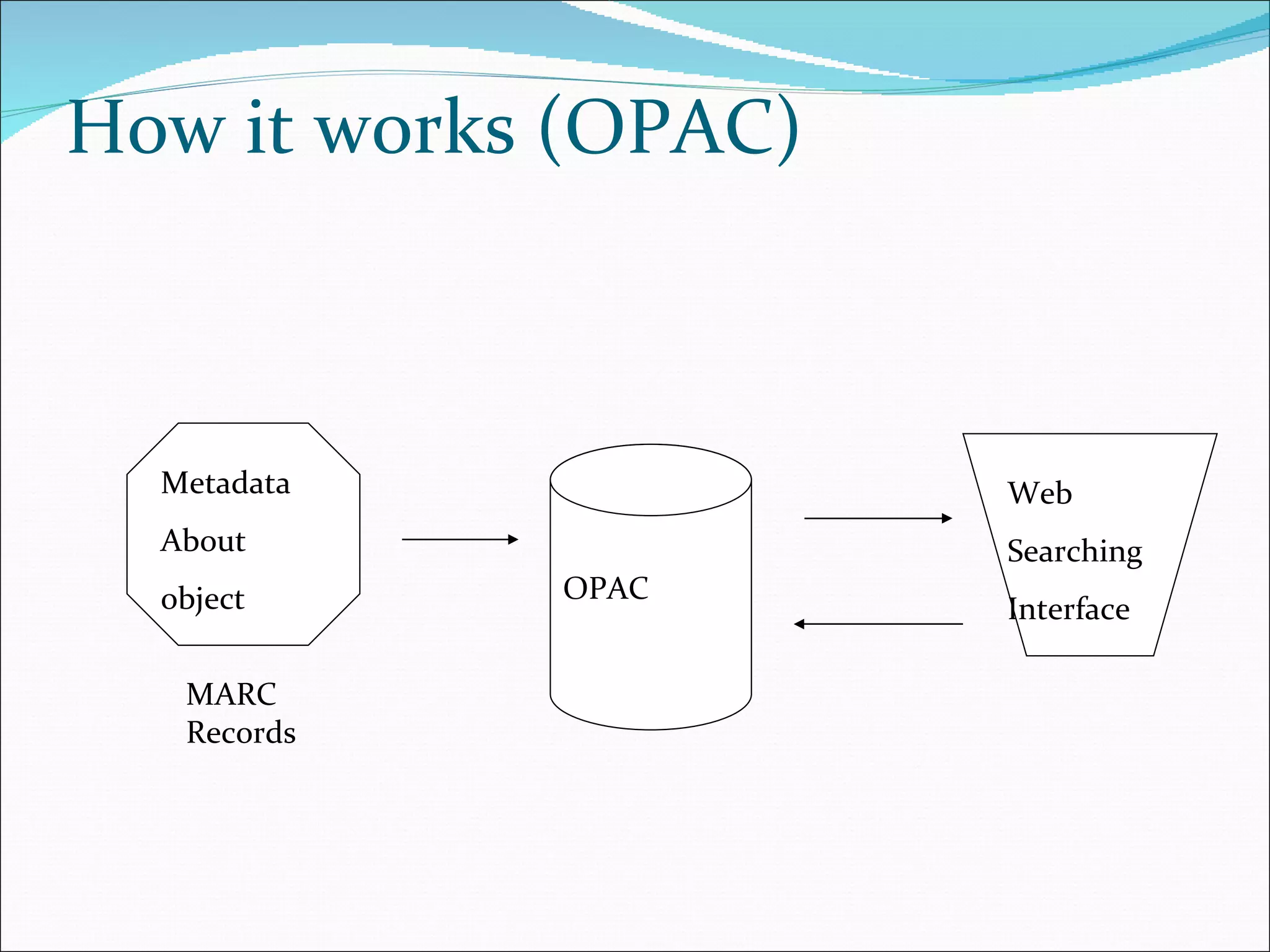
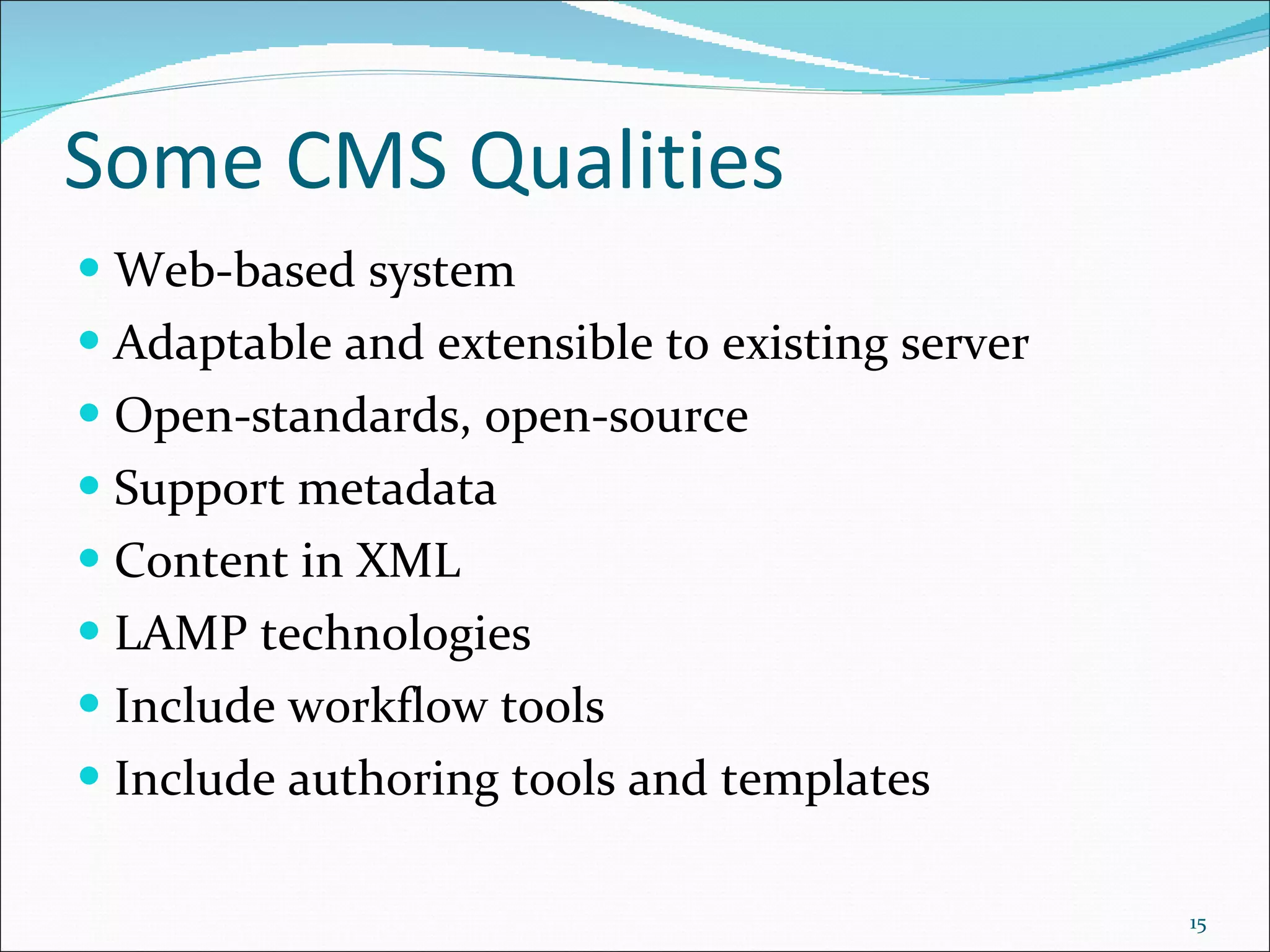
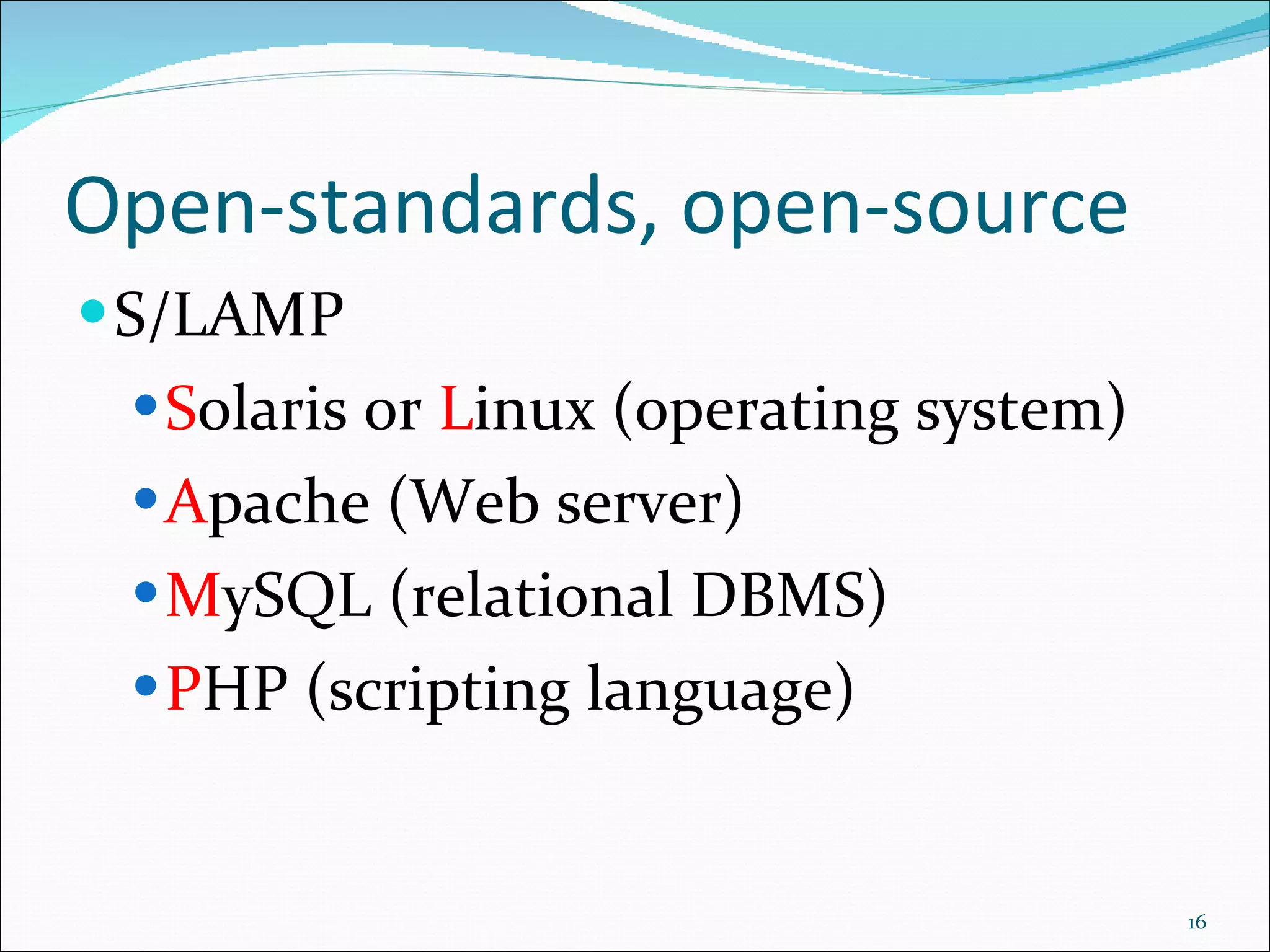
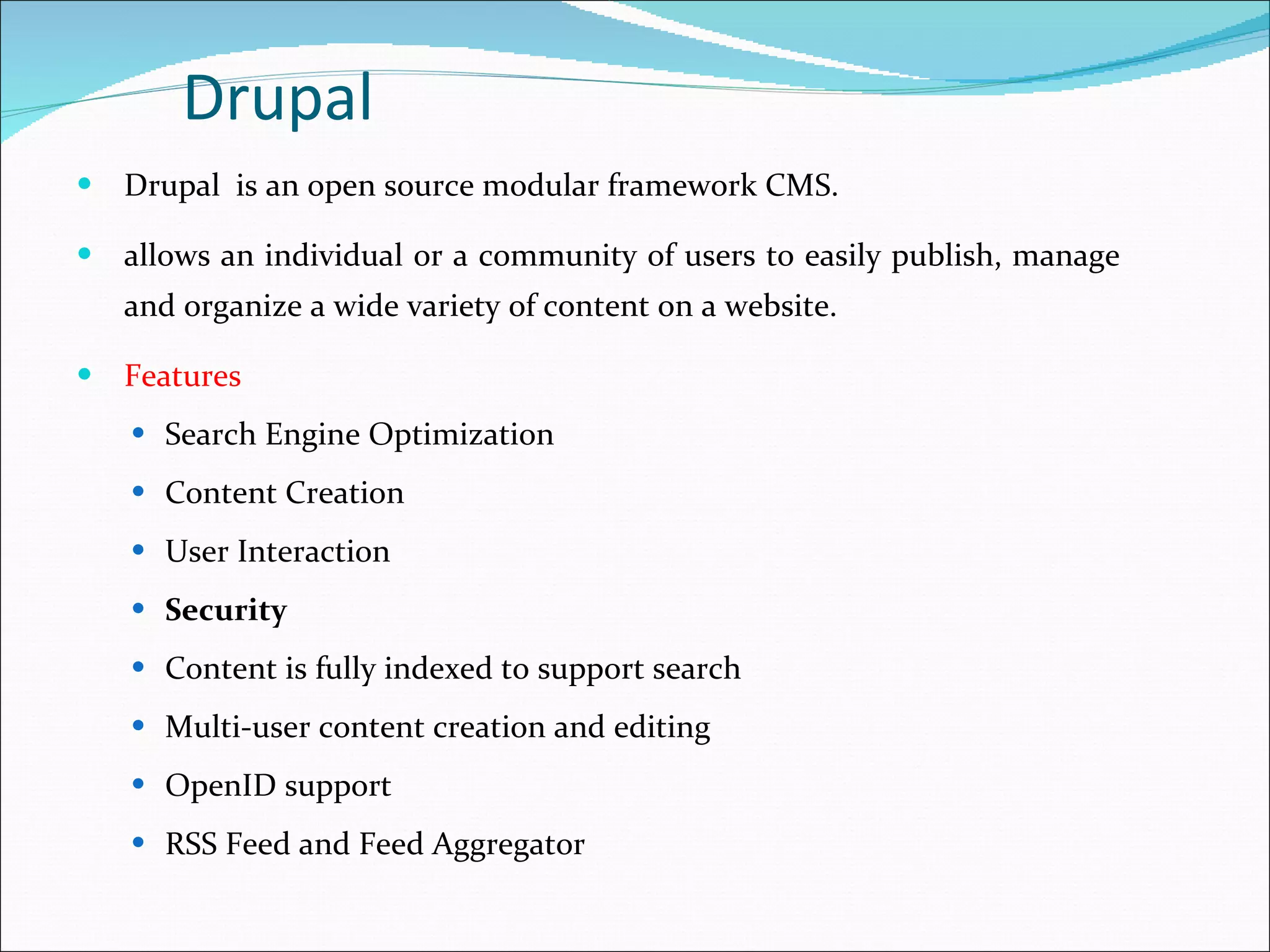
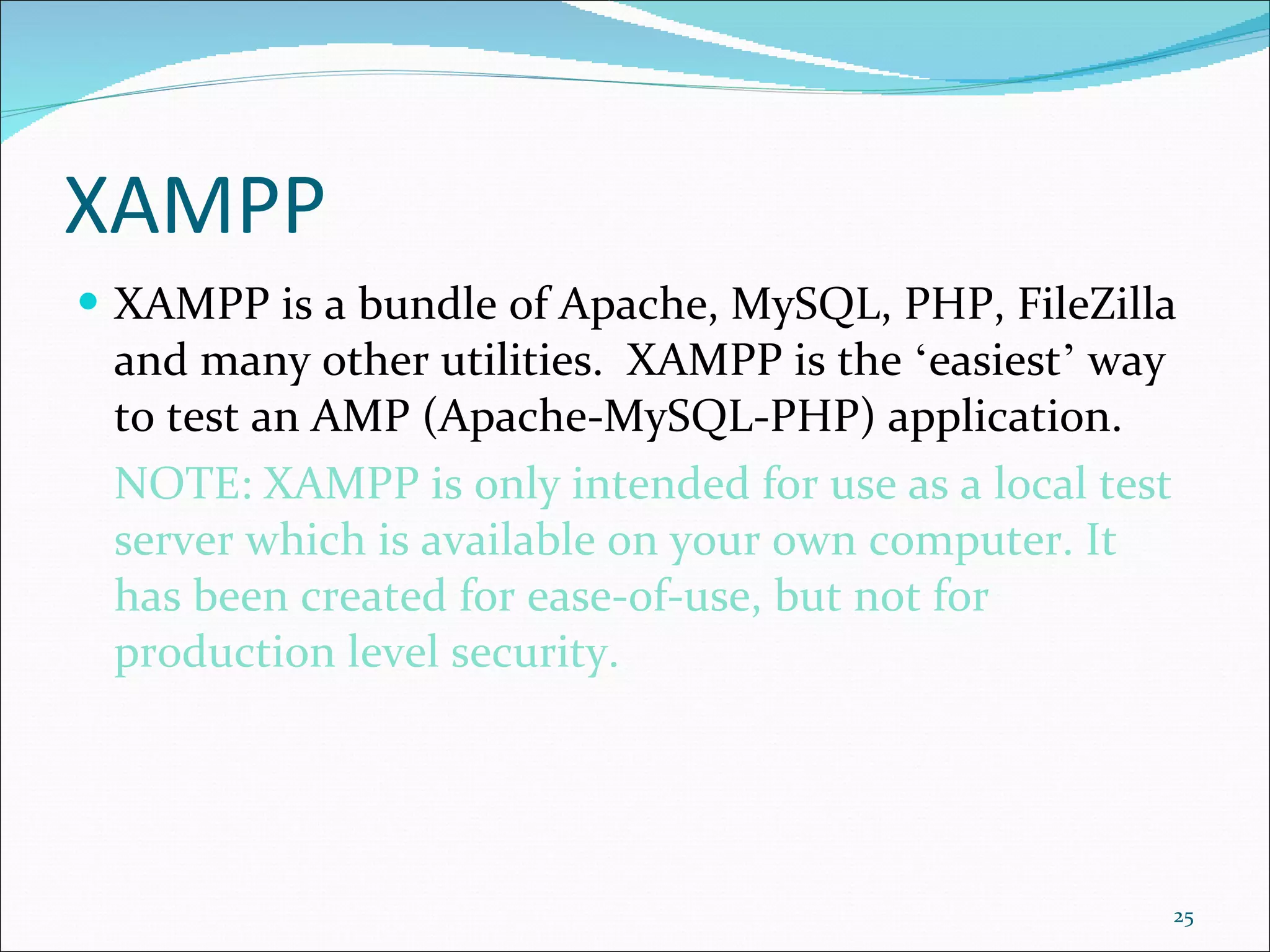
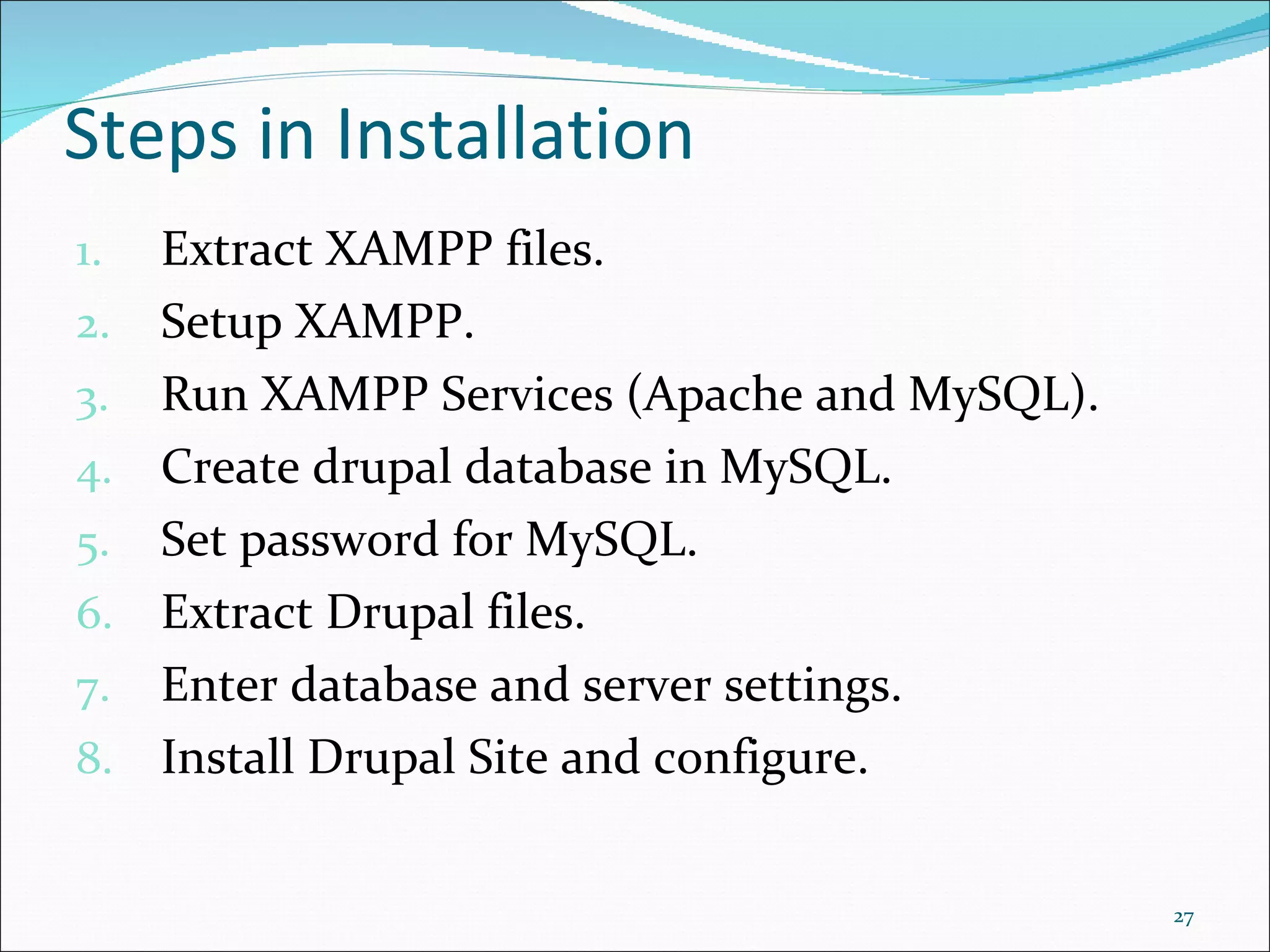
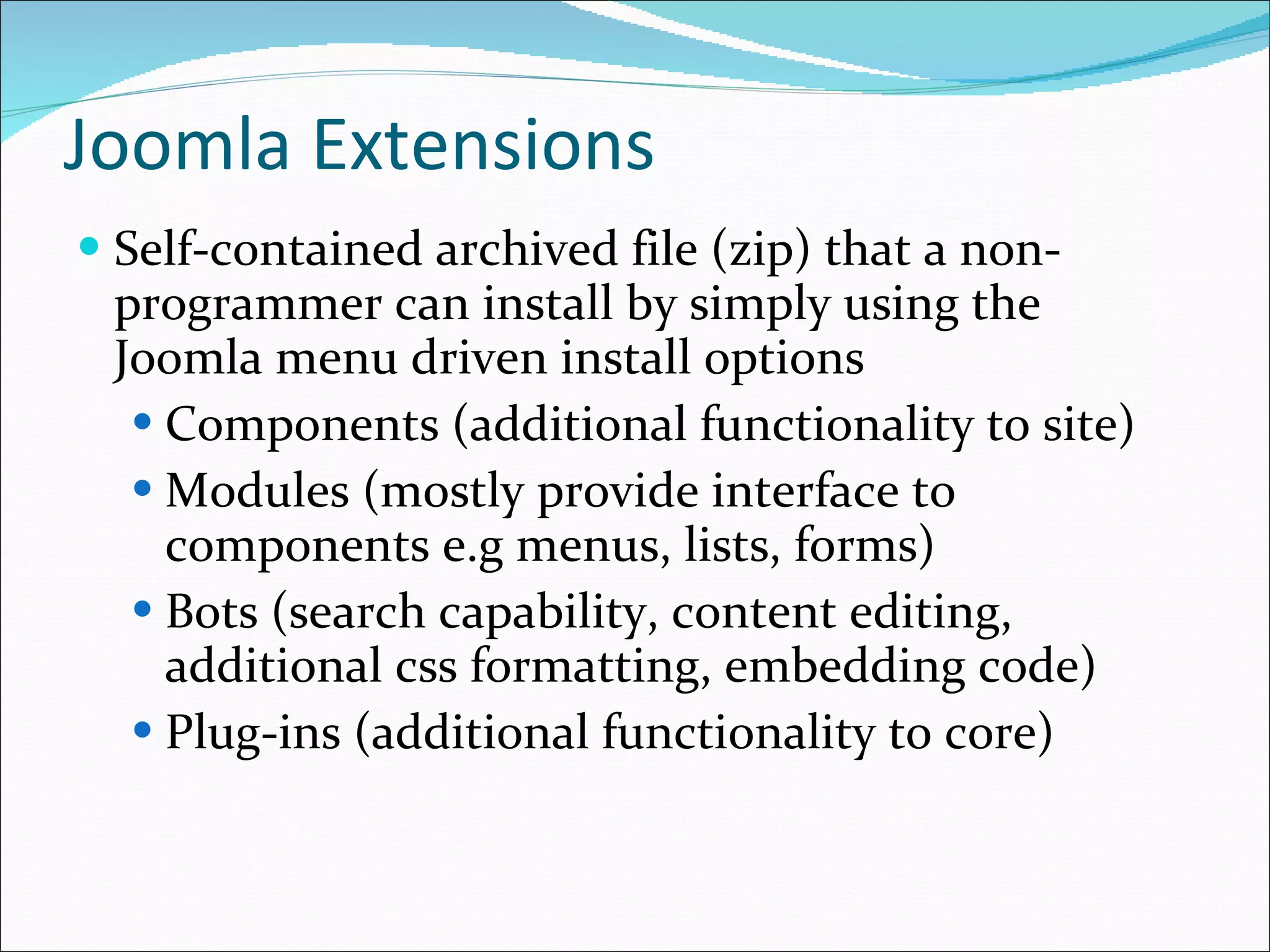
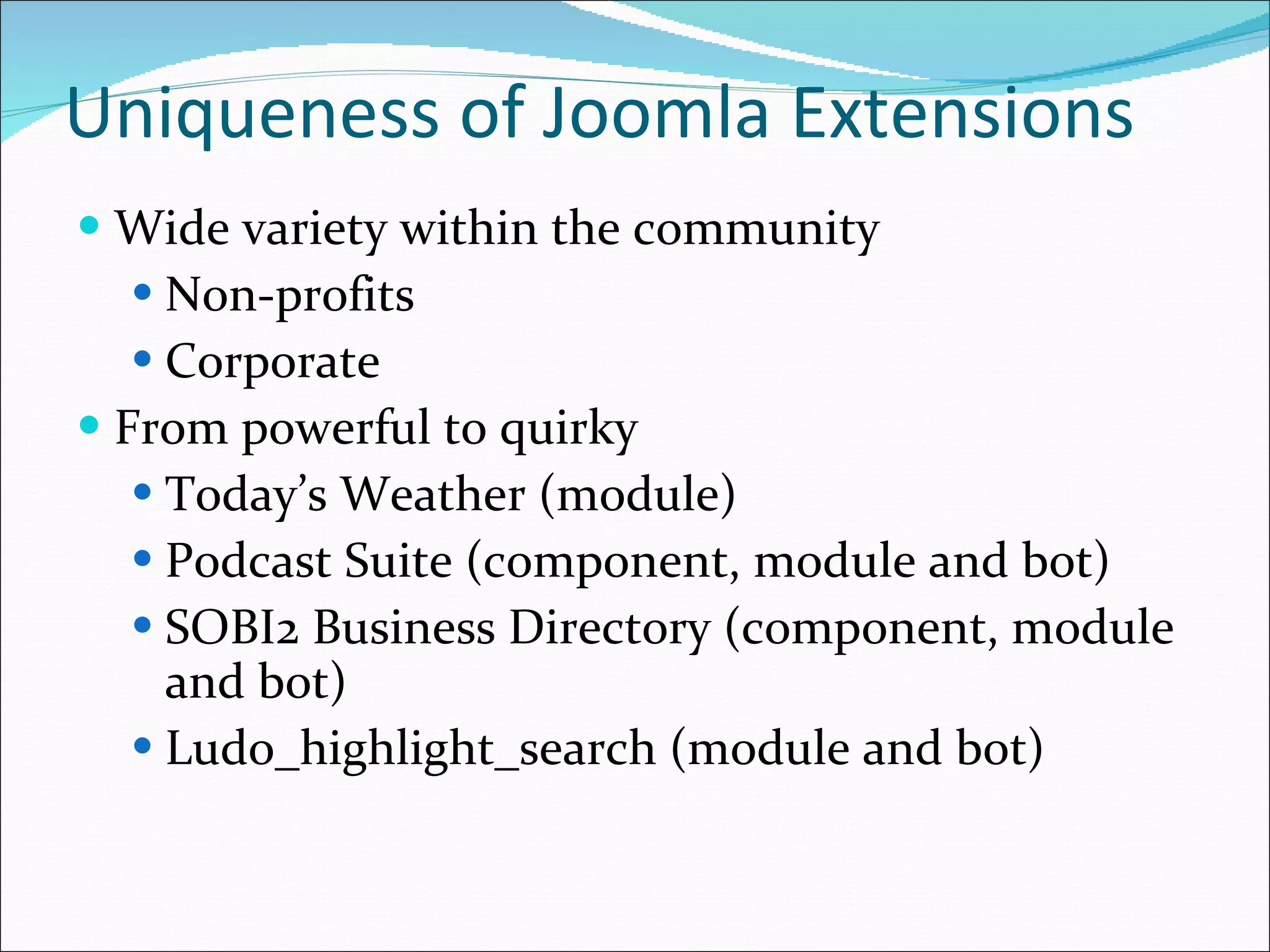
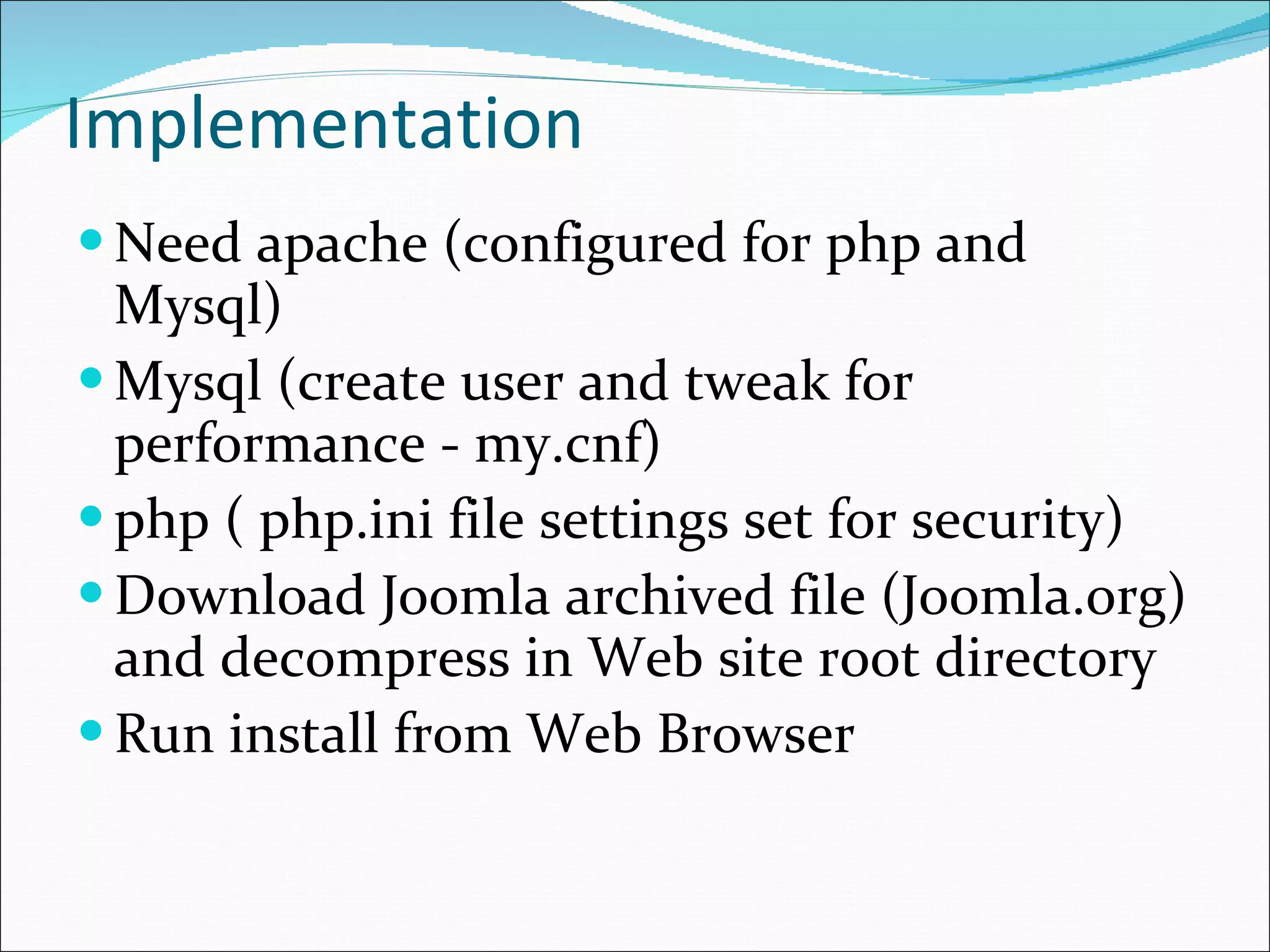
This document discusses content management systems (CMS), including what content is, where it resides, major CMS components, how CMS works, qualities of CMS, and examples of popular CMS like Drupal and Joomla. It provides descriptions of Drupal and Joomla, explaining their features and how they can be installed using XAMPP locally for testing purposes.
![Dr. M.Madhusudhan [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cmsanoverview-111205023708-phpapp02/75/Cms-an-overview-1-2048.jpg)