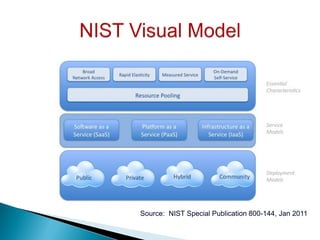
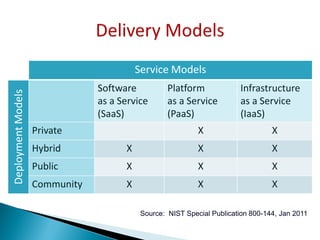
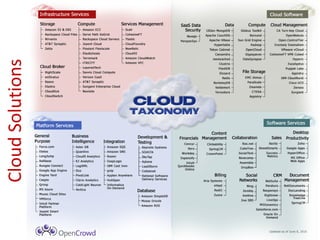
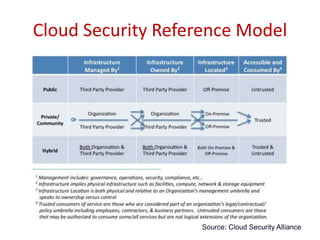
The document discusses cloud security, outlining its definition as a sub-domain of computer security and reviewing its growing importance due to increasing cloud computing adoption and associated risks. It identifies key dimensions of cloud security, critical areas to focus on, and approaches to mitigating risks, including the necessity for standardized frameworks and transparency in services. Key takeaways emphasize the evolving nature of cloud security and the collaborative efforts required from government, industry, and academia to enhance protections.