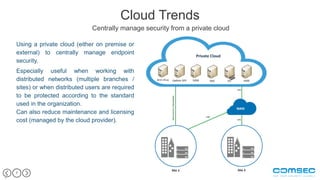
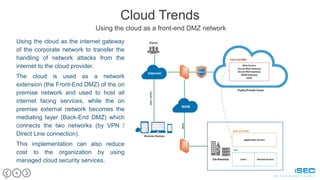
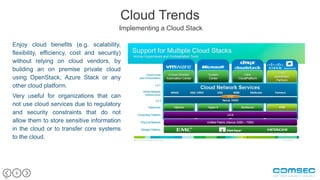
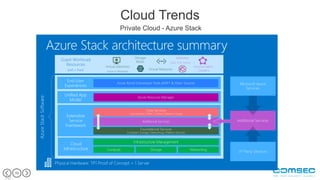
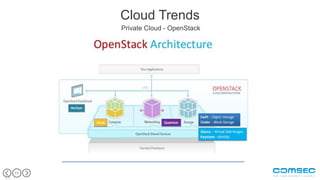
This document outlines the challenges and critical threats to cloud security, emphasizing issues like lack of control, insufficient encryption, and the risk of data breaches. It identifies eight major threats including weak authentication, insider threats, and DDoS attacks, suggesting measures such as encryption and multi-factor authentication to mitigate risks. The text also discusses trends in cloud security management, such as utilizing private clouds and transforming cloud services into a front-end DMZ network to enhance security.