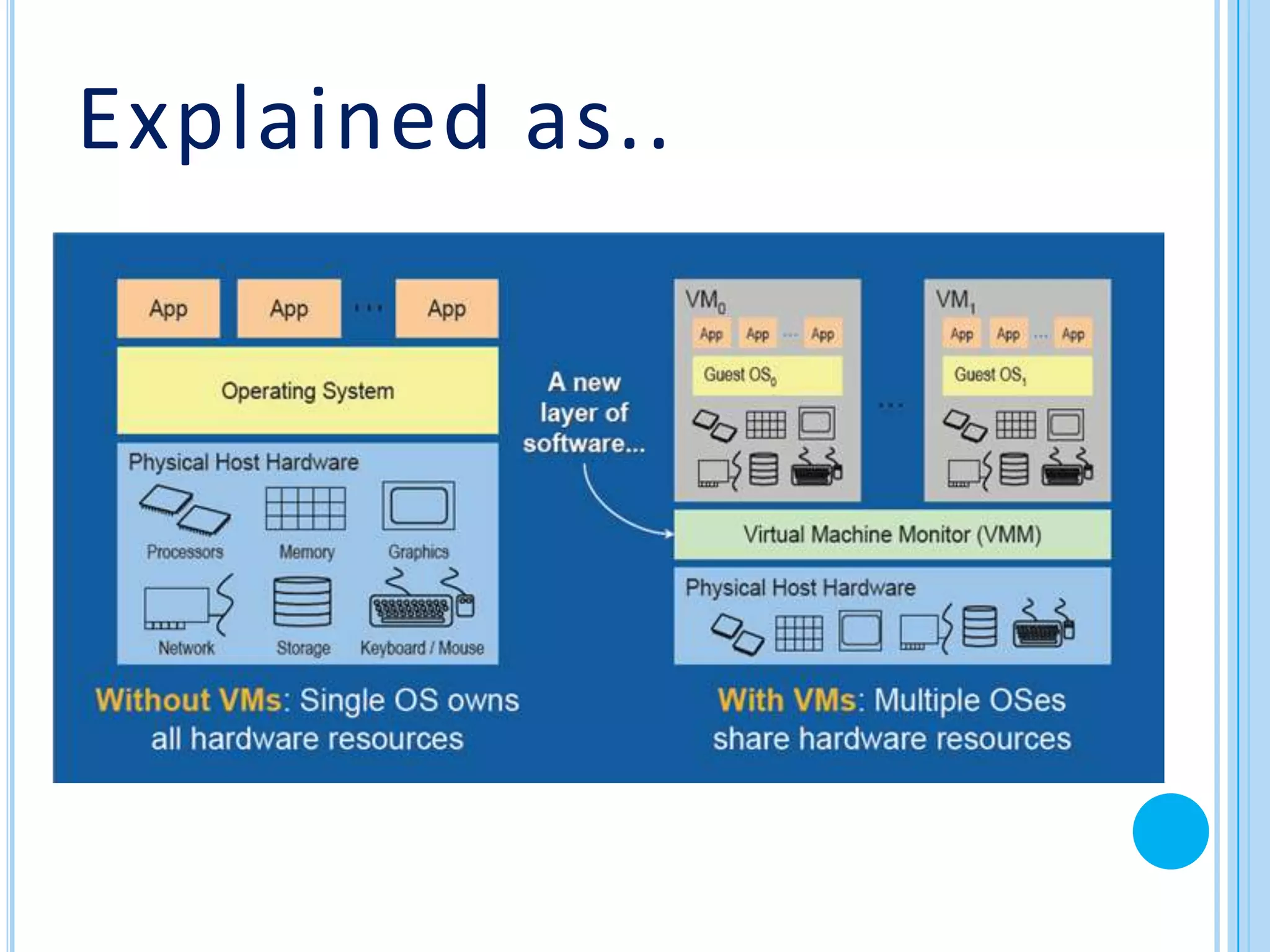
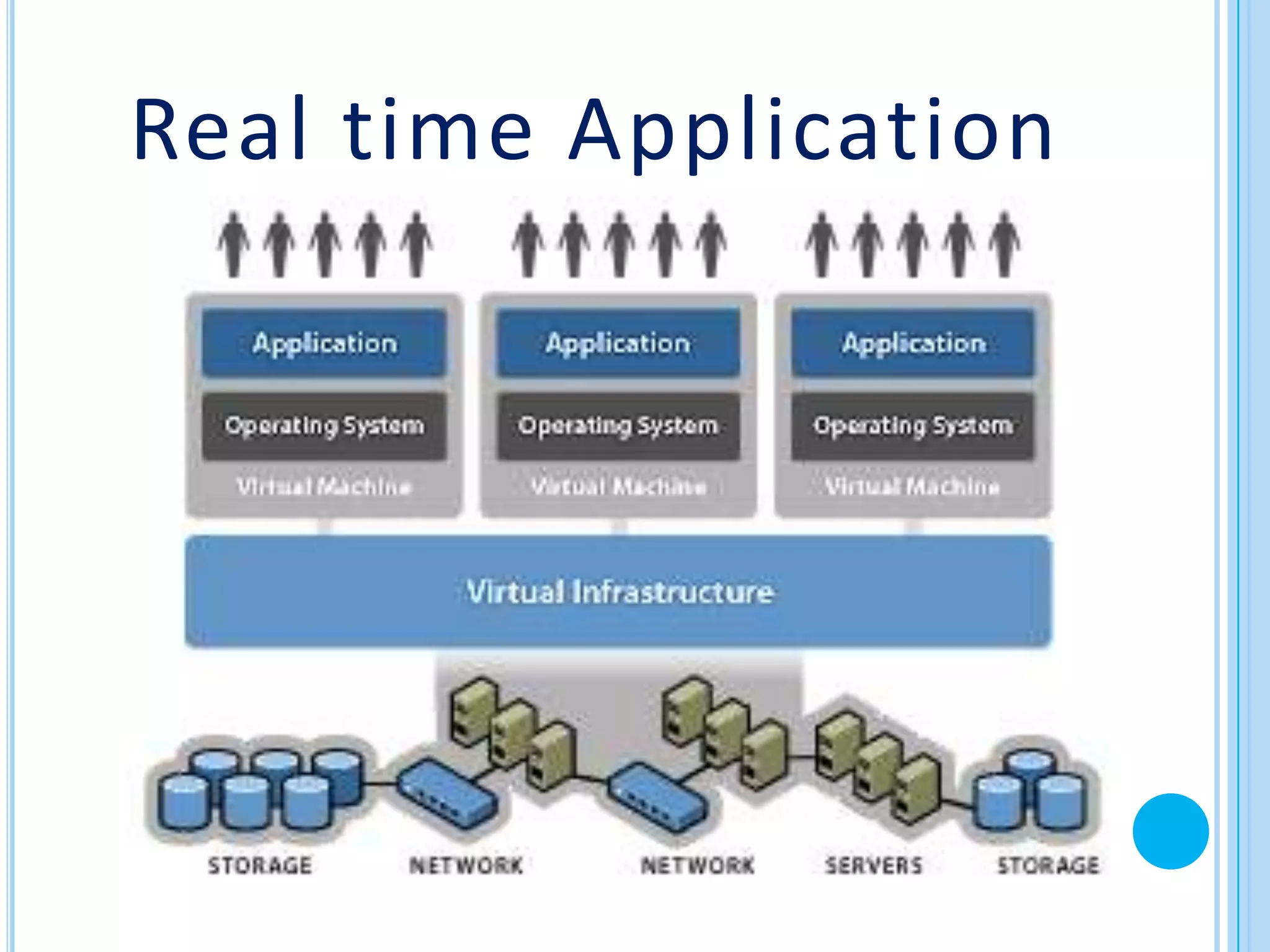
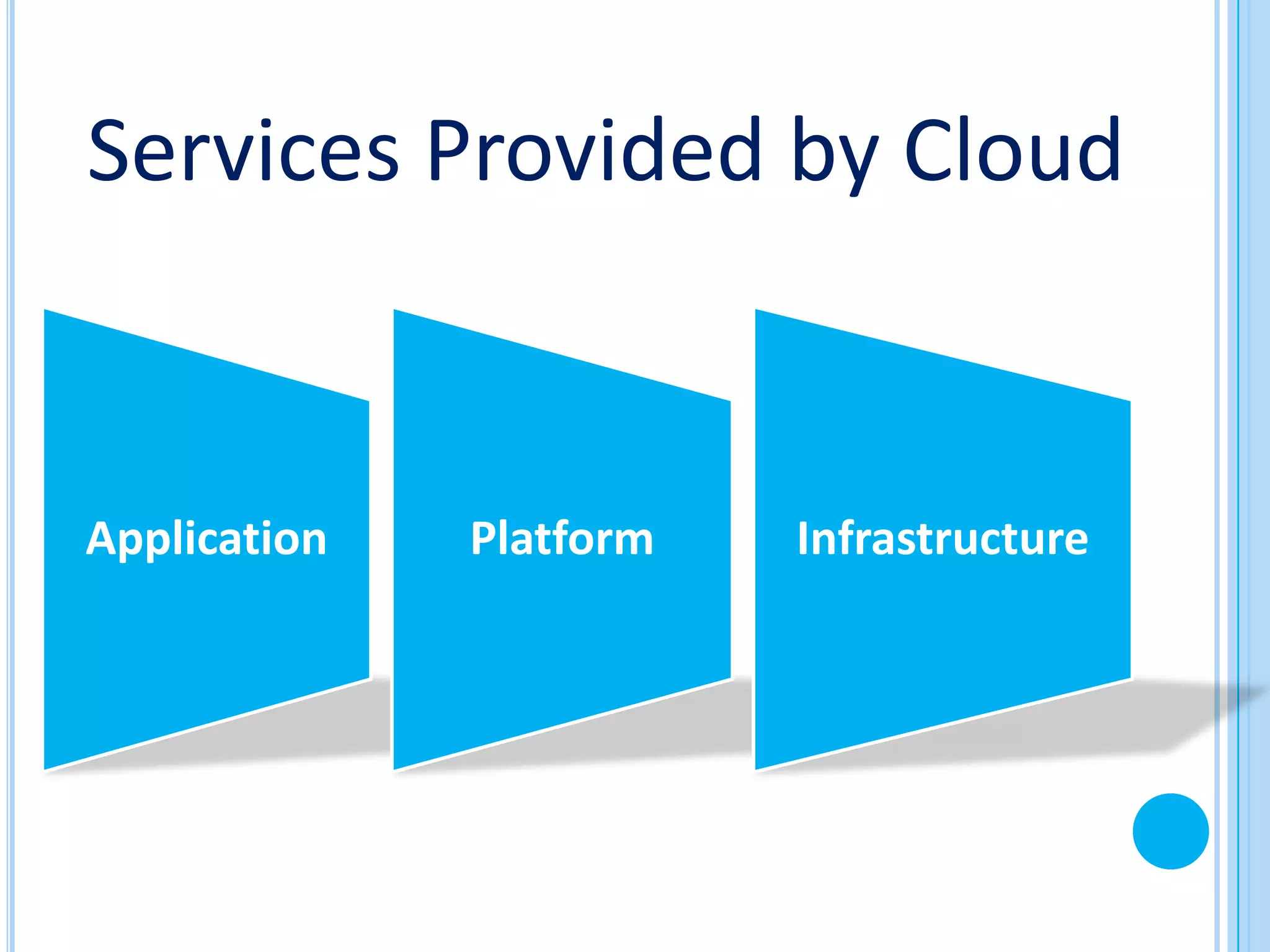
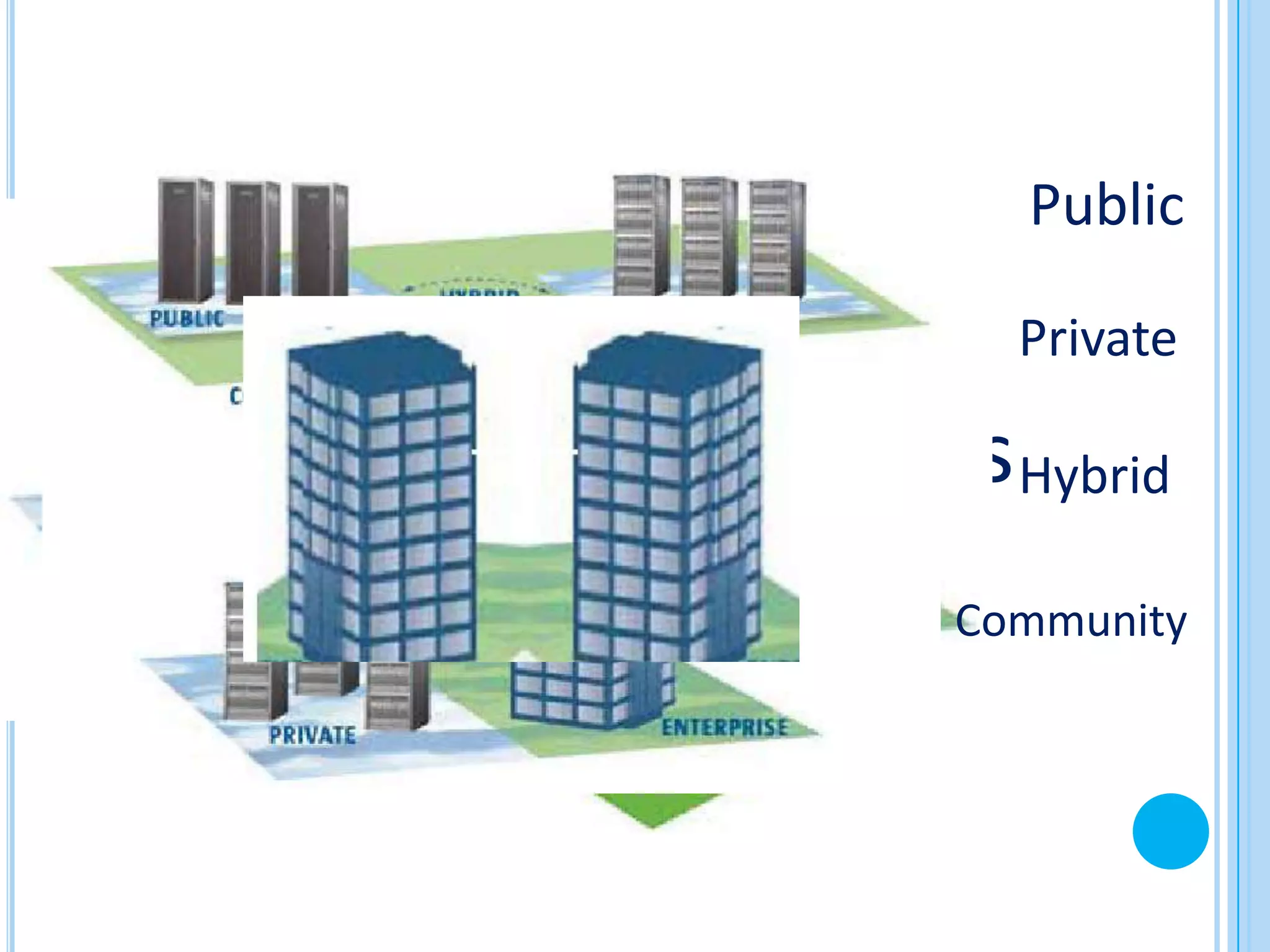
The document provides an overview of cloud computing. It defines cloud computing and discusses its history from the 1960s concept of computing as a utility to modern cloud platforms. The document outlines different cloud service models including Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). It discusses major cloud providers like Amazon, Google, Microsoft and IBM and different deployment models. The document notes both benefits of cloud computing like reduced costs, flexibility and drawbacks around security, internet dependence and transition challenges.