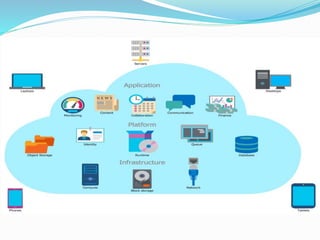
Cloud computing allows users to access files, applications, and other IT resources over the internet rather than through direct access to a local server or storage device. It offers various benefits including reduced costs since companies only pay for the computing resources they need, improved mobility as data is accessible from anywhere via an internet connection, and high availability since cloud providers aim to maintain 99.99% uptime. Cloud services allow companies to reduce their data center footprint or eliminate it altogether while still maintaining IT capabilities in a flexible and cost-effective manner.