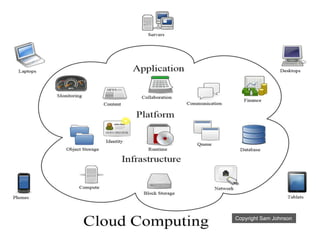
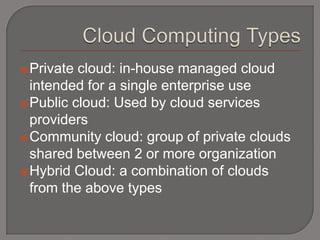
The document discusses different types of cloud computing including Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). It provides examples of each type and their main uses and benefits. The document also covers private vs public vs hybrid clouds and some security and legal issues related to cloud computing. It concludes that SaaS and IaaS are continuing to grow in popularity as more companies offer competitive prices for software solutions and organizations seek higher return on investment.