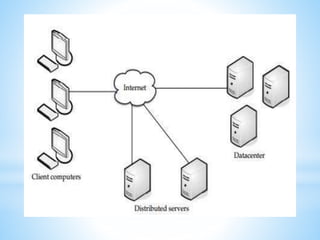
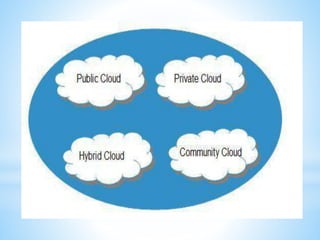
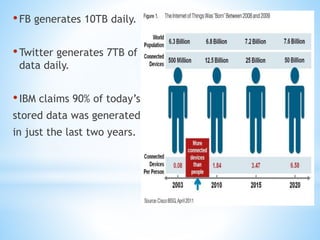
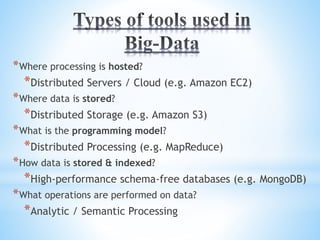
Cloud computing involves delivering computing services over the internet. It has three main components: client computers, distributed servers located in different geographic locations, and data centers housing servers and applications. There are three main service models: Software as a Service (SaaS) which provides required software; Platform as a Service (PaaS) which provides operating systems and networks; and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) which provides basic network access. Deployment models include public, private, hybrid, and community clouds based on access restrictions. Big data refers to very large amounts of digital data that cannot be analyzed with traditional techniques, and requires distributed processing across cloud infrastructure to gain insights.