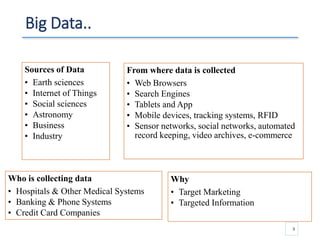
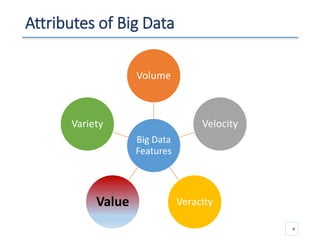
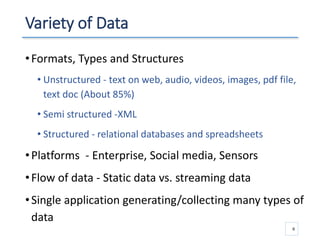
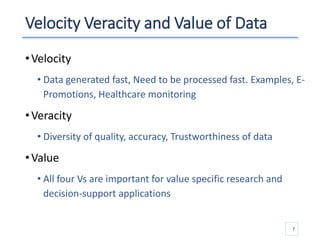
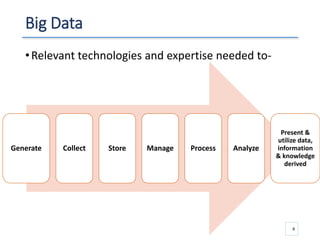
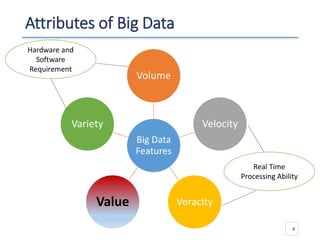
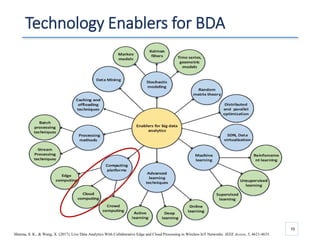
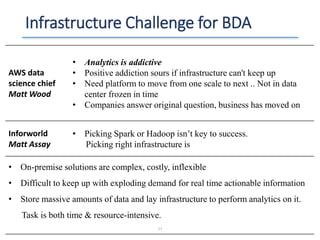
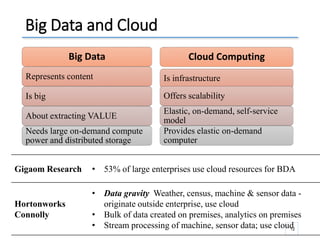
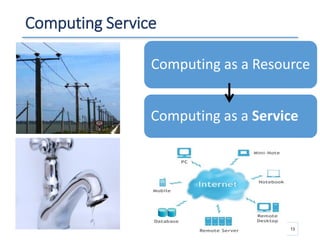
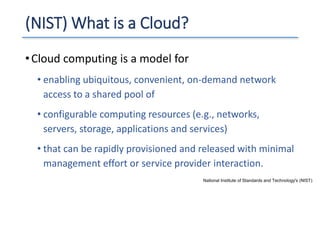
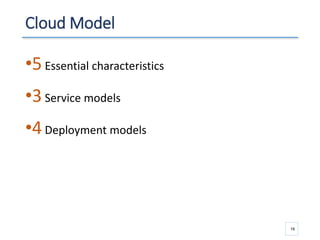
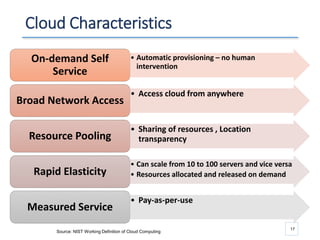
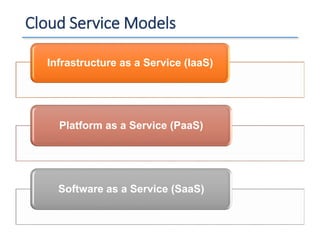
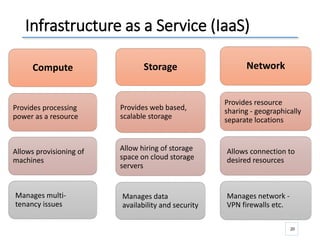
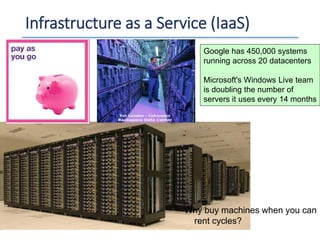
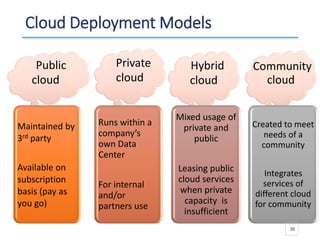
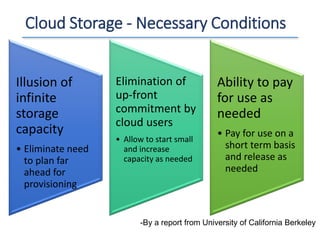
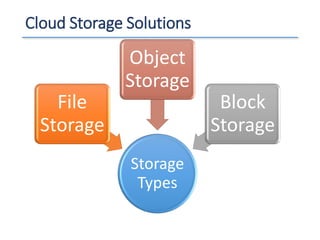
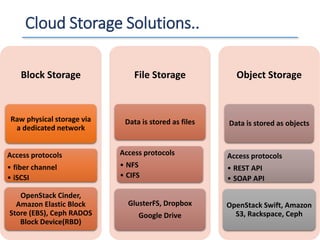
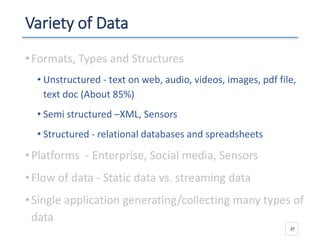
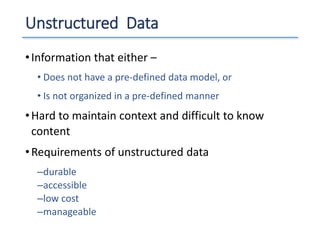
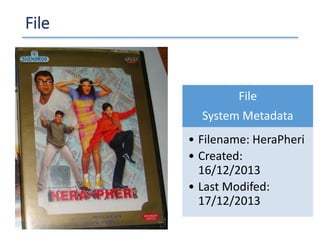
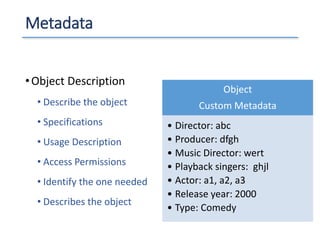
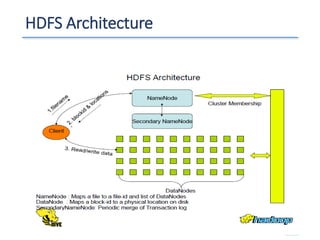
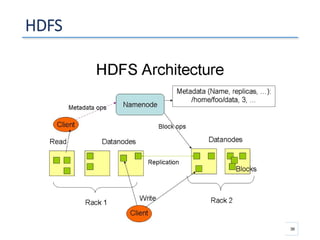
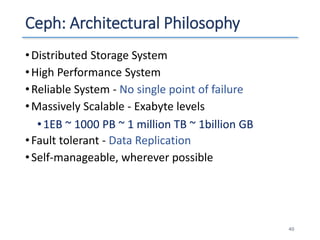
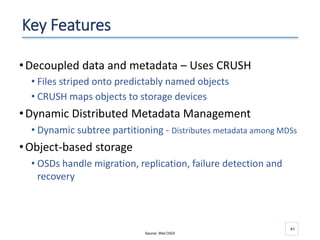
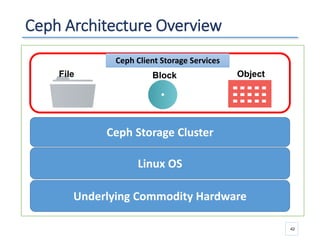
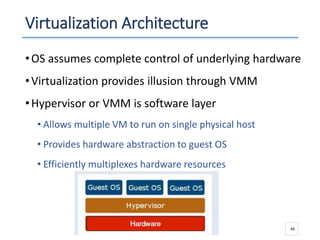
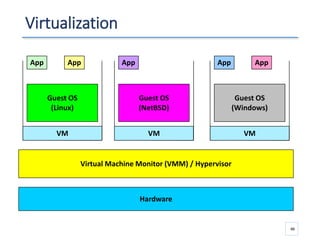
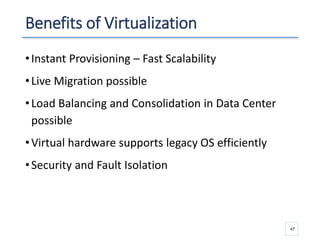
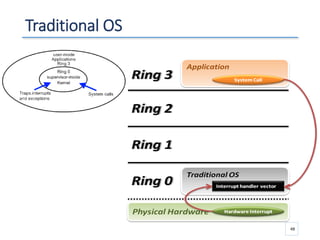
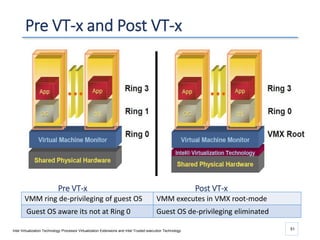
The document outlines a seminar presented by Dr. Anita Goel on recent trends in big data and cloud computing, covering topics such as the sources and attributes of big data, as well as various aspects of cloud computing including storage types and deployment models. It highlights the importance of infrastructure and scalability in handling large data volumes and discusses the need for modern storage solutions like software-defined storage and object storage. Additionally, the presentation emphasizes the role of virtualization and various technologies that enable big data analytics.