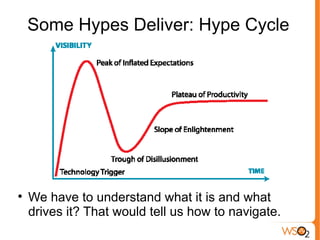
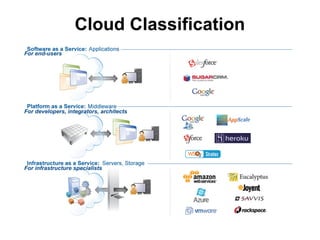
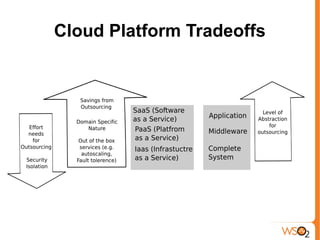
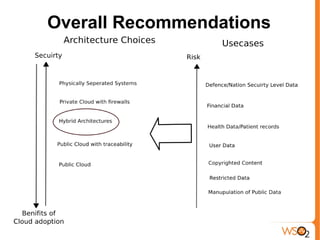
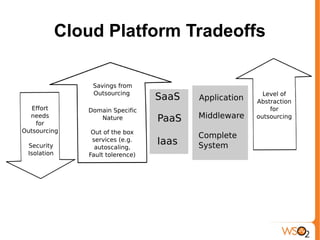
This document provides an overview of cloud computing and virtualization trends. It discusses what cloud computing is by comparing it to electricity as a utility. The document outlines the benefits of cloud computing such as reduced costs, ability to scale up and down as needed, and pay per use. It also covers drivers of cloud computing like unused computing power at large tech companies. The document classifies cloud models and provides examples of infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS). It addresses potential impacts of cloud computing and dangers/concerns regarding privacy, security, performance, and challenges.