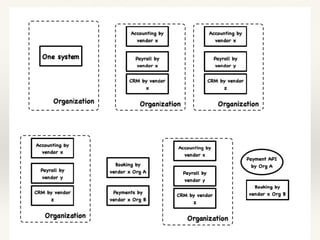
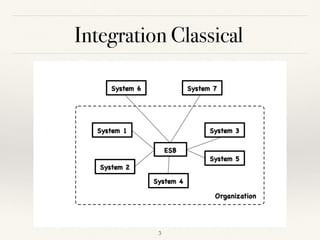
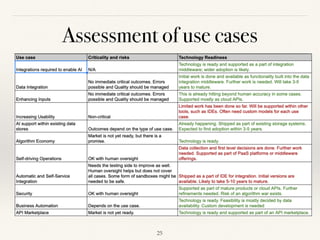
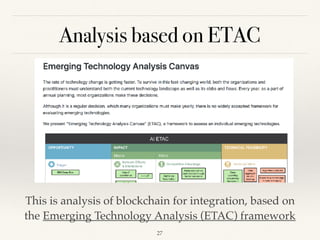
This document discusses how AI could shape future integrations. It begins by explaining different types of tasks that AI can perform, such as those that can be precisely explained versus those requiring examples and feedback to learn. The document then covers benefits of AI like speed, lower costs, and ability to learn and extrapolate. It discusses using AI for cost savings, competitive advantages, and new revenue streams through insights. Challenges of AI like lack of data and skilled professionals are presented along with risks such as bias, privacy issues, and how mistakes can be more harmful than for humans. Various use cases of AI in integration are explored such as enhancing inputs, security, and automatic integration. The document concludes that AI will create many new integration opportunities