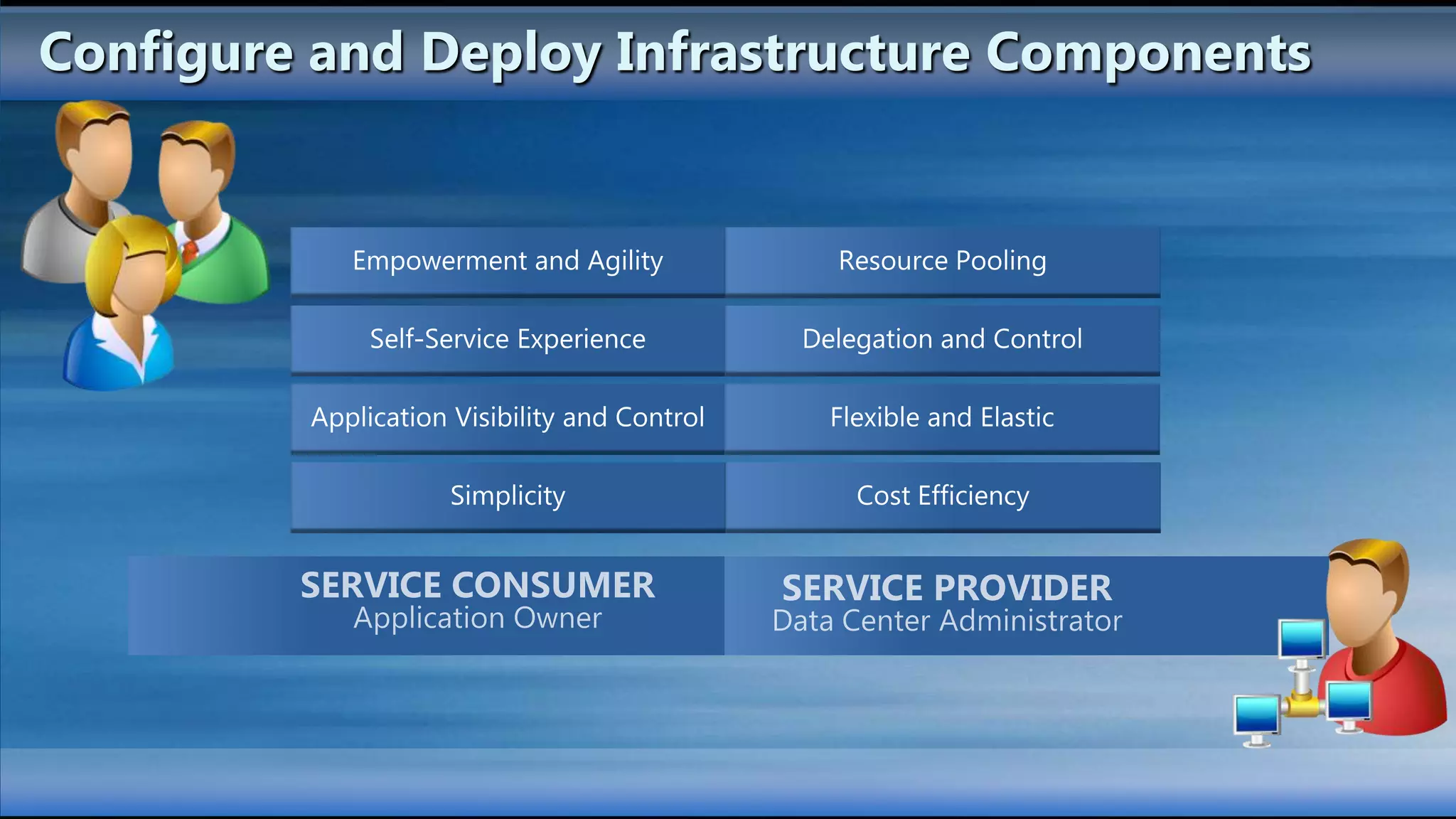
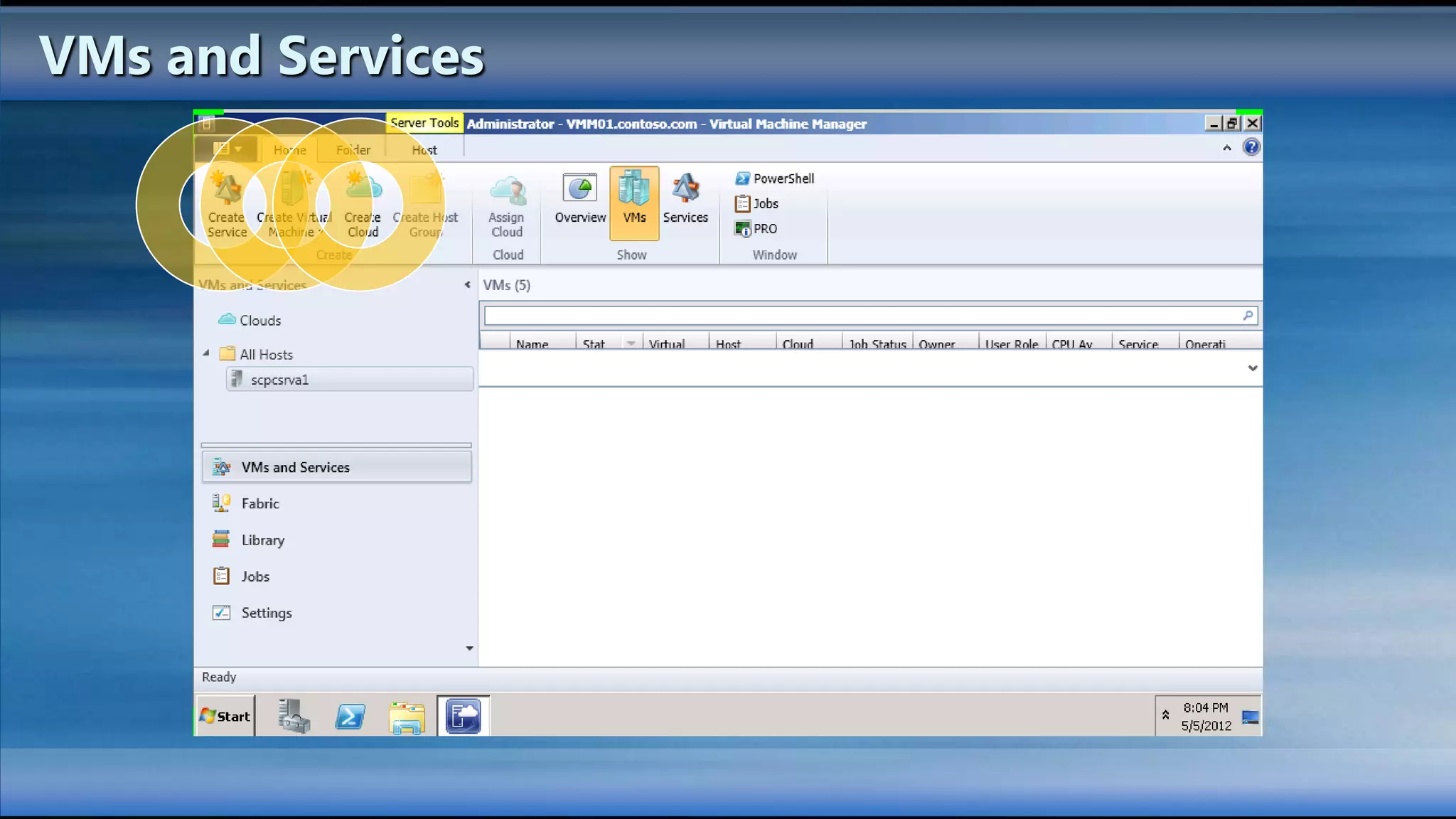
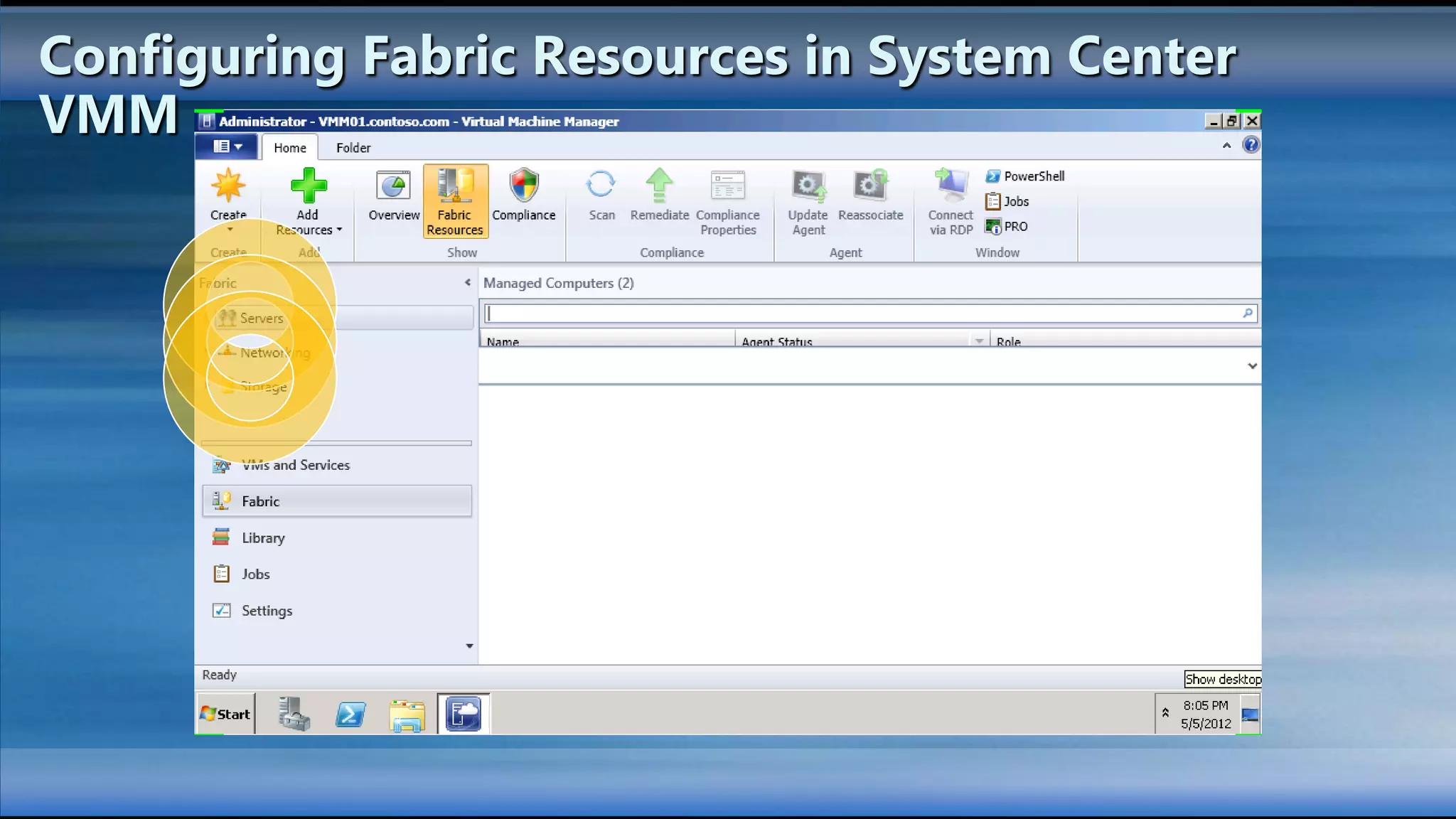
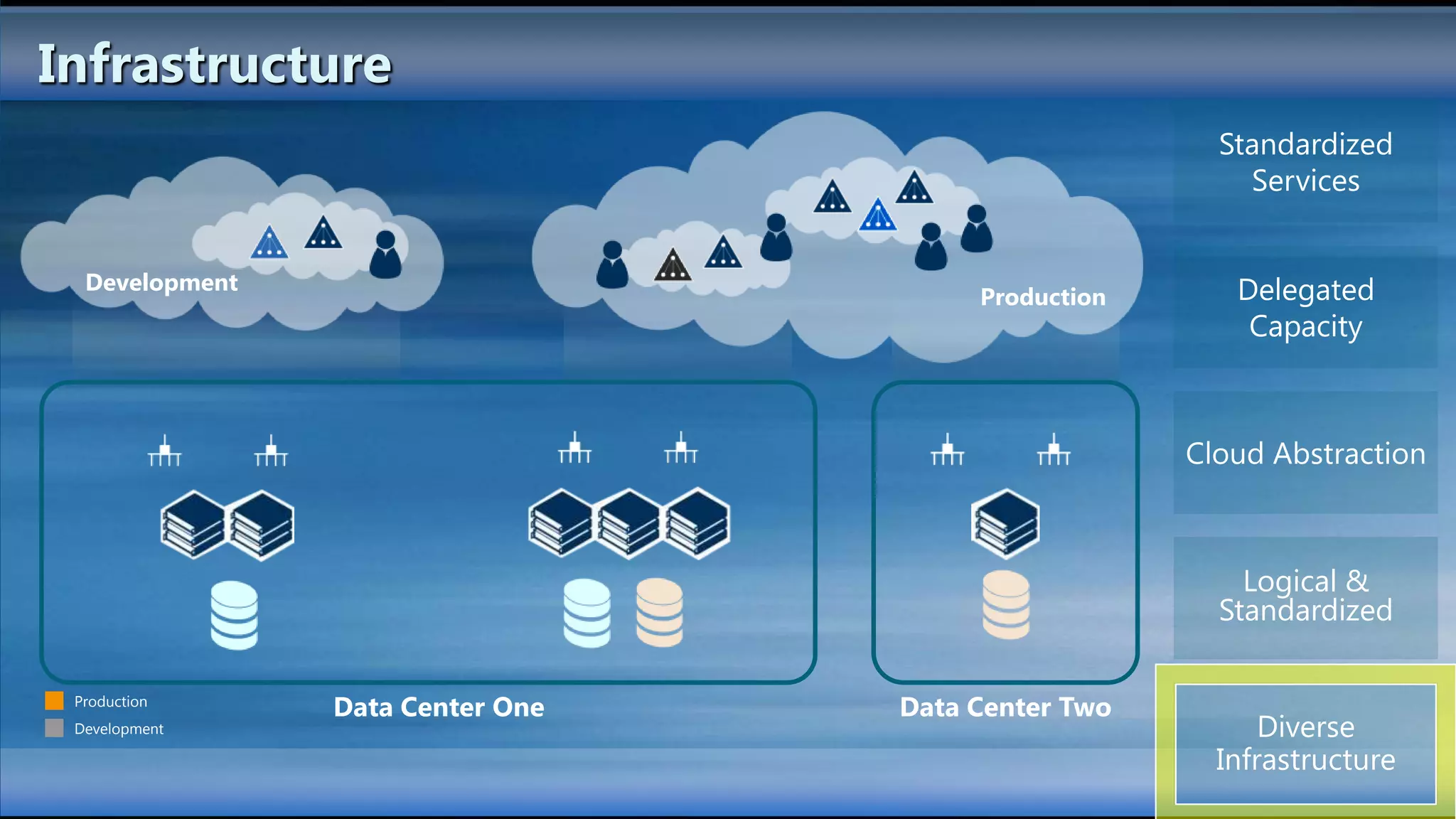
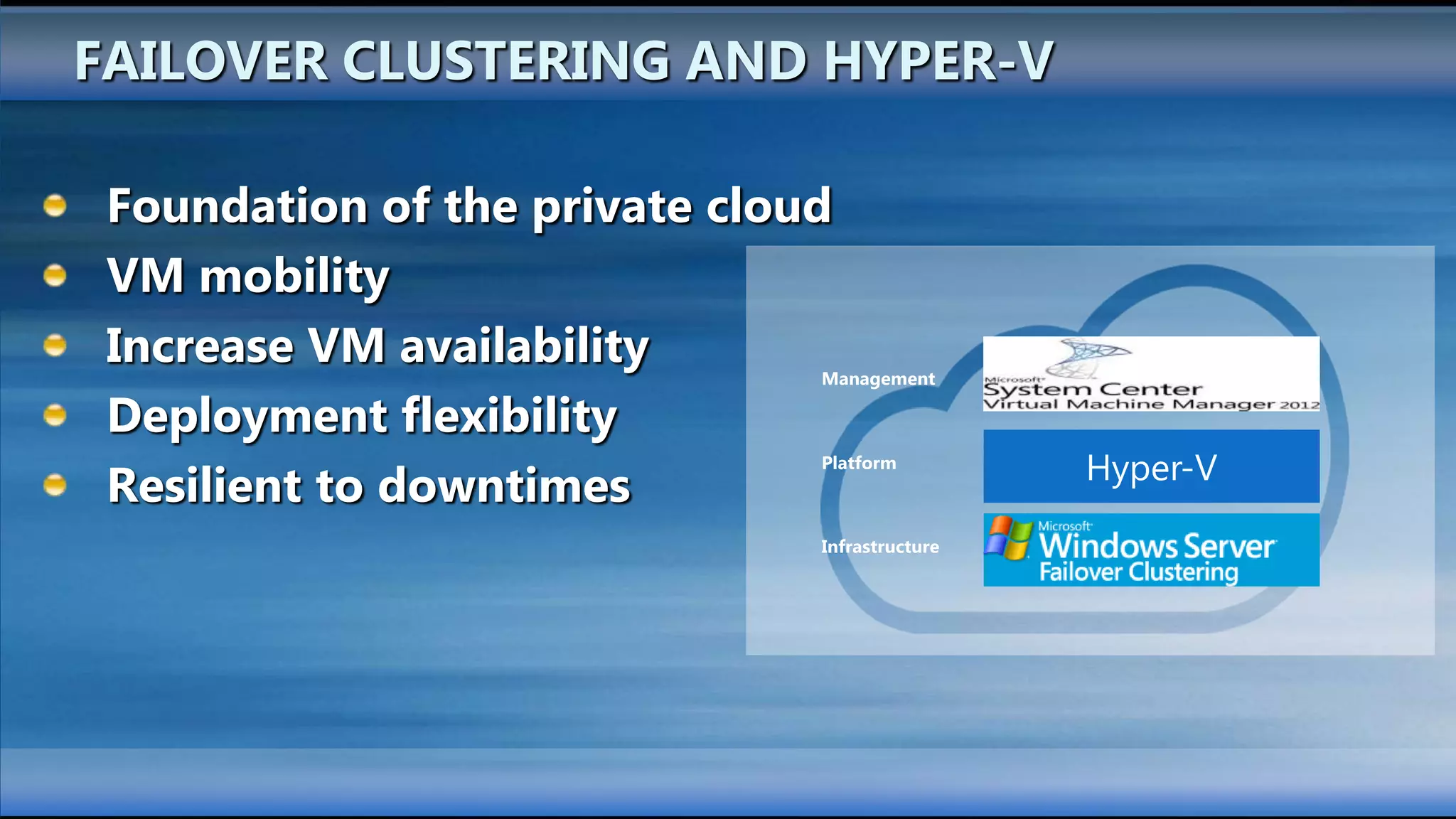
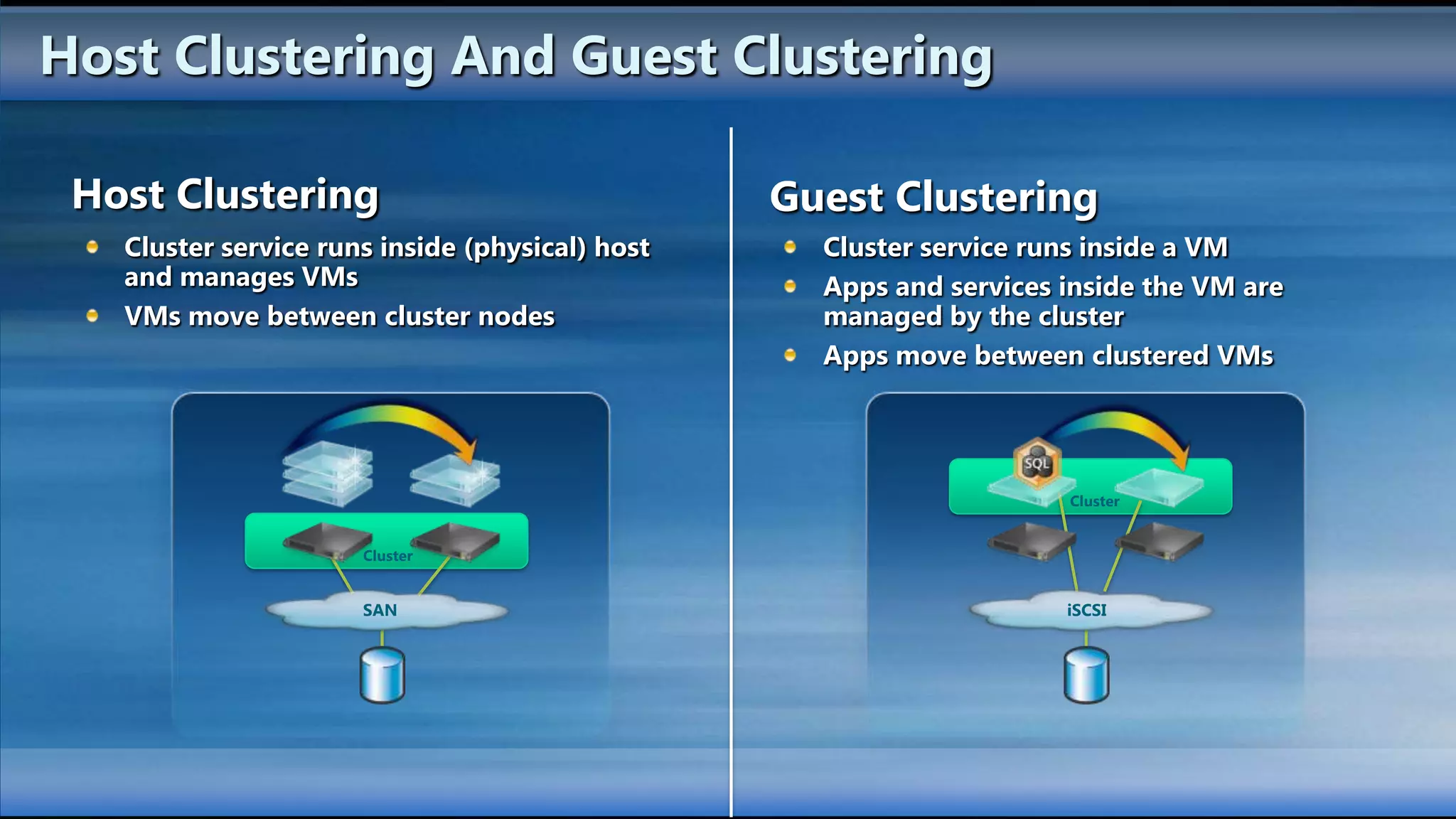
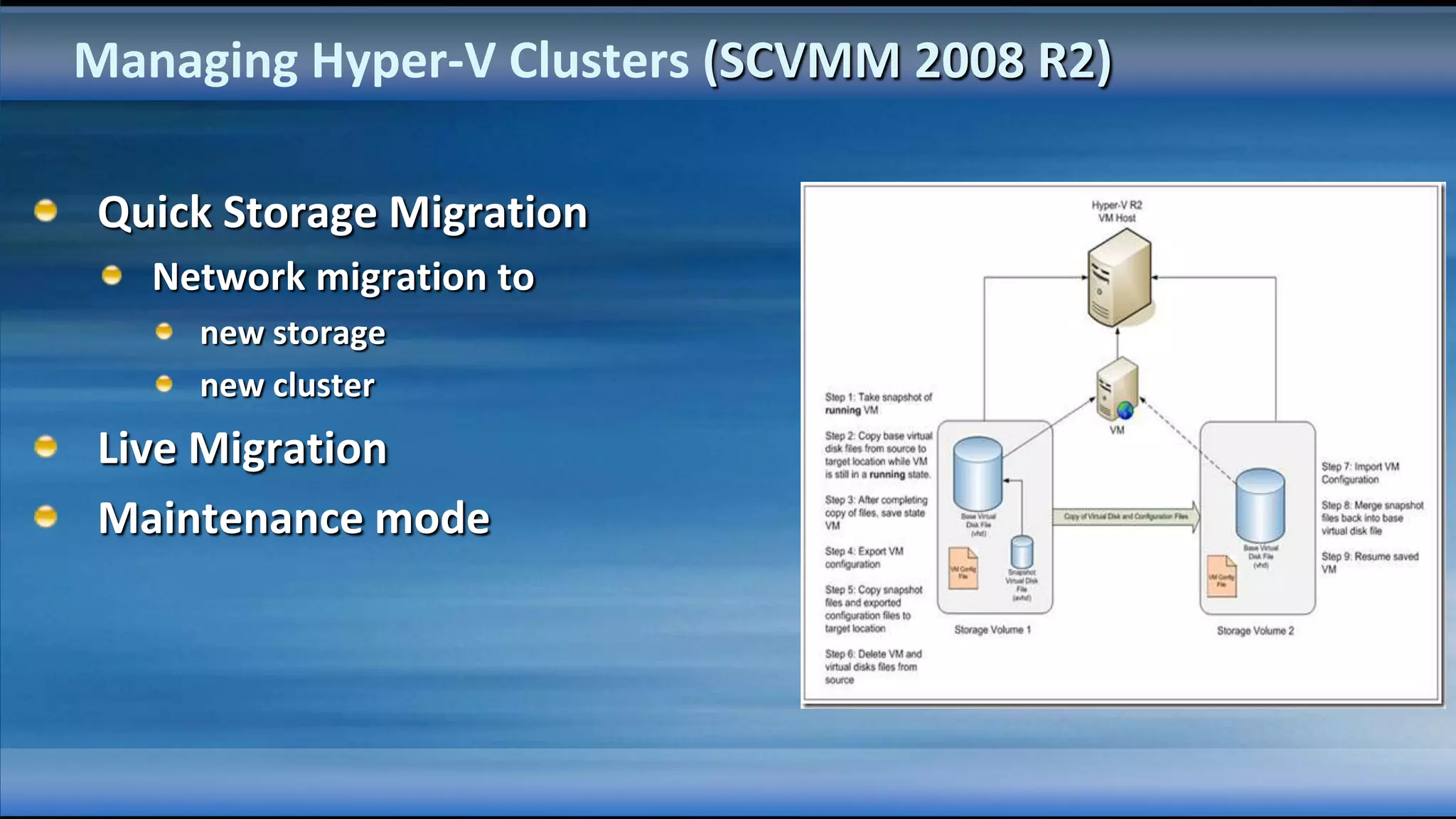
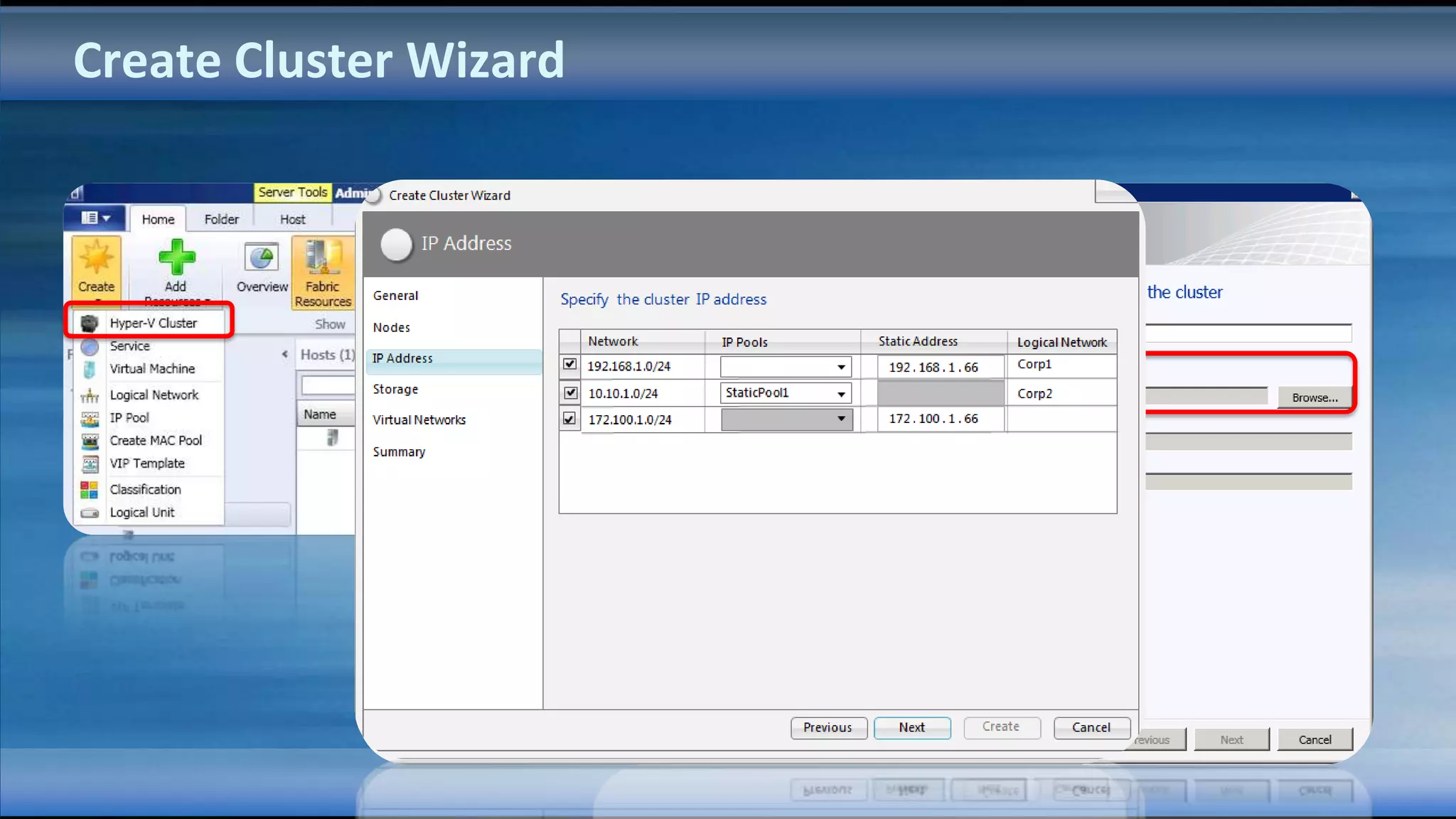
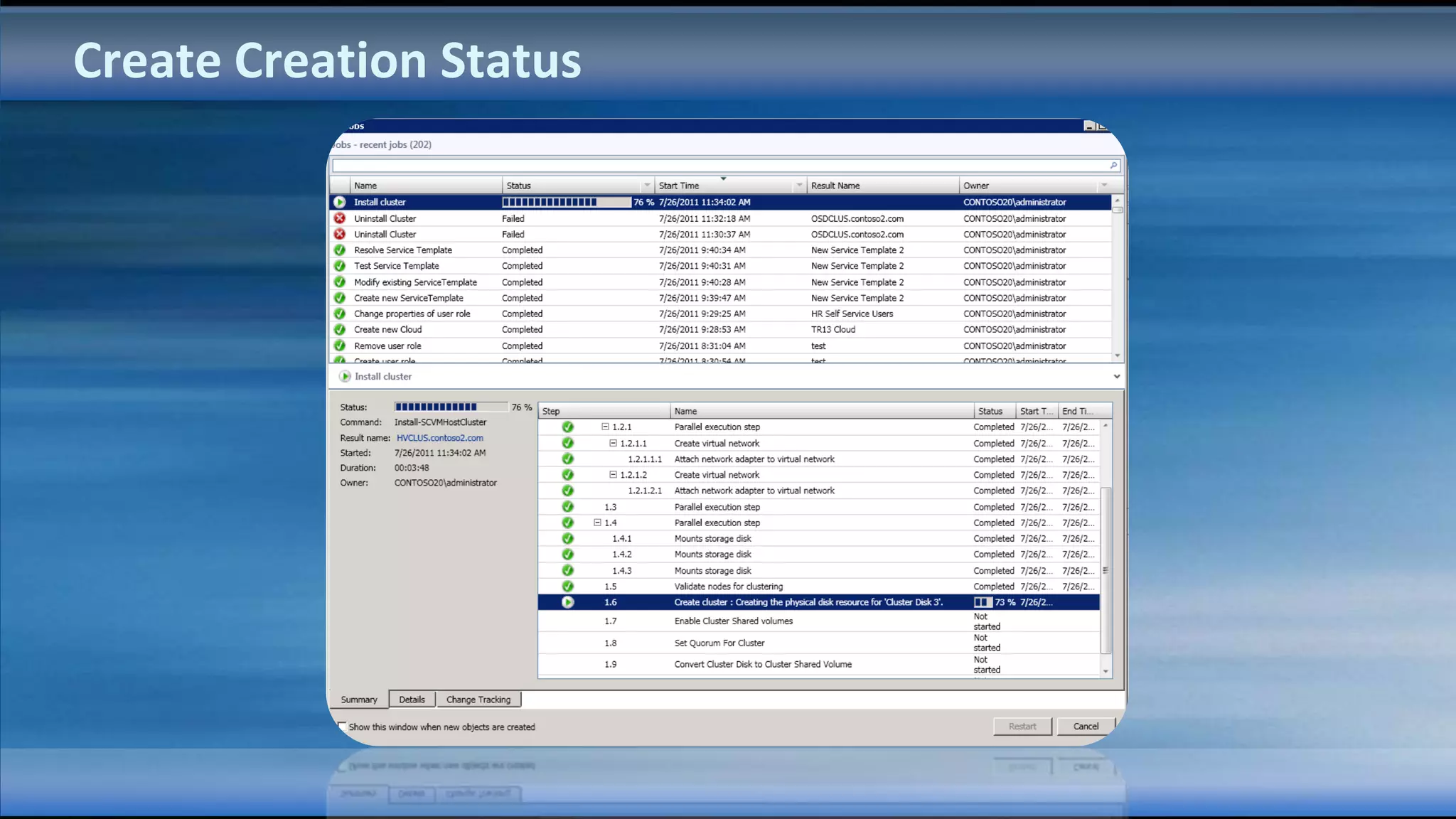
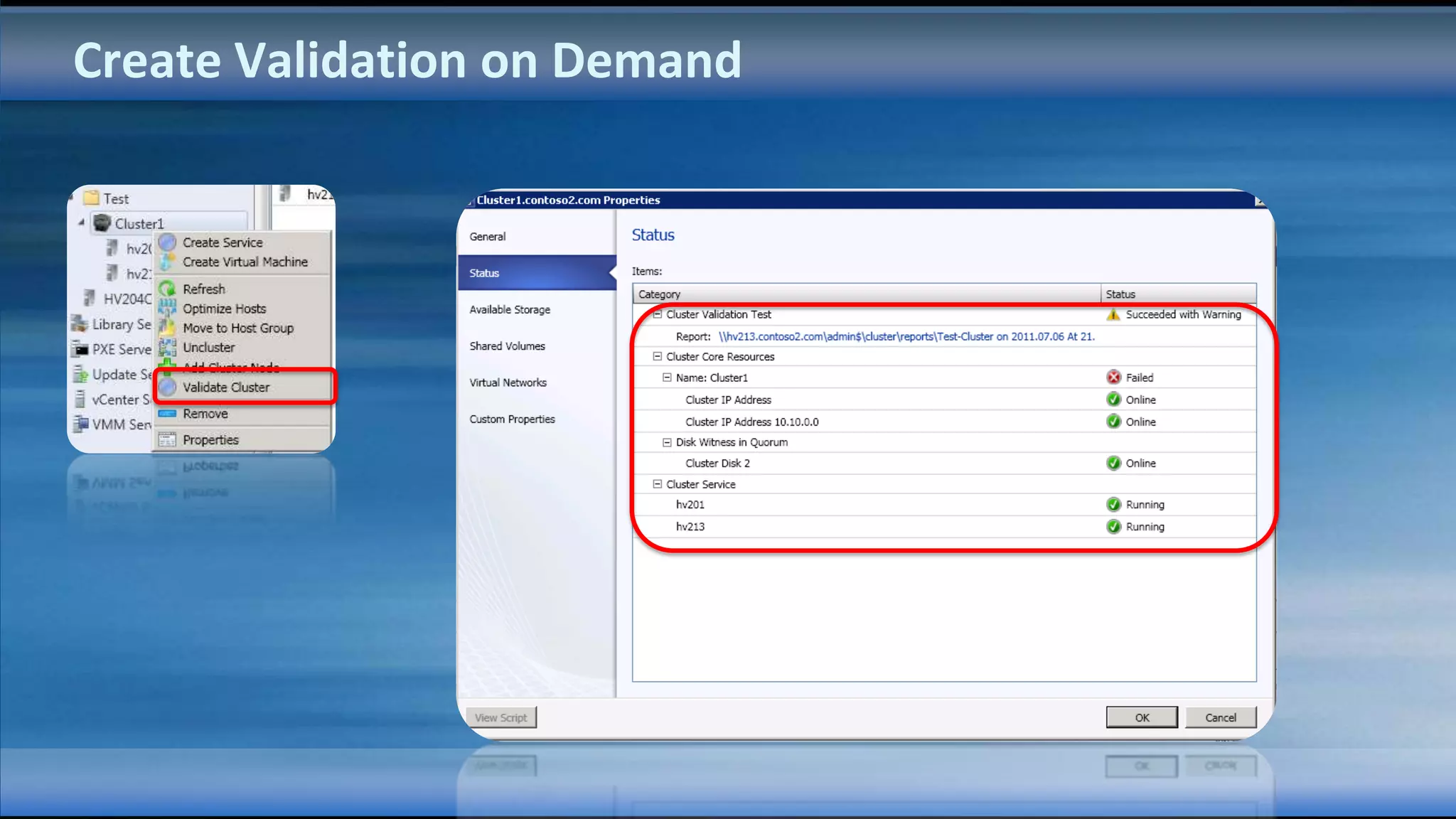
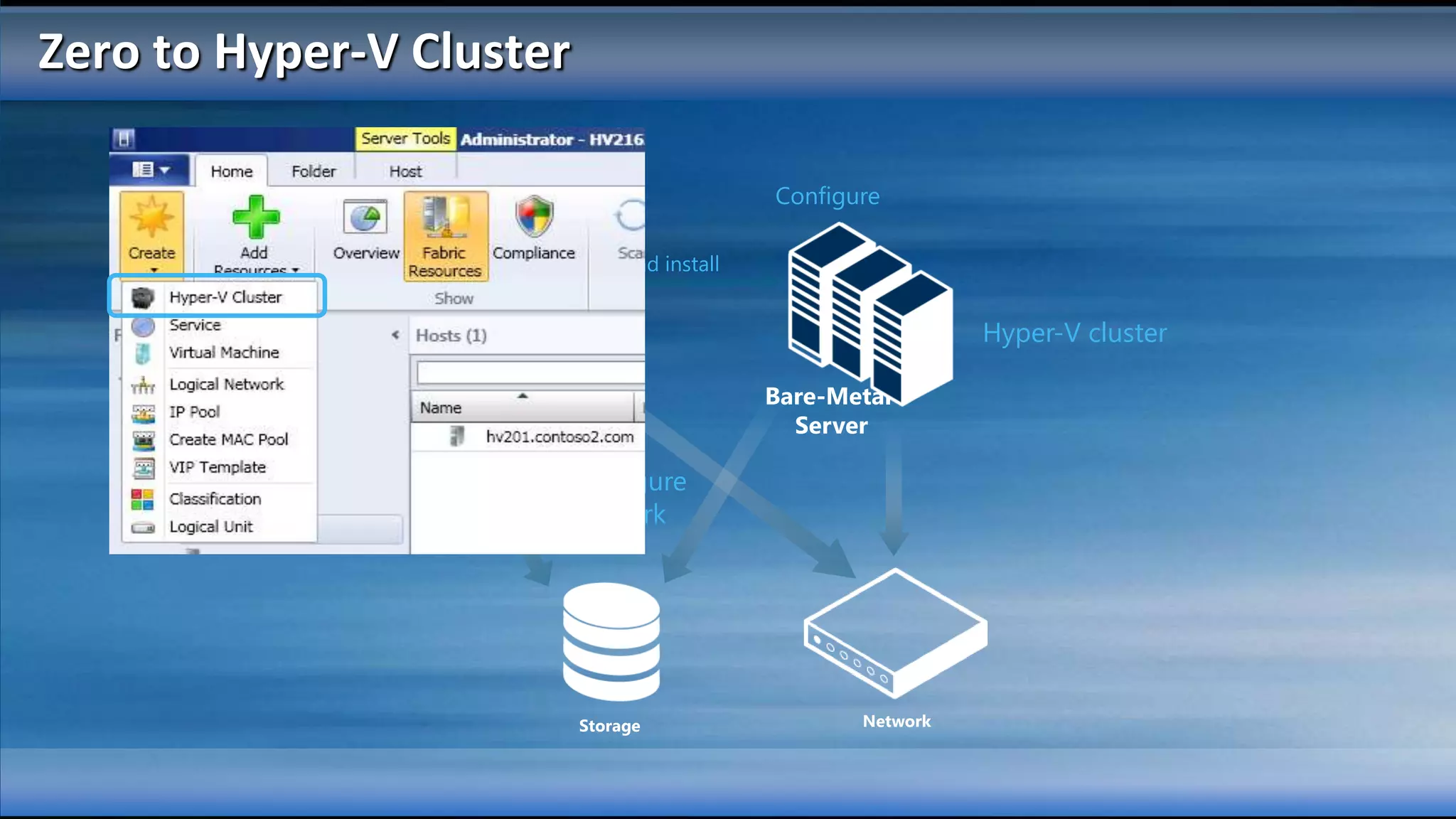
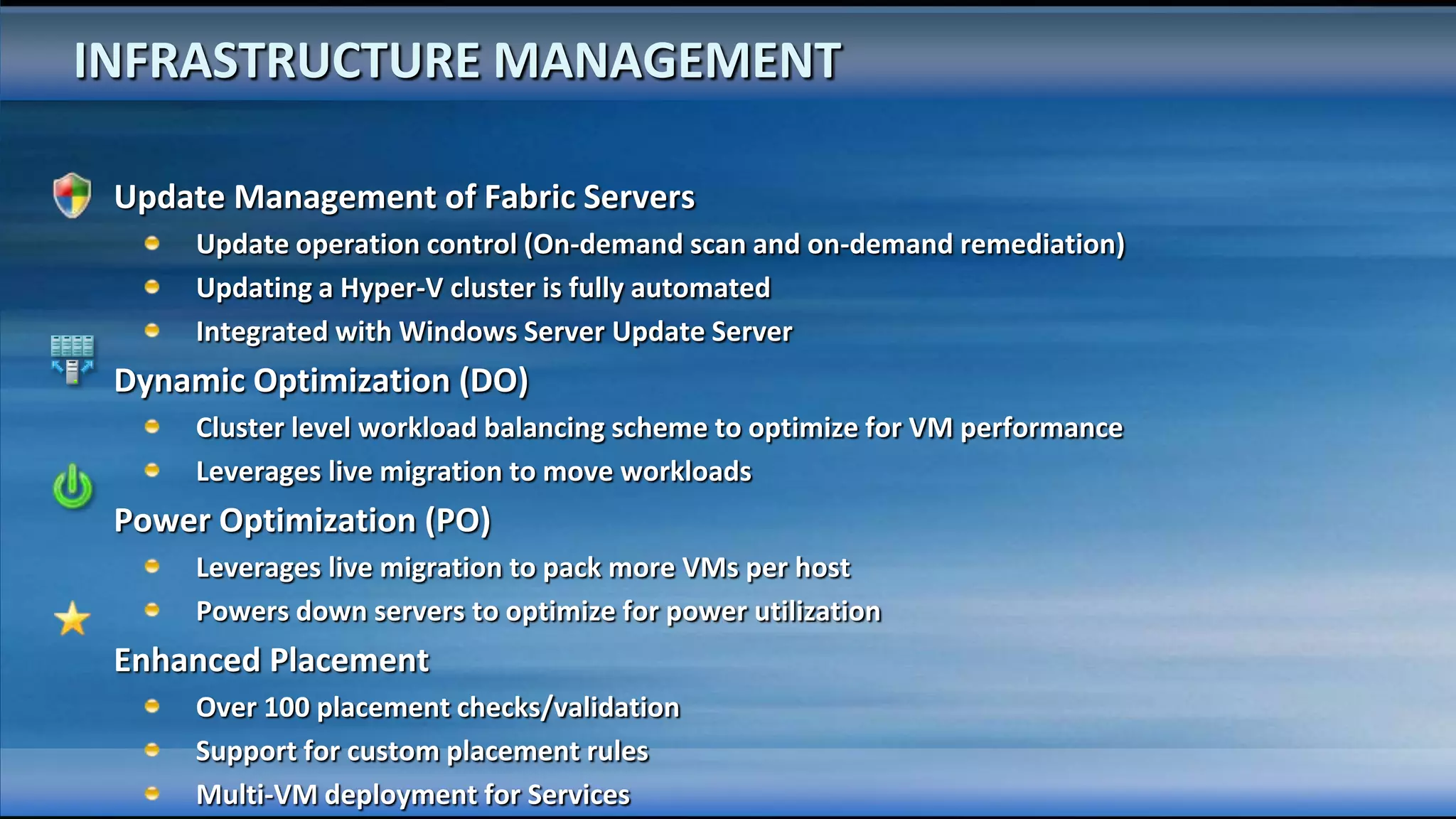
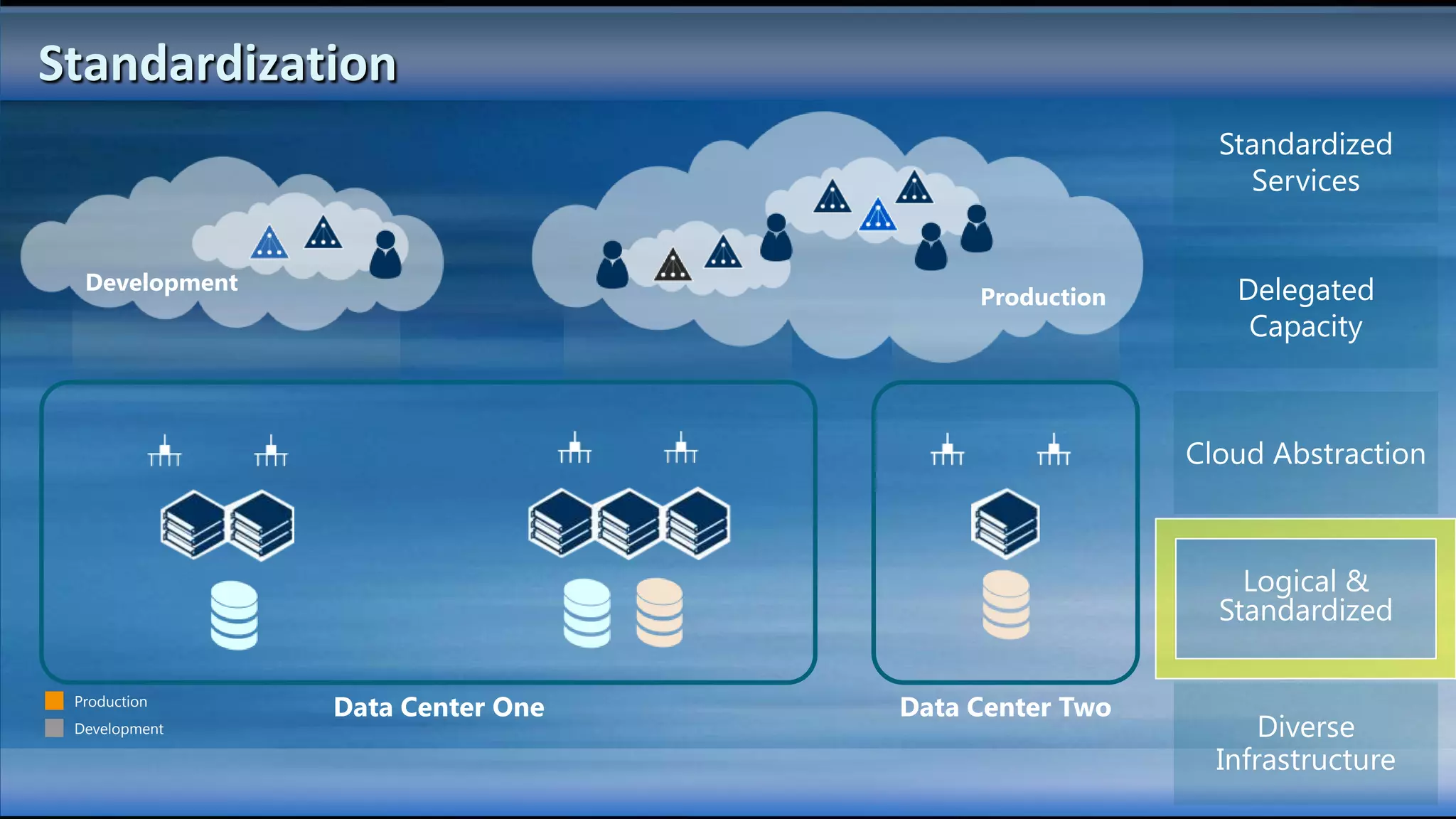
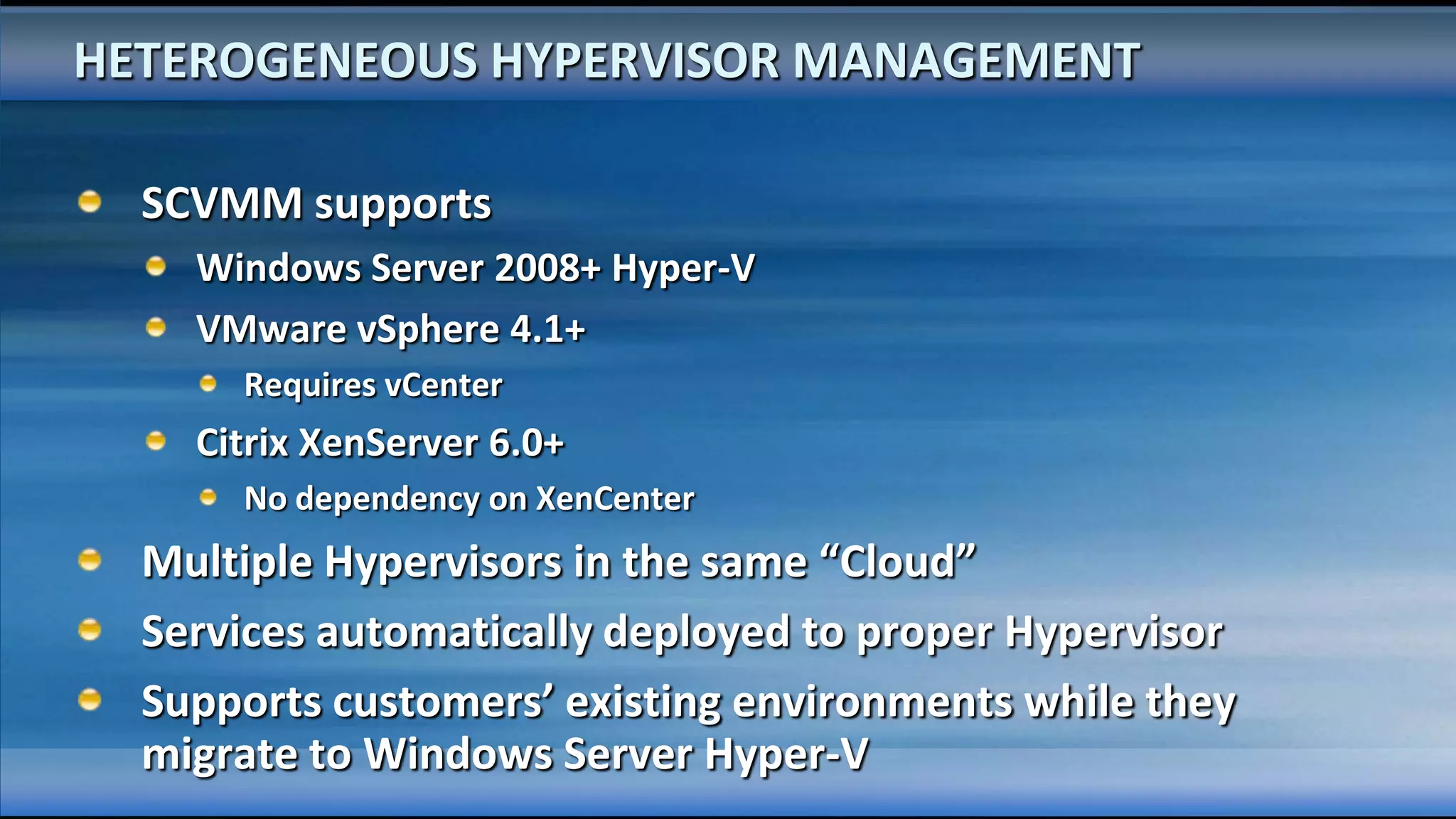
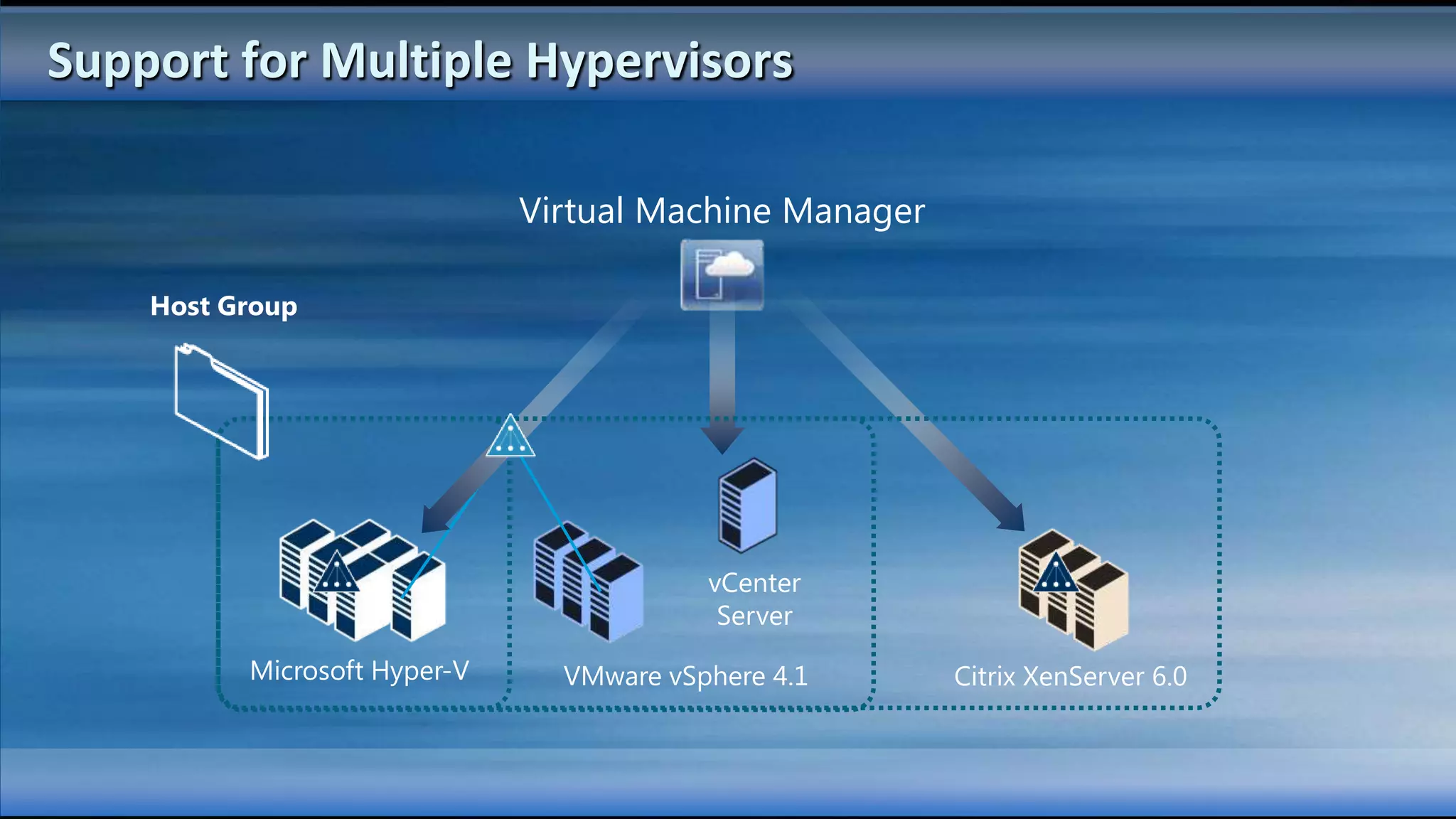
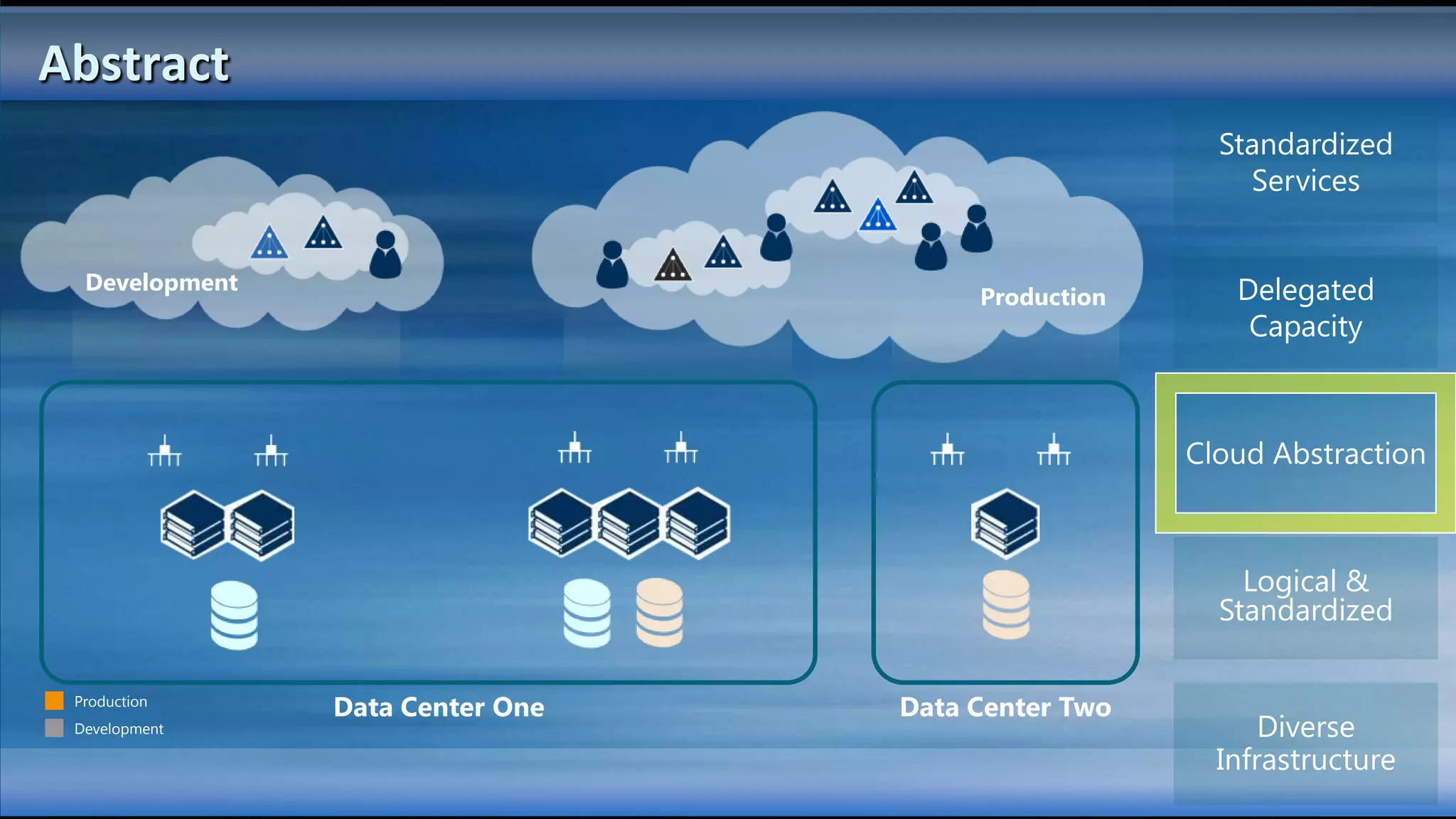
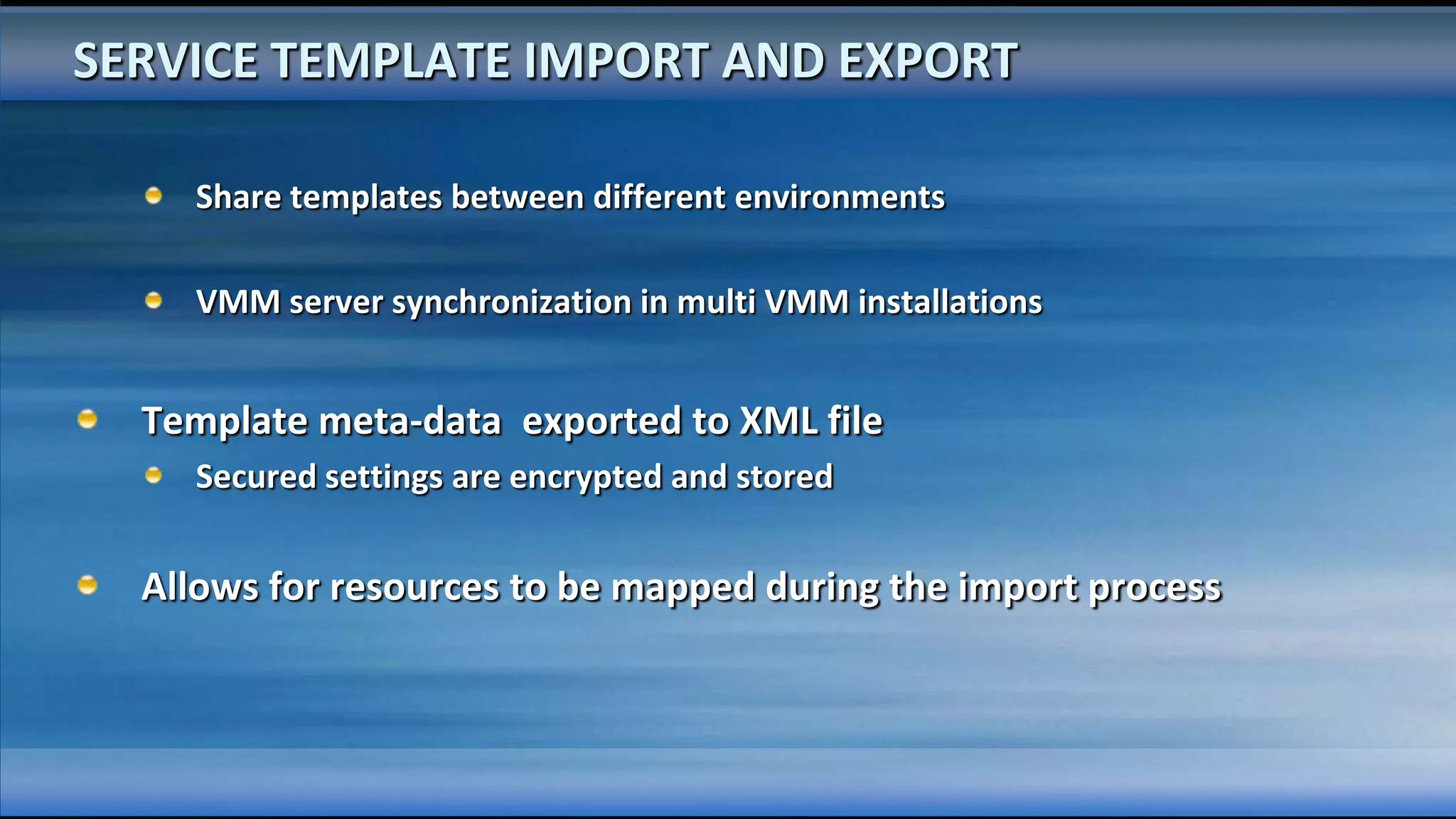
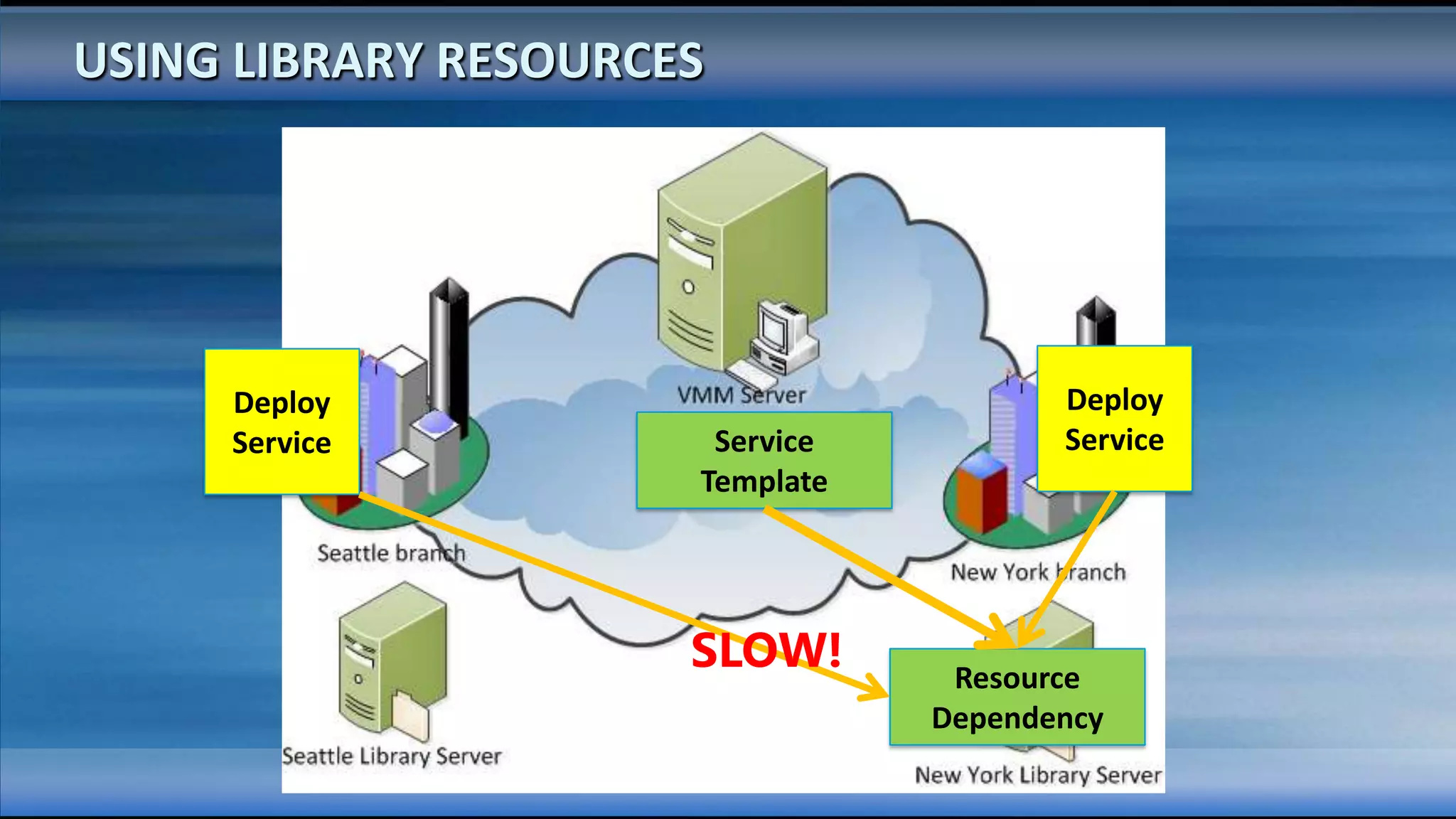
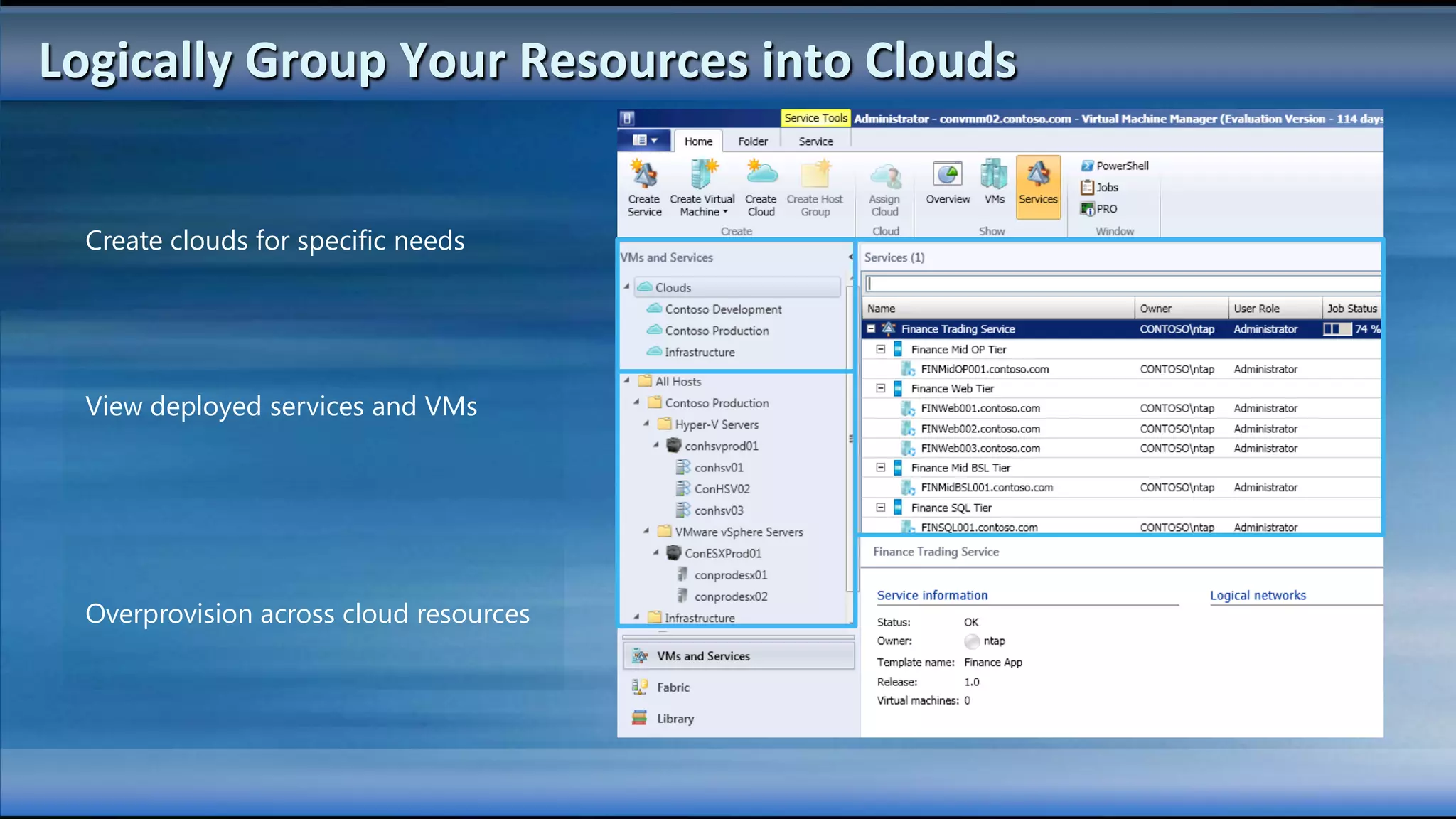
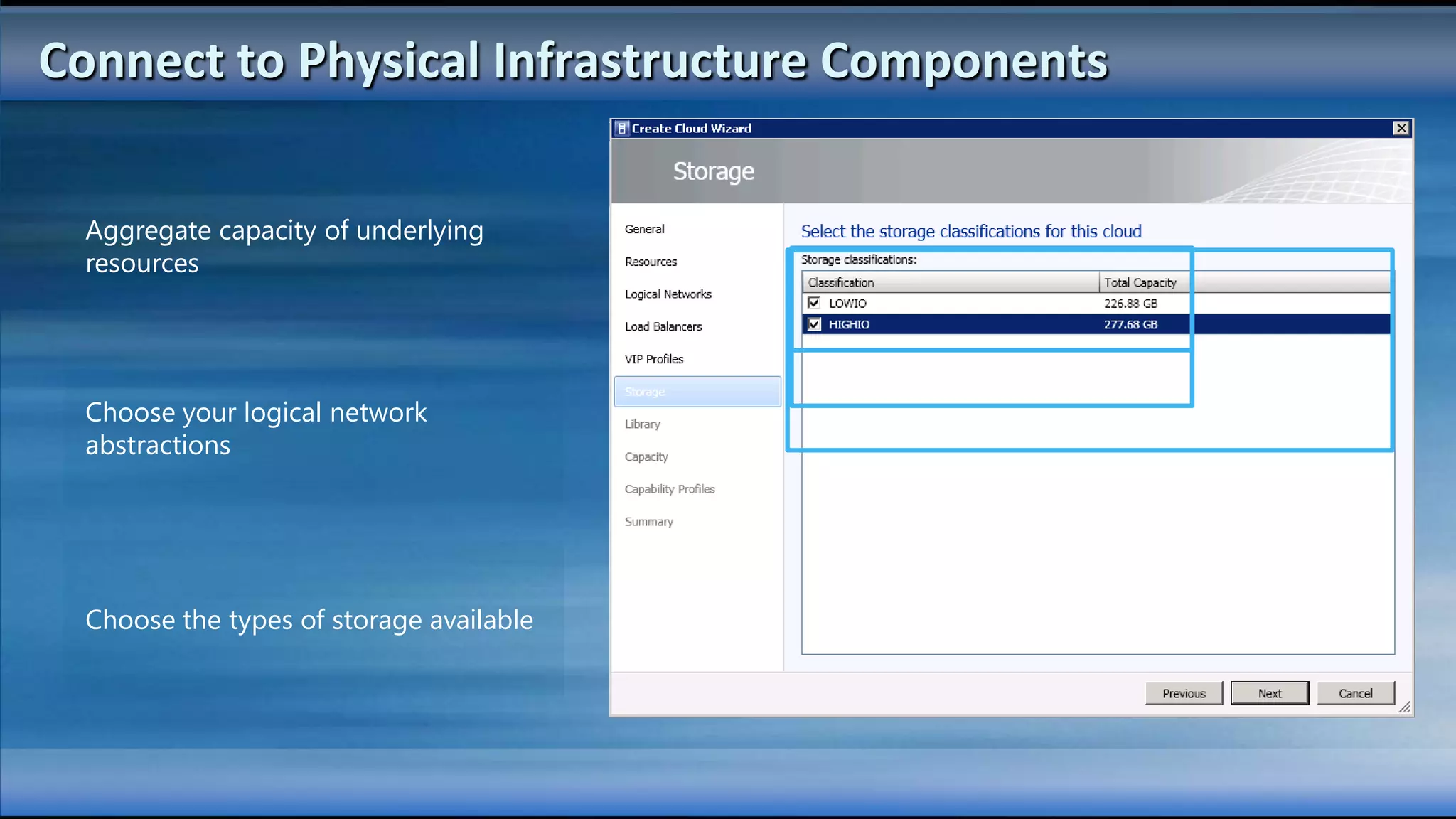
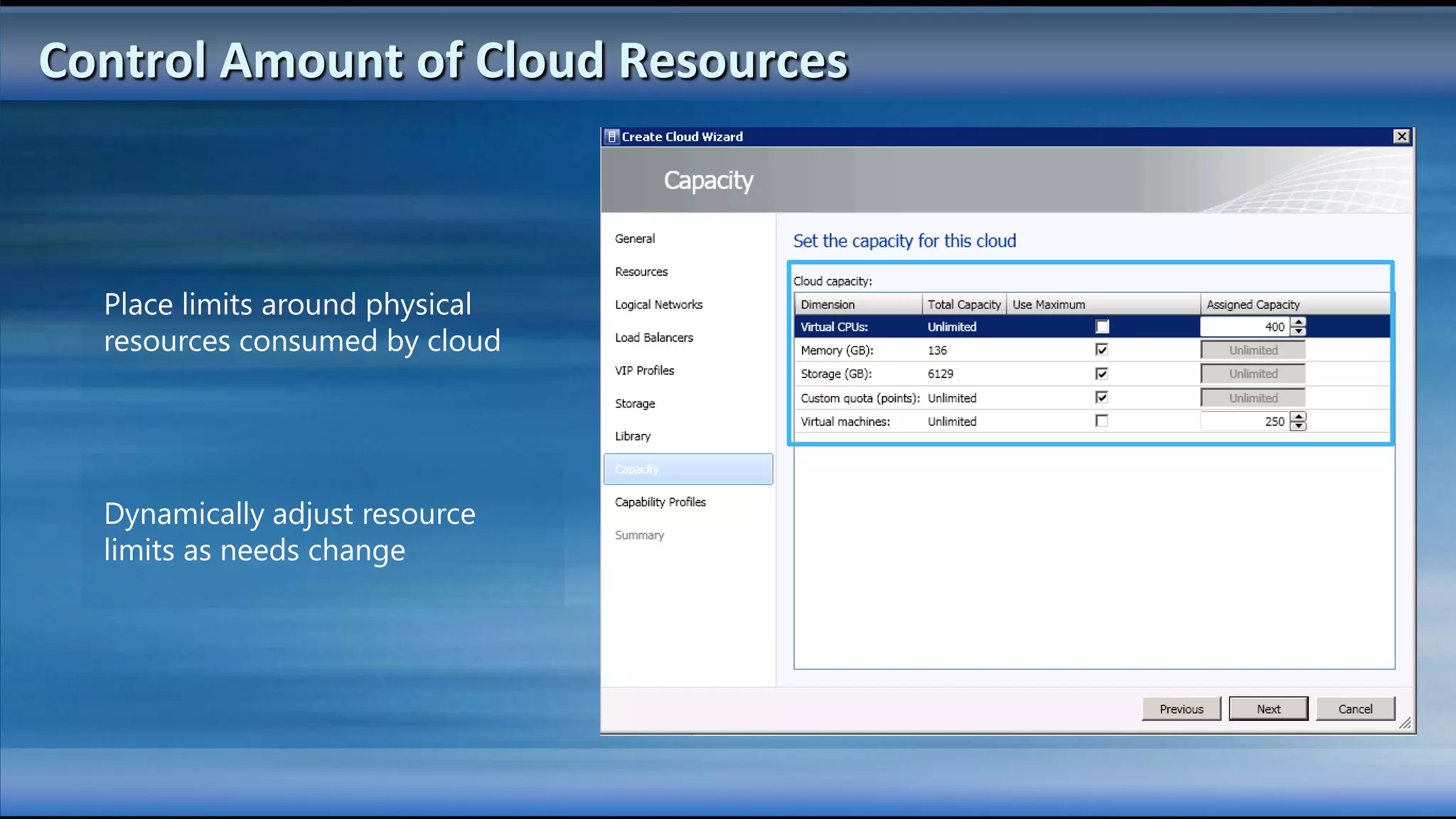
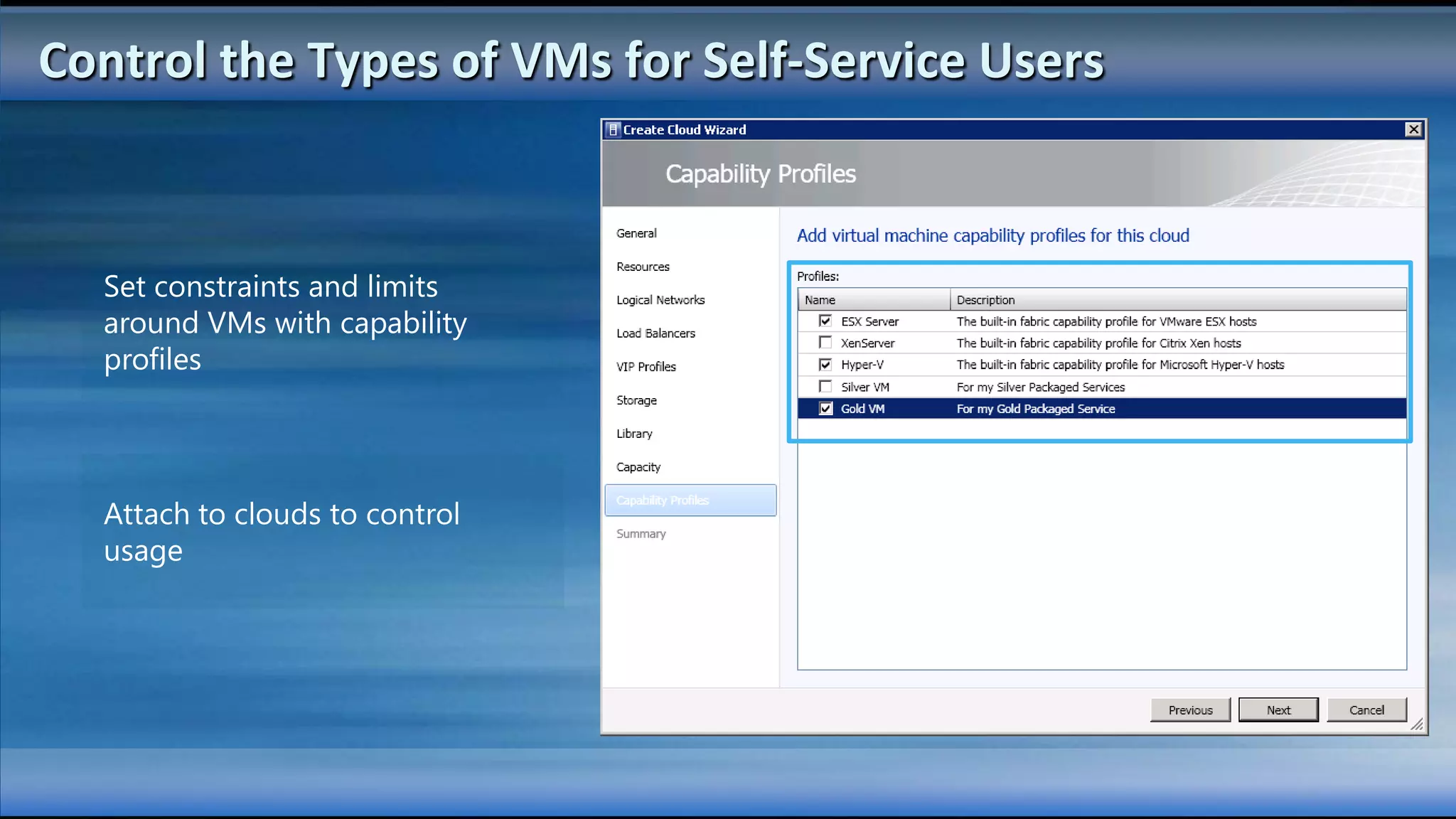
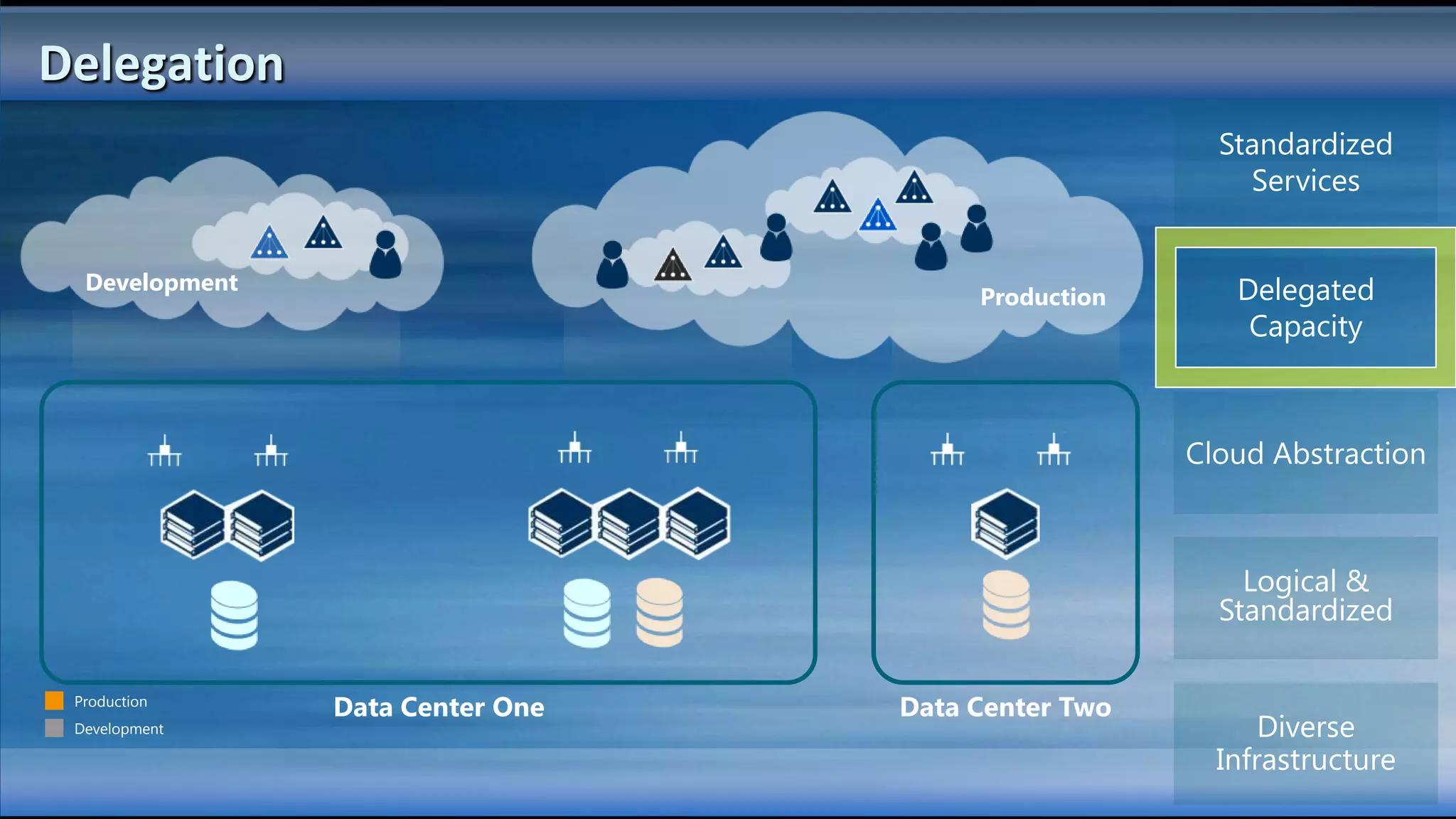
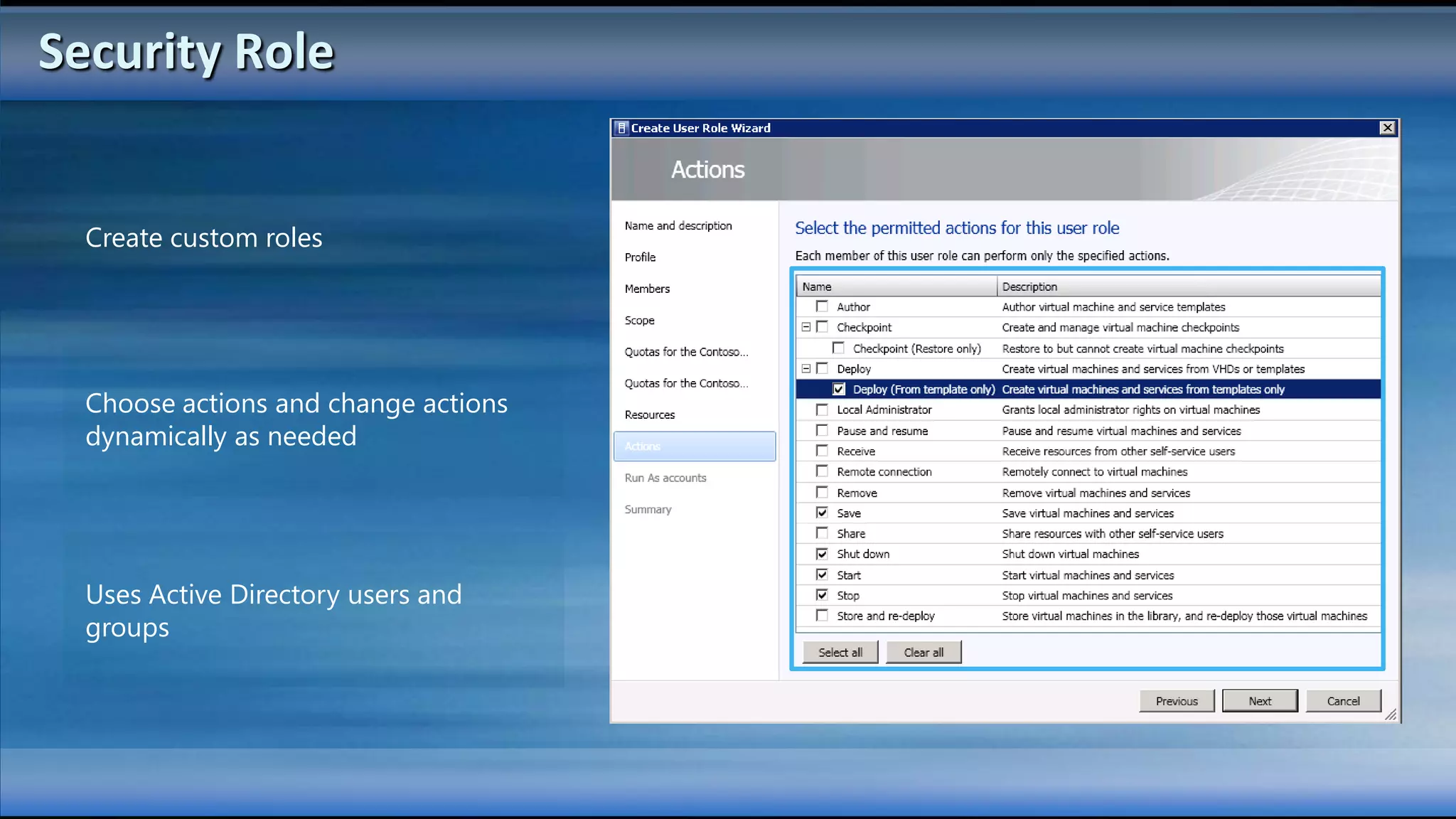
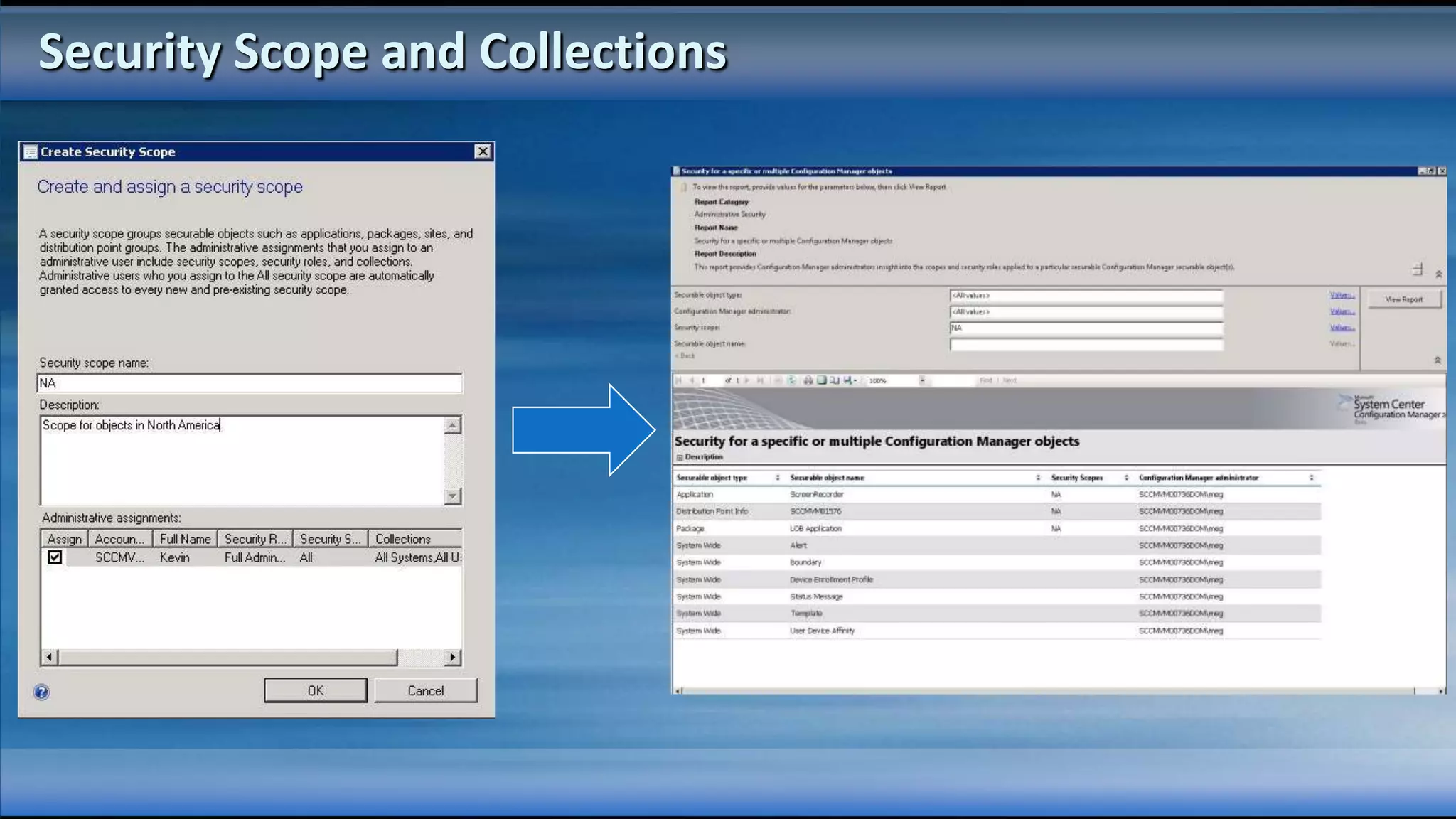
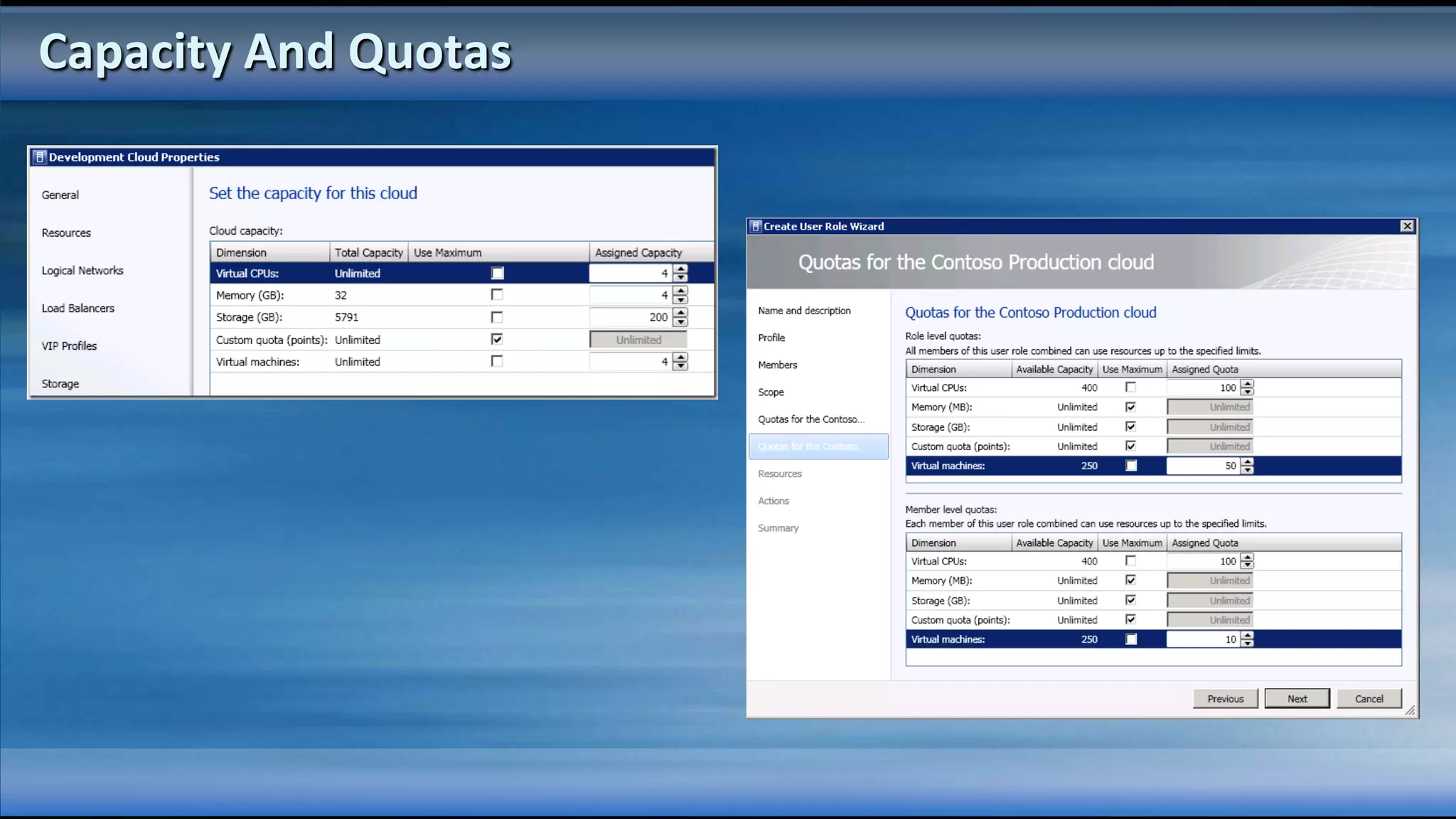
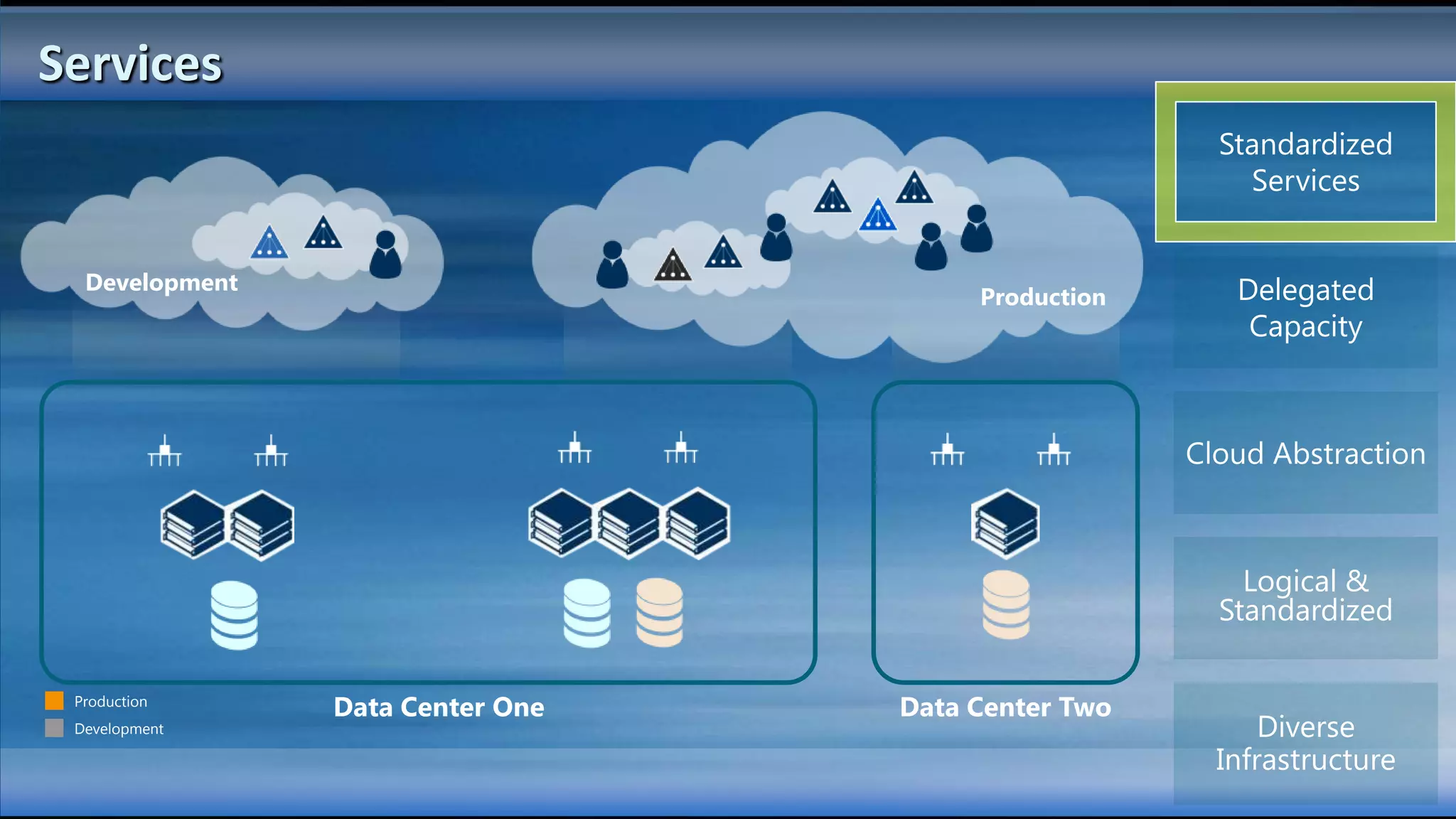
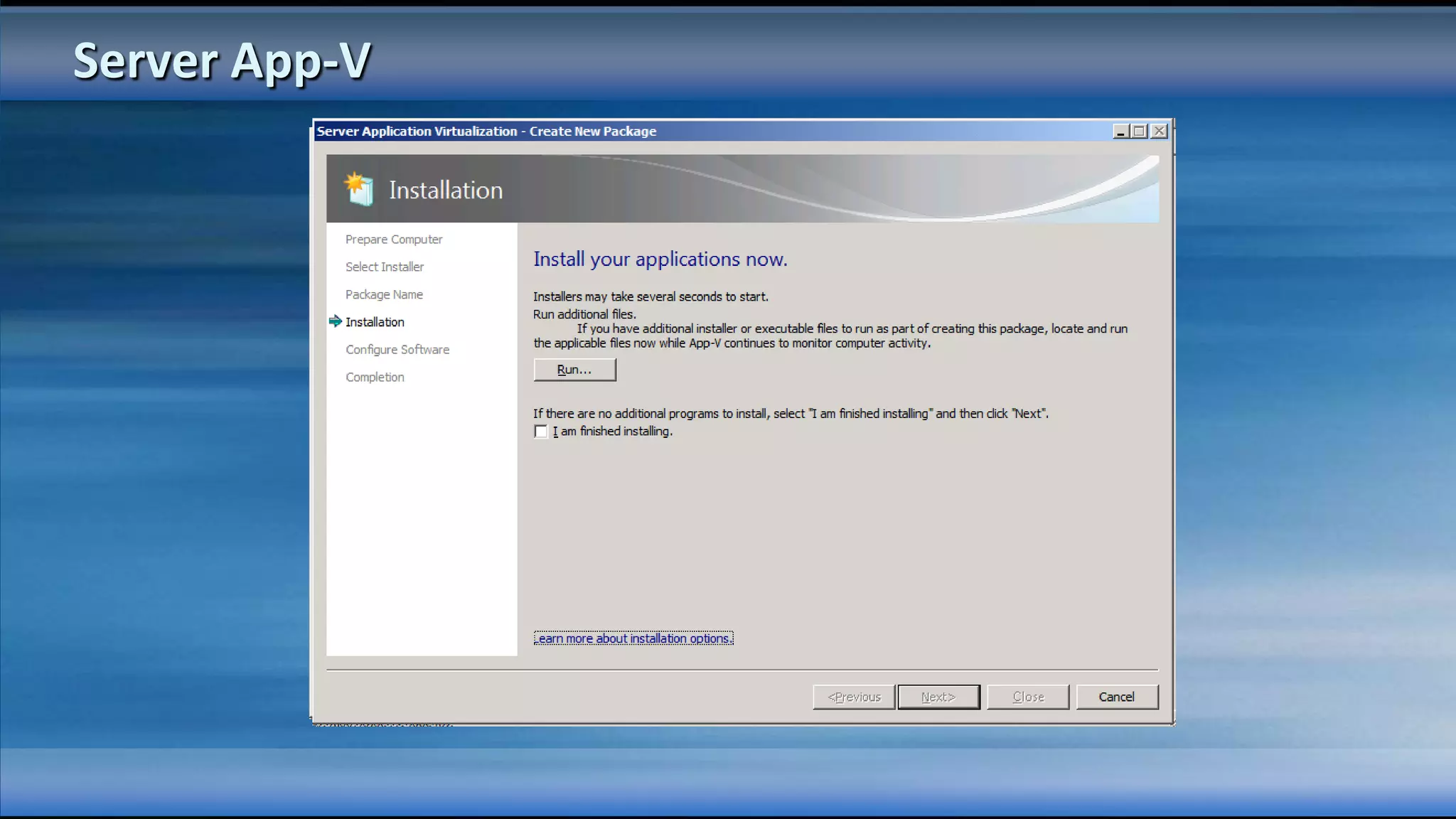
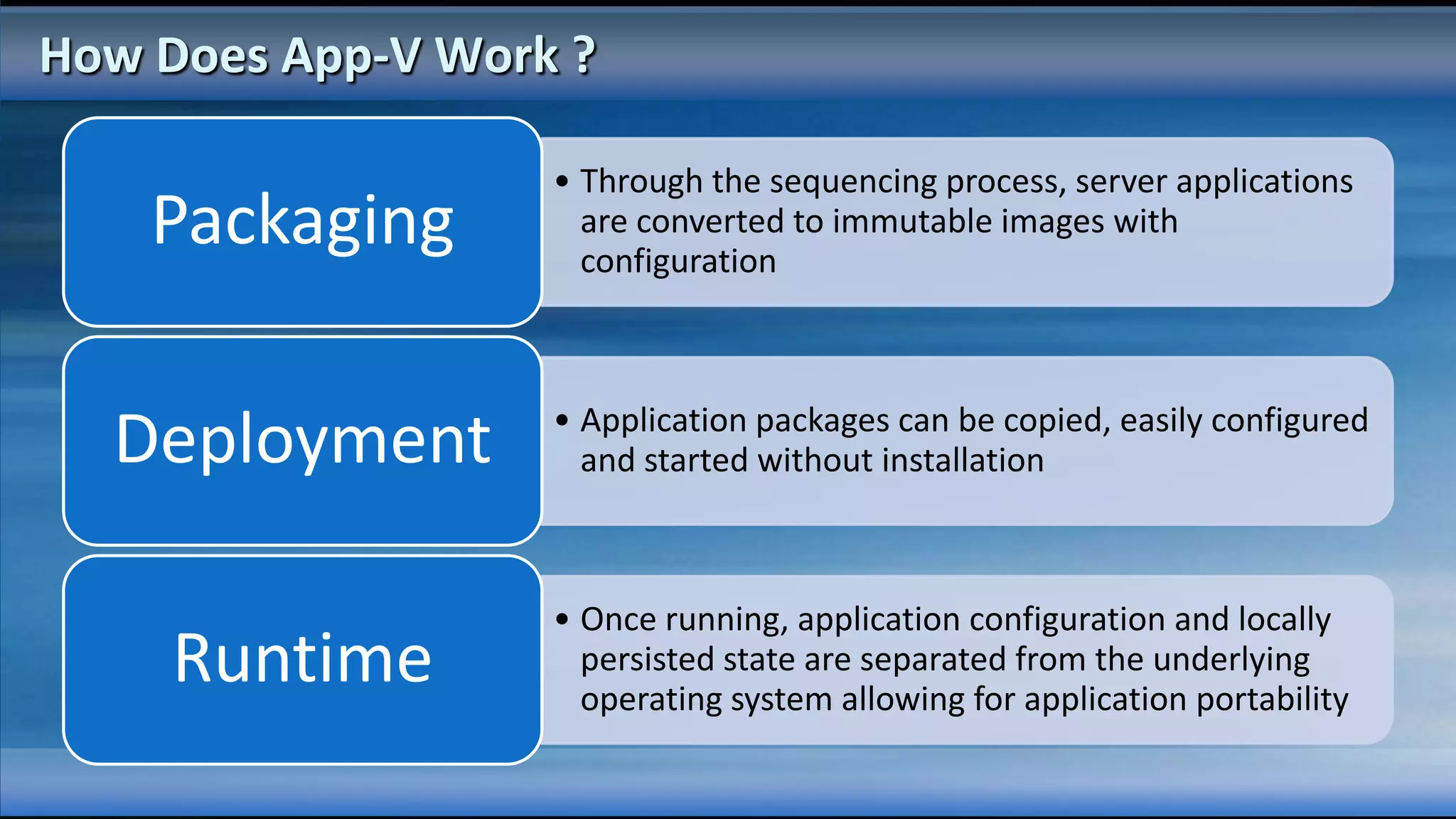
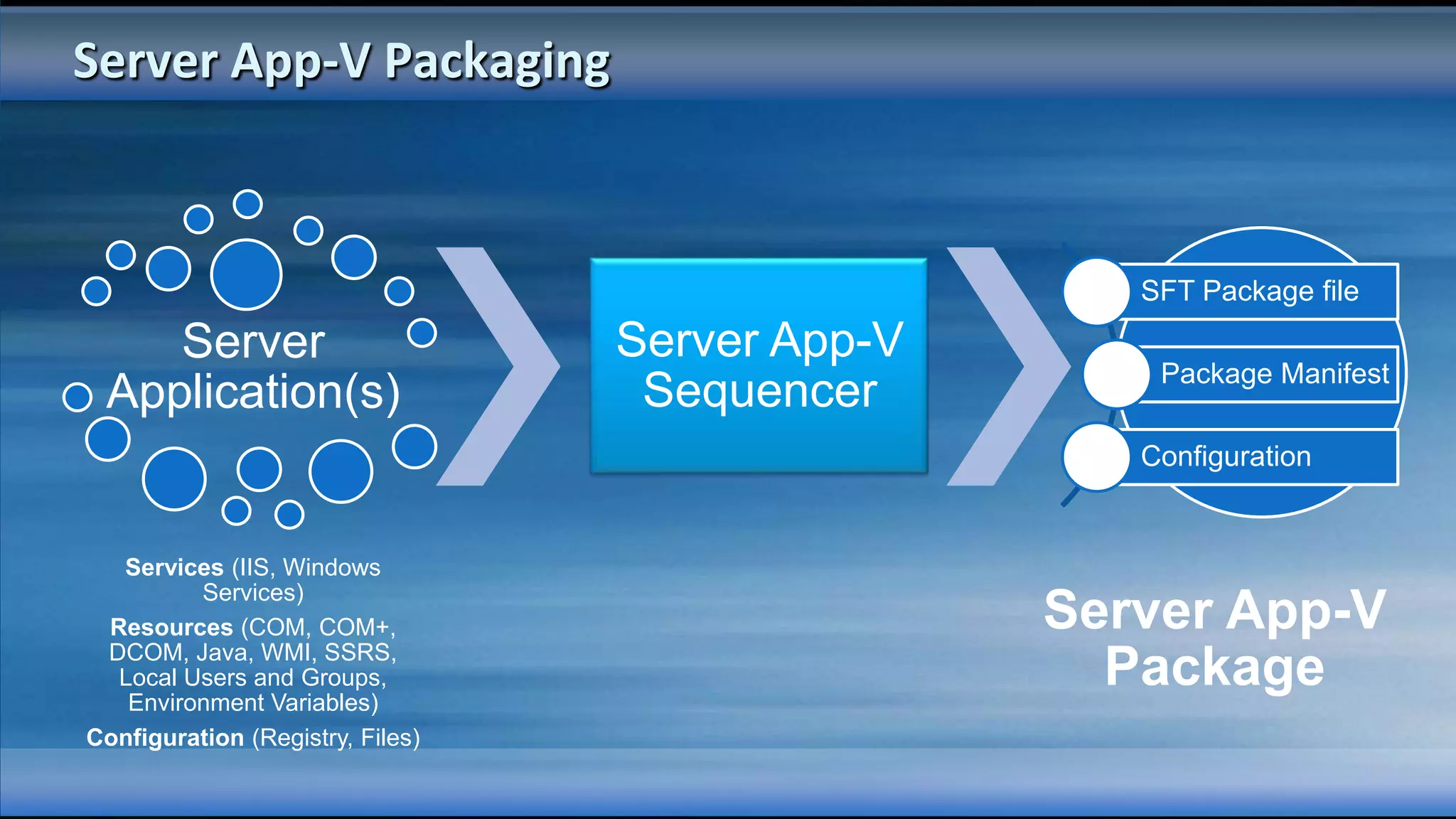
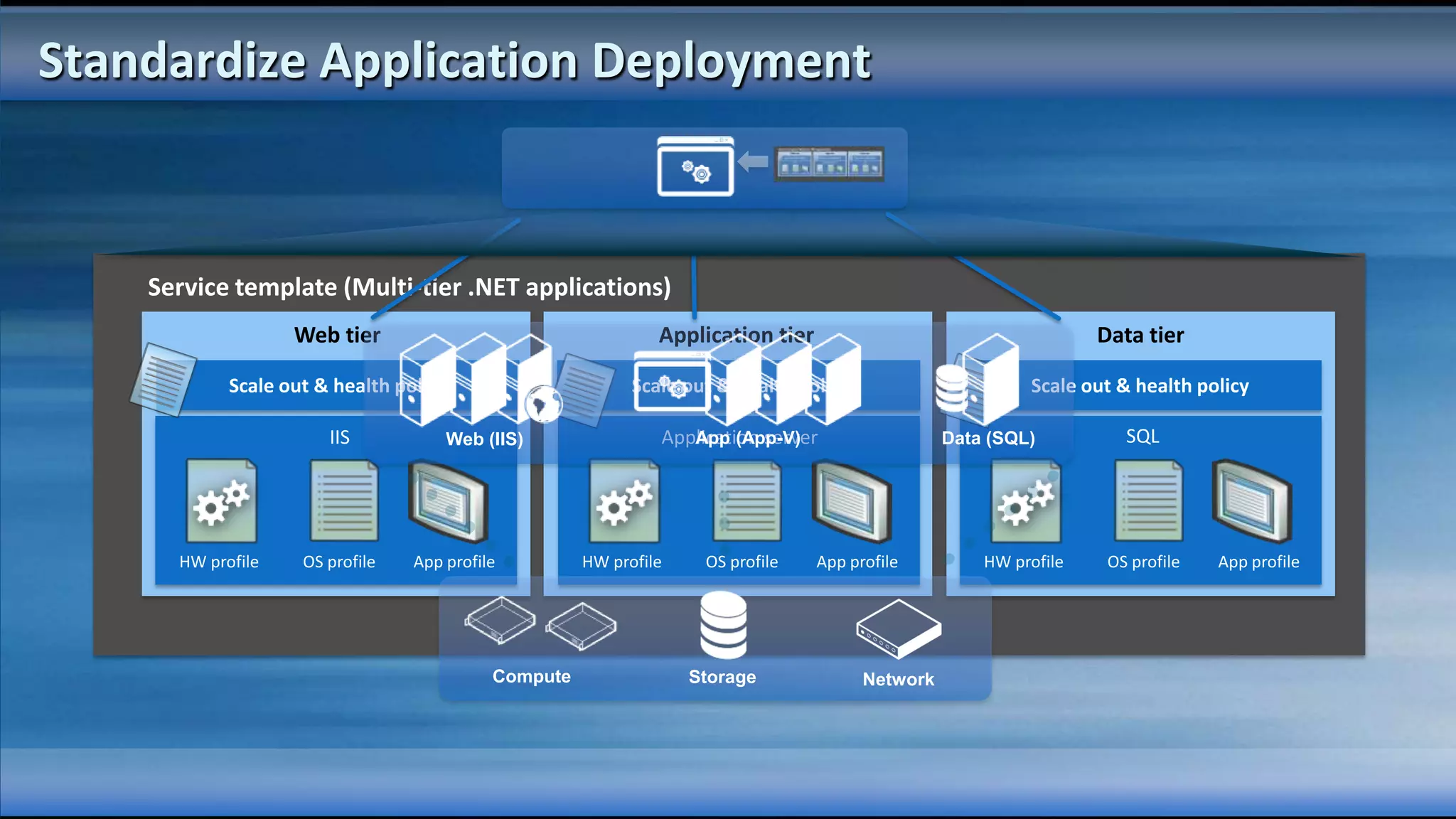
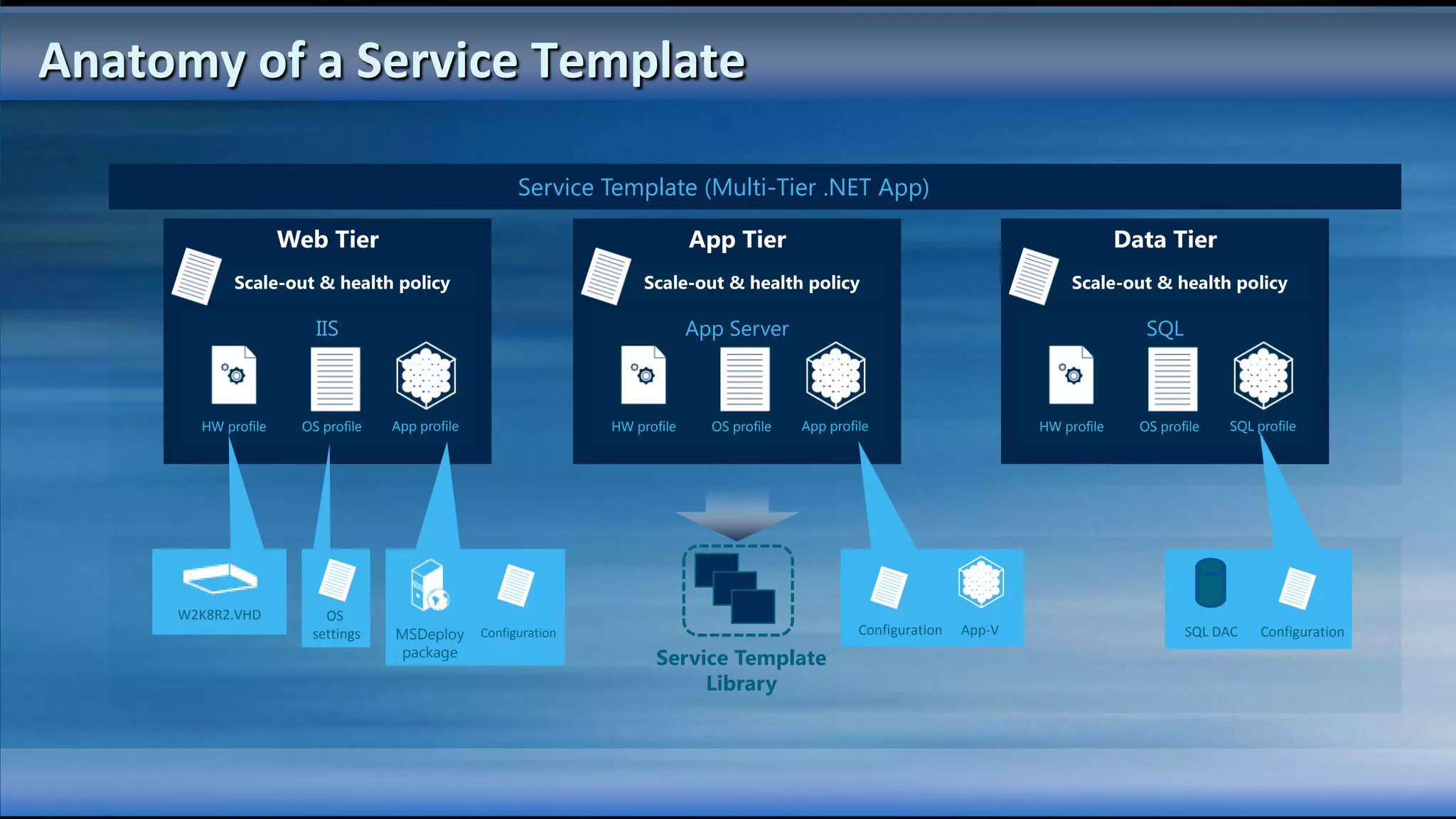
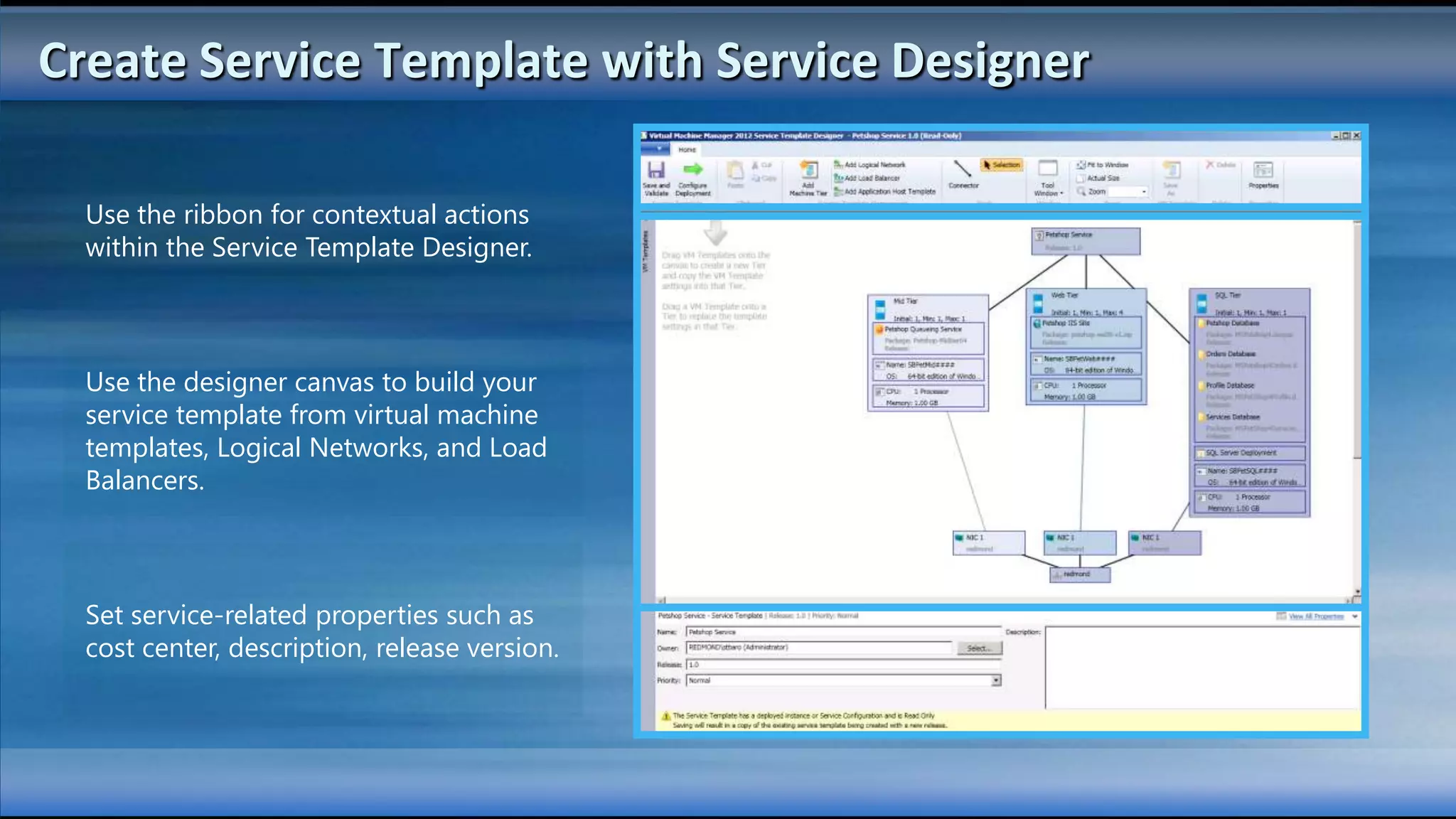
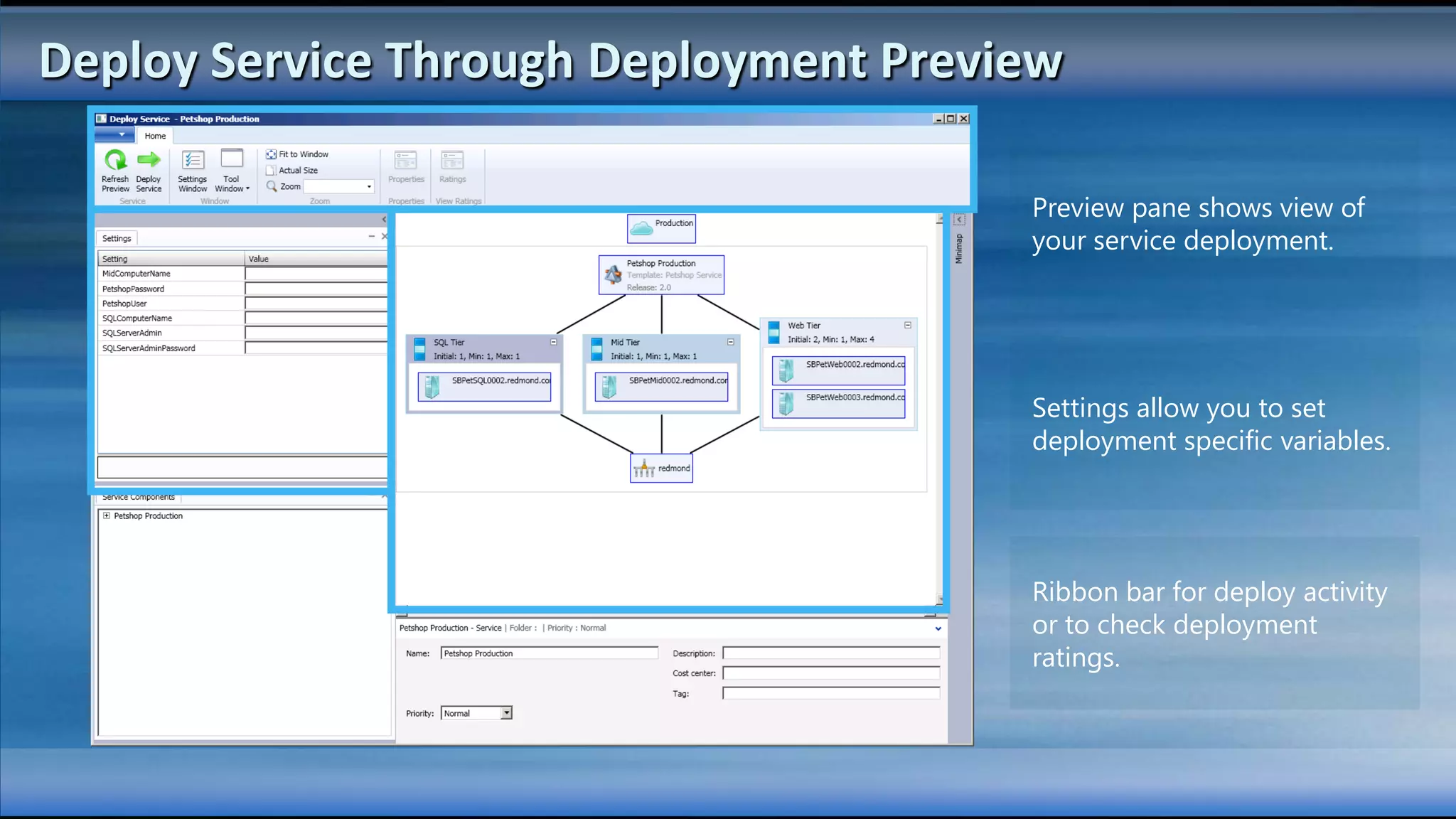
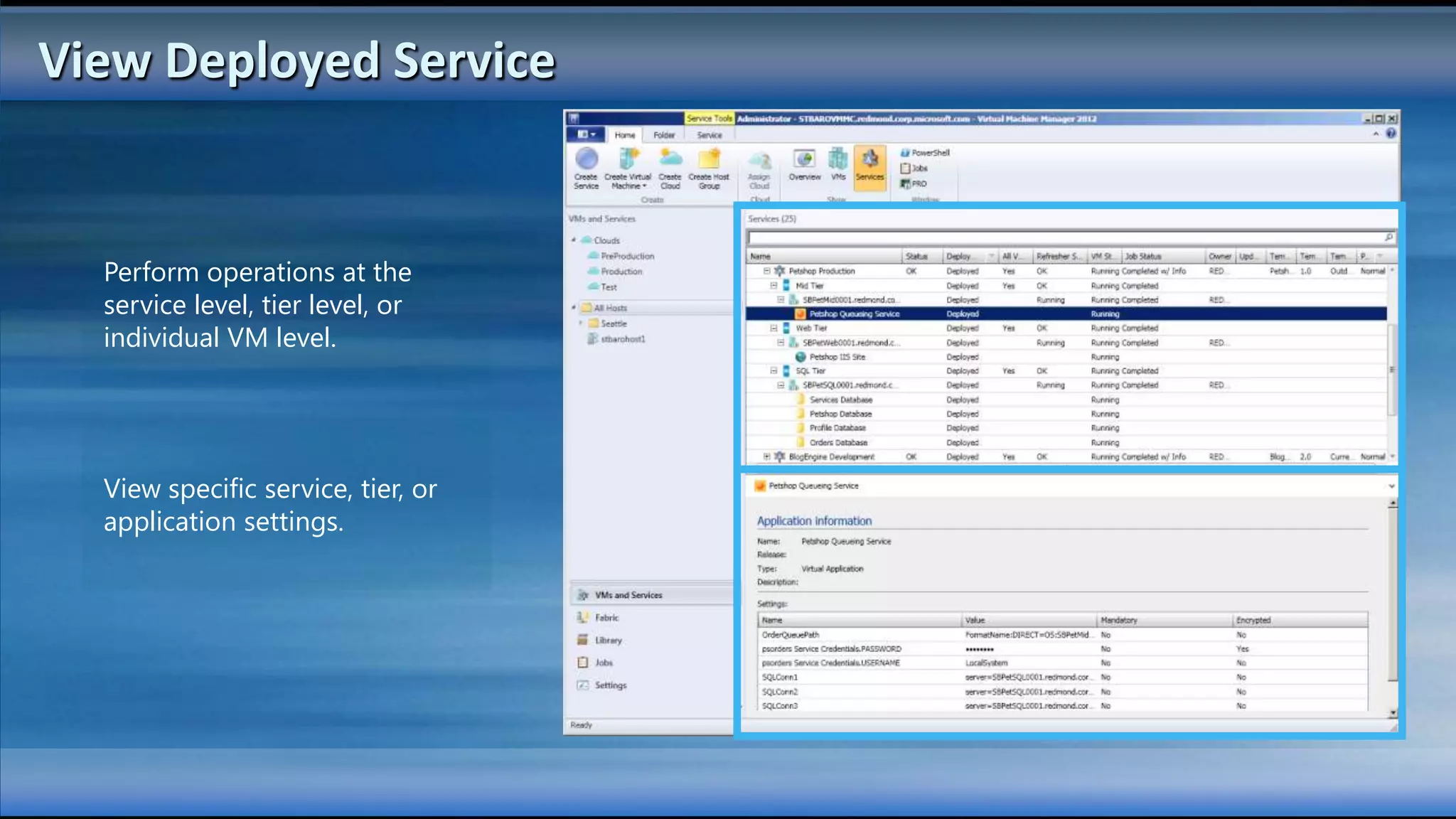
The document outlines the configuration and deployment of private cloud infrastructure using System Center VMM 2012, focusing on aspects such as standardization, abstraction, and delegation. It covers components like hyper-v clustering, virtual machine mobility, and service templates, emphasizing the importance of resource management and scalability. Additionally, it discusses the integration of multiple hypervisors and the role of App-V in application deployment within the cloud environment.