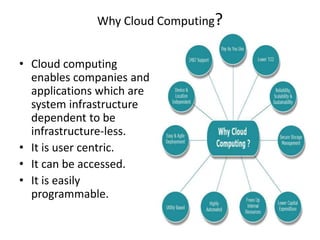
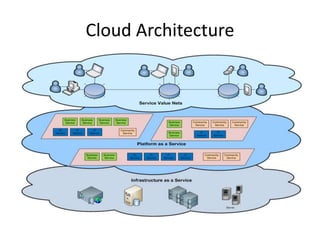
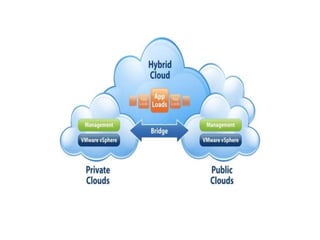
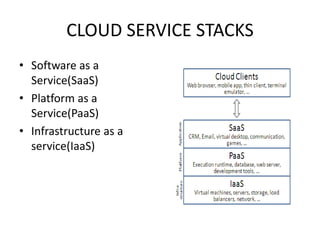
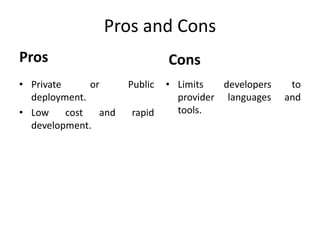
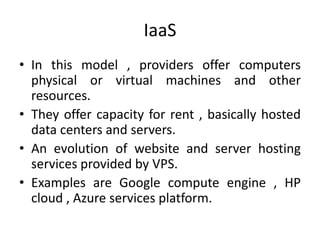
Cloud computing involves delivering computing services over the Internet. It relies on sharing resources rather than having local servers. There are different types of cloud services including Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). SaaS provides access to application software in the cloud. PaaS delivers computing platforms for developing applications. IaaS offers physical or virtual machines and other resources that can be rented.