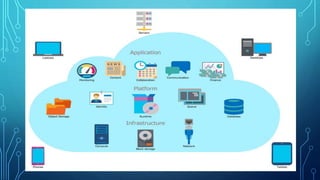
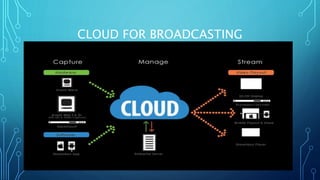
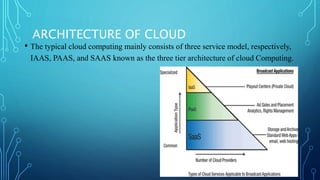
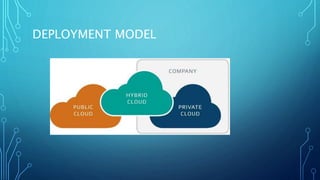
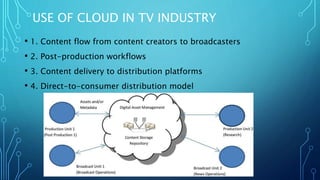
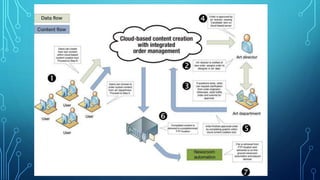
The document discusses cloud broadcasting, highlighting its historical evolution and the transition from traditional baseband to broadband services for multimedia transmission. It outlines the cloud's architecture, deployment models, and the benefits and challenges faced by broadcasters including security issues and the need for new technologies. The workflow of cloud broadcasting enhances collaboration in media production while addressing various security concerns like SQL injection and data breaches.