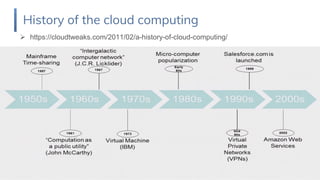
Cloud fundamentals were presented covering key topics:
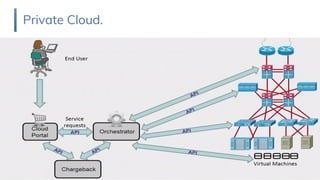
1. Cloud computing is defined by its on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling and rapid elasticity characteristics. It has deployment models of private, public, hybrid and community clouds.
2. There are three main service models - Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides virtualization and servers, PaaS provides platforms and software, and SaaS provides applications.
3. Security concerns in public clouds include shadow IT, lack of control, and availability issues; while costs can be hidden and workload management is important