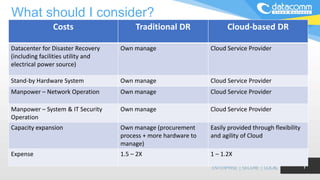
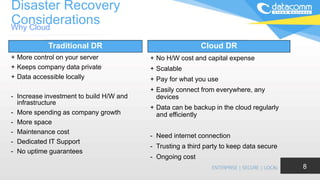
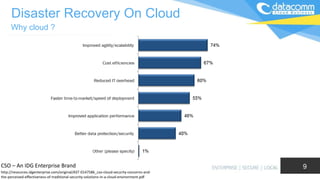
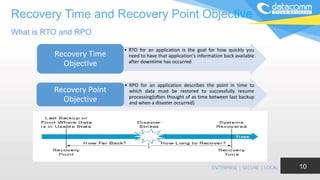
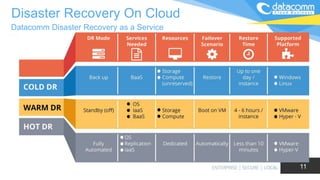
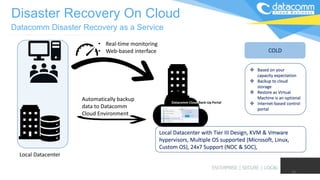
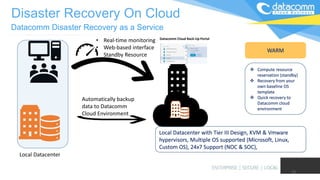
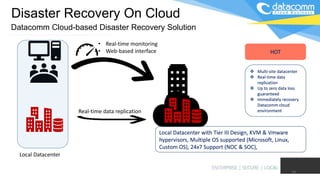
The document discusses cloud-based disaster recovery (DRaaS), emphasizing its significance in mitigating business disruptions caused by various disasters, including power failures and human errors. It outlines the challenges of traditional disaster recovery approaches, such as complexity and lack of automation, while showcasing the advantages of cloud solutions, including cost-effectiveness and scalability. Key features highlighted include real-time data replication, automated backups, and comprehensive support for auditing and compliance.