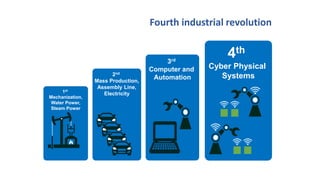
The document discusses the history of industrial revolutions from the first to the fourth revolution. It outlines the key technologies and transformations that occurred in each revolution. The first revolution involved mechanization powered by steam engines. The second revolution brought about mass production using assembly lines and electricity. The third revolution saw the rise of automation and computer technology. The fourth and current revolution is characterized by cyber-physical systems, cloud computing, additive manufacturing, the internet of things, autonomous robots, and enhanced cybersecurity.