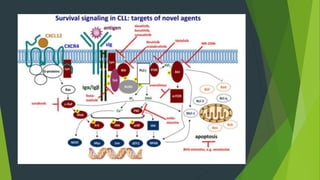
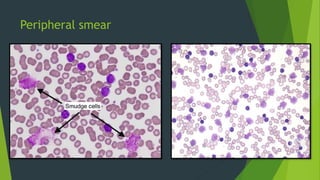
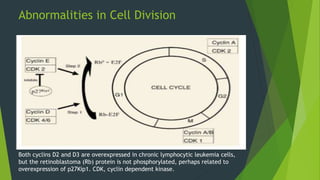
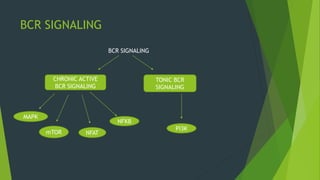
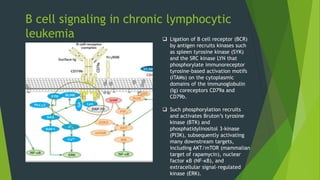
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is derived from CD5+ B cells and is driven by genetic lesions and interactions with the microenvironment. CLL cells have abnormalities in apoptosis pathways like high Bcl-2 and FLIP expression that make them resistant to death signals. They also show chronic B-cell receptor signaling from tonic or antigen stimulation. The microenvironment protects CLL cells through cytokines and cell-cell contact with nurse-like cells and stromal cells. CLL cells harbor genetic changes like 13q14 deletions, trisomy 12, and mutations in NOTCH1 and SF3B1 that contribute to pathogenesis. Antigen stimulation may select for the restricted immunoglobulin repertoire in C

















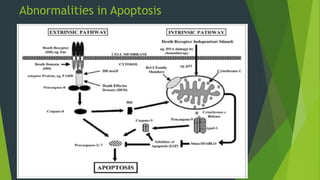
![ The extrinsic apoptotic pathway plays a major role in apoptosis.
Six known death receptors (DRs) including tumor necrosis factor(TNF),
Fas(APO-1 or CD95), and DR4/DR5 (receptors for TNF-related apoptosis
induce ligand [TRAIL]).
Contain a cytosolic domain called the death domain, which recruits
adaptor proteins such as Fadd/Mort-1 to the receptor complex after
binding to ligand.
The recruiter adaptor protein has a death domain end and a death
effector domain (DED).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cllpathogenesisandtargetedtherapy-180829185640/85/Cll-pathogenesis-and-targeted-therapy-21-320.jpg)





















![ NOTCH1 mutations
Restricted to the C-terminal PEST [proline (P), glutamate (E), serine (S),
and threonine (T)] domain
normally limits the intensity and duration of NOTCH1 signaling.
Removal of the PEST domain impairs the degradation of NOTCH1
allowing accumulation of the active form of NOTCH1.
One recurrent mutation (c.7544_7545delCT) accounts for ∼77% of all
NOTCH1 mutations in CLL-
Can be rapidly detected by a simple polymerase chain reaction–based
strategy- providing a potential approach for a first-level
screening of NOTCH1 alterations.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cllpathogenesisandtargetedtherapy-180829185640/85/Cll-pathogenesis-and-targeted-therapy-46-320.jpg)