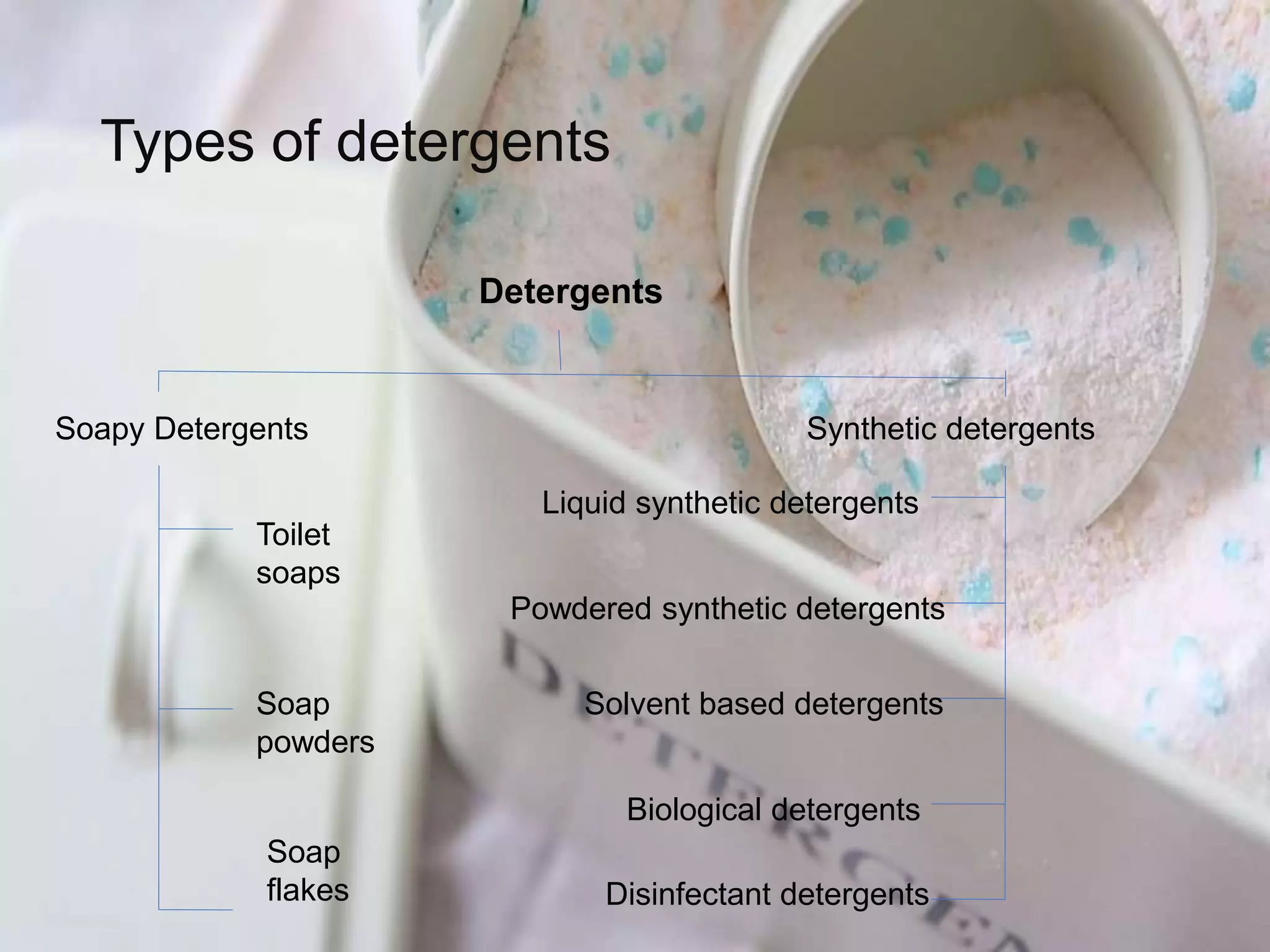
The document discusses various types of cleaning agents used in hotels including water, detergents, abrasives, reagents, organic solvents, disinfectants and bleaches, glass cleaners, polishes, and floor sealers. It also covers the proper storage of cleaning agents which involves using strong racks, keeping the storage area clean, ventilated, and locked when not in use as well as first in first out rotation of stocks.