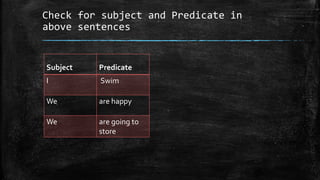
This document discusses clauses and phrases. It defines clauses as groups of words that contain both a subject and predicate, while phrases do not contain both. There are three types of dependent clauses: adjective clauses, which modify nouns; adverb clauses, which modify verbs, adjectives or other adverbs; and noun clauses, which act as the subject, direct object, indirect object or object of a preposition in a sentence. Independent clauses can stand alone as complete sentences, while dependent clauses cannot. The document also provides examples to illustrate the different types of clauses and phrases.