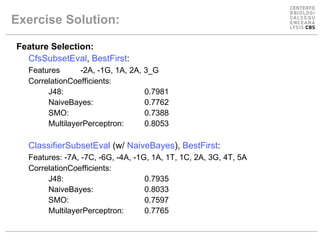
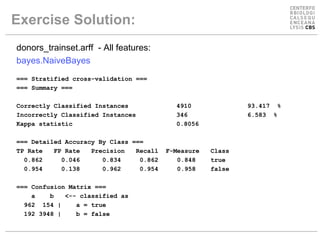
The document discusses experiments using different machine learning classifiers and feature representations on a genetic sequence dataset. It shows the results of using J48, Naive Bayes, and SMO classifiers with the full feature set and a reduced binary encoding. Feature selection techniques were able to improve performance for some classifiers by identifying relevant features. No single method performed best, demonstrating the need to test multiple approaches.
![Classification by Machine Learning Approaches - Exercise Solution Michael J. Kerner – [email_address] Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Technical University of Denmark](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classification-by-machine-learning-approaches3005/85/Classification-by-Machine-Learning-Approaches-1-320.jpg)


![@RELATION donors.train @ATTRIBUTE -7_A {0,1} @ATTRIBUTE -7_T {0,1} @ATTRIBUTE -7_C {0,1} [...] @ATTRIBUTE 6_A {0,1} @ATTRIBUTE 6_T {0,1} @ATTRIBUTE 6_C {0,1} @ATTRIBUTE 6_G {0,1} @ATTRIBUTE class {true,false} @DATA 0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,true 0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,true [...] Exercise Solution: @RELATION donors.train @ATTRIBUTE -7 {A,C,G,T} @ATTRIBUTE -6 {A,C,G,T} @ATTRIBUTE -5 {A,C,G,T} @ATTRIBUTE -4 {A,C,G,T} [...] @ATTRIBUTE +3 {A,C,G,T} @ATTRIBUTE +4 {A,C,G,T} @ATTRIBUTE +5 {A,C,G,T} @ATTRIBUTE +6 {A,C,G,T} @ATTRIBUTE splicesite {true,false} @DATA C,T,C,C,G,A,A,A,G,G,A,T,T,true T,C,A,G,A,A,G,G,A,G,G,G,C,true T,T,G,G,A,A,G,T,C,G,C,A,G,true [..] donors_trainset.arff Binary Feature Encoding donors_trainset_diffencod.arff Fewer features Four (nominal) values per feature](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classification-by-machine-learning-approaches3005/85/Classification-by-Machine-Learning-Approaches-5-320.jpg)