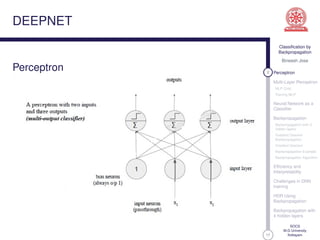
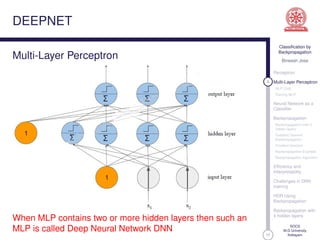
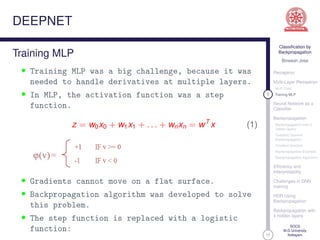
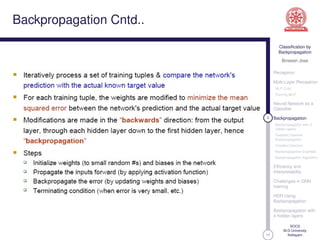
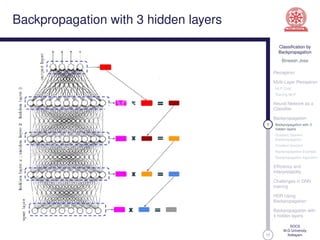
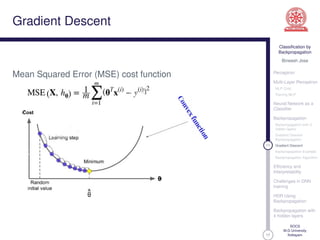
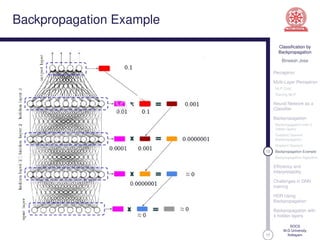
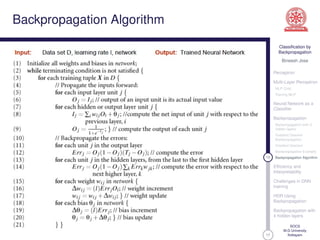
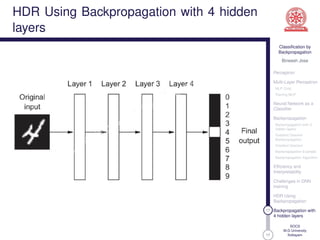
This document discusses classification using backpropagation in deep neural networks. It provides an overview of key concepts like perceptrons, multi-layer perceptrons, training MLPs, neural networks as classifiers, backpropagation, backpropagation with 3 hidden layers, gradient descent backpropagation, and challenges in deep neural network training. The document is authored by Bineesh Jose, a research scholar at the School of Computer Science, M G University in Kottayam.