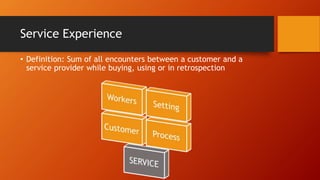
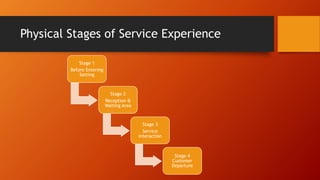
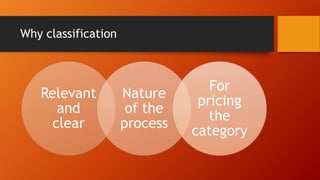
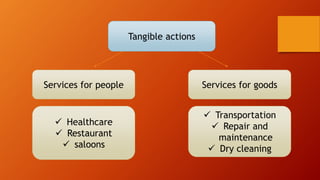
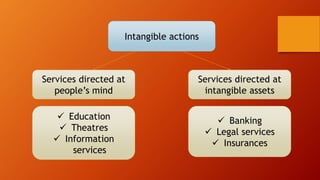
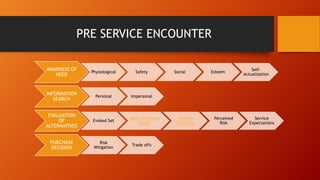
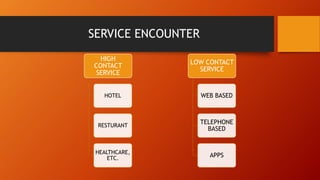
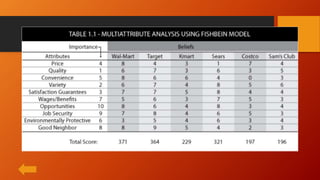
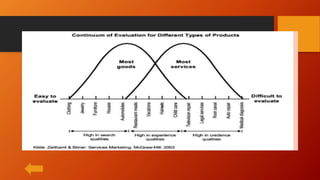
This document discusses key concepts related to services marketing. It defines what services are, noting they are deeds, processes, and performances provided by one entity for another. It outlines four main characteristics of services: intangibility, heterogeneity, inseparability, and perishability. The document also discusses the importance of the services sector, defines customer experience, and maps the physical stages a customer goes through during a service experience. It provides examples of these stages for banking services. Finally, it covers classifications of services and the consumer buying decision process as it relates to pre, during, and post service encounters.