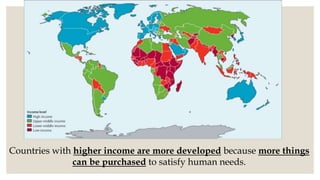
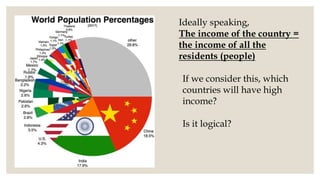
The document discusses development, highlighting the differences between growth and development and exploring various developmental goals across different demographics. It emphasizes that development is subjective and can mean different things to different groups, leading to potential conflicts in aspirations. Additionally, it examines national development metrics, including income measures, and the importance of public facilities and quality of life indicators.
























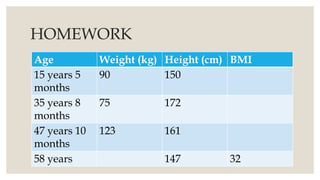
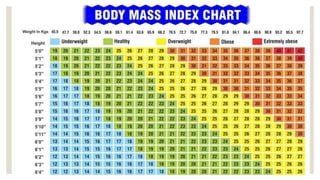
![BODY MASS INDEX [BMI]
Important means
to understand
nutrition level of
person.
Calculation
1. take the weight
in kilograms (kg)
2. convert the
height measured
in centimetres
into metres (m)
3. BMI = kg/m2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/economicschapter1development-240507185946-449d255b/85/Economics_Chapter-1_Development-pptx-class-10-31-320.jpg)


![HOMEWORK [Mark in Textbook]
4. What is the main criterion used by the World Bank in classifying different
countries? What are the limitations of this criterion, if any?
5. In what respects is the criterion used by the UNDP for measuring
development different from the one used by the World Bank?
6. Why do we use averages? Are there any limitations to their use? Illustrate
with your own examples related to development.
9. Why is the issue of sustainability important for development?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/economicschapter1development-240507185946-449d255b/85/Economics_Chapter-1_Development-pptx-class-10-37-320.jpg)
