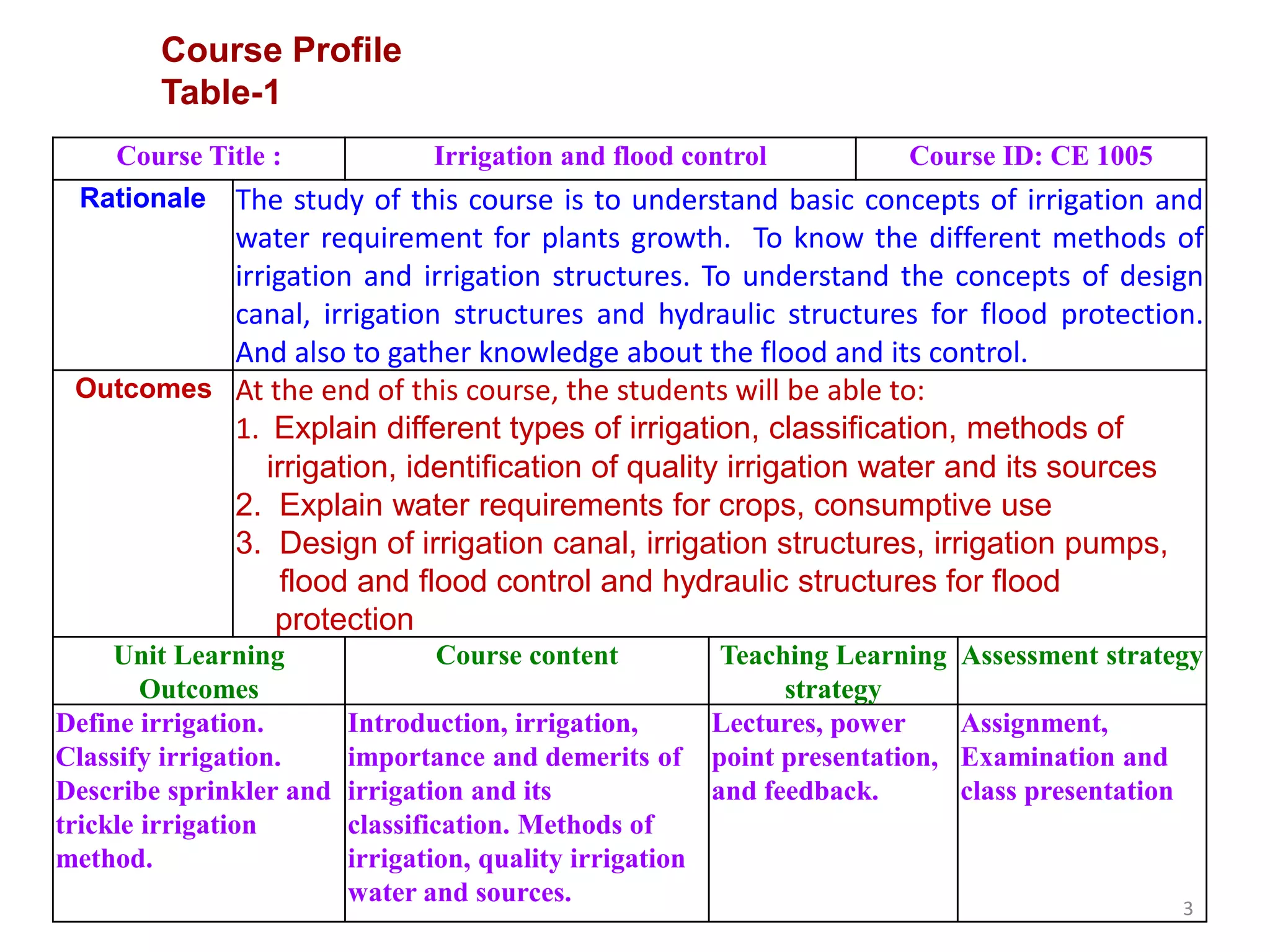
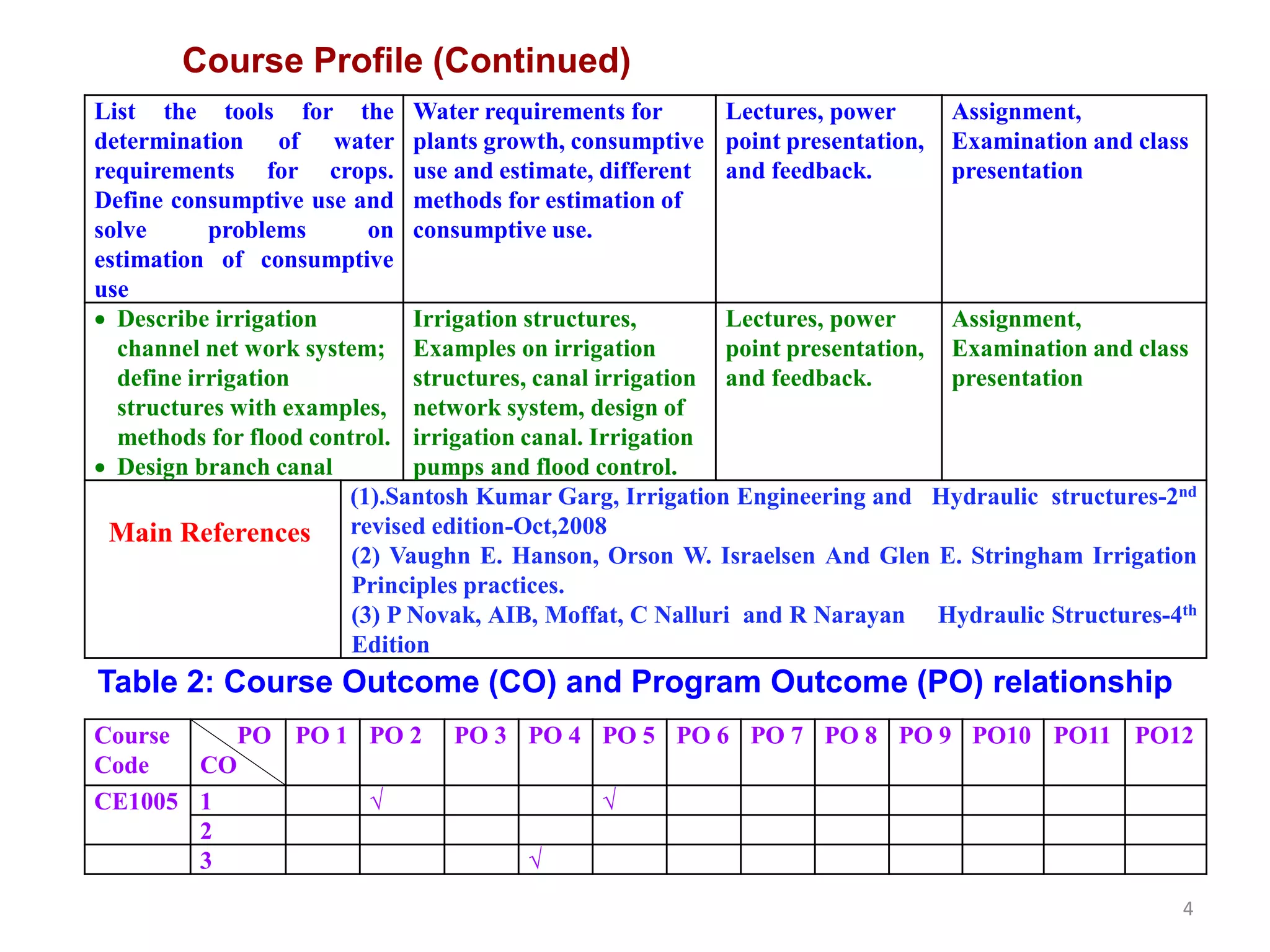
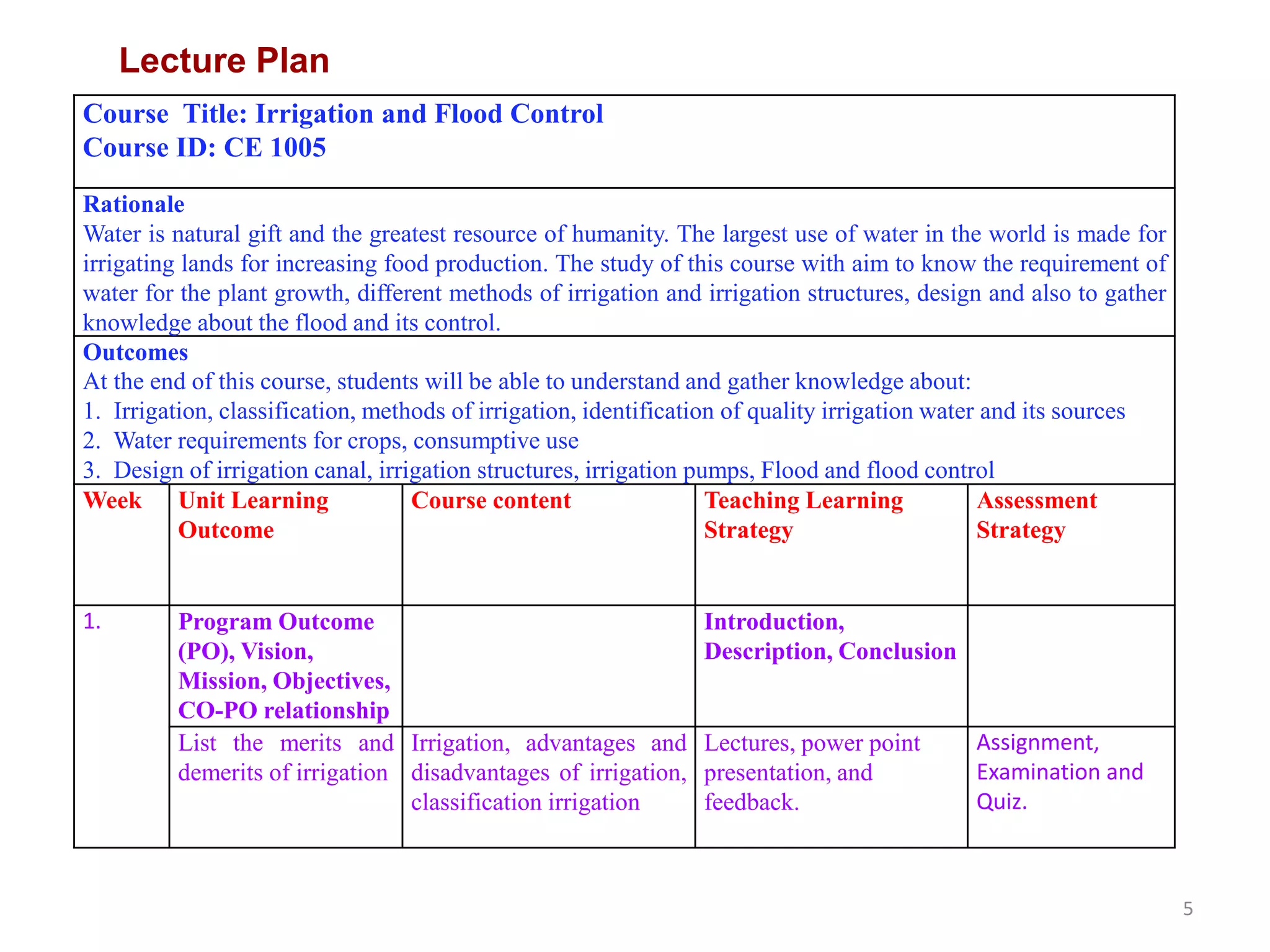
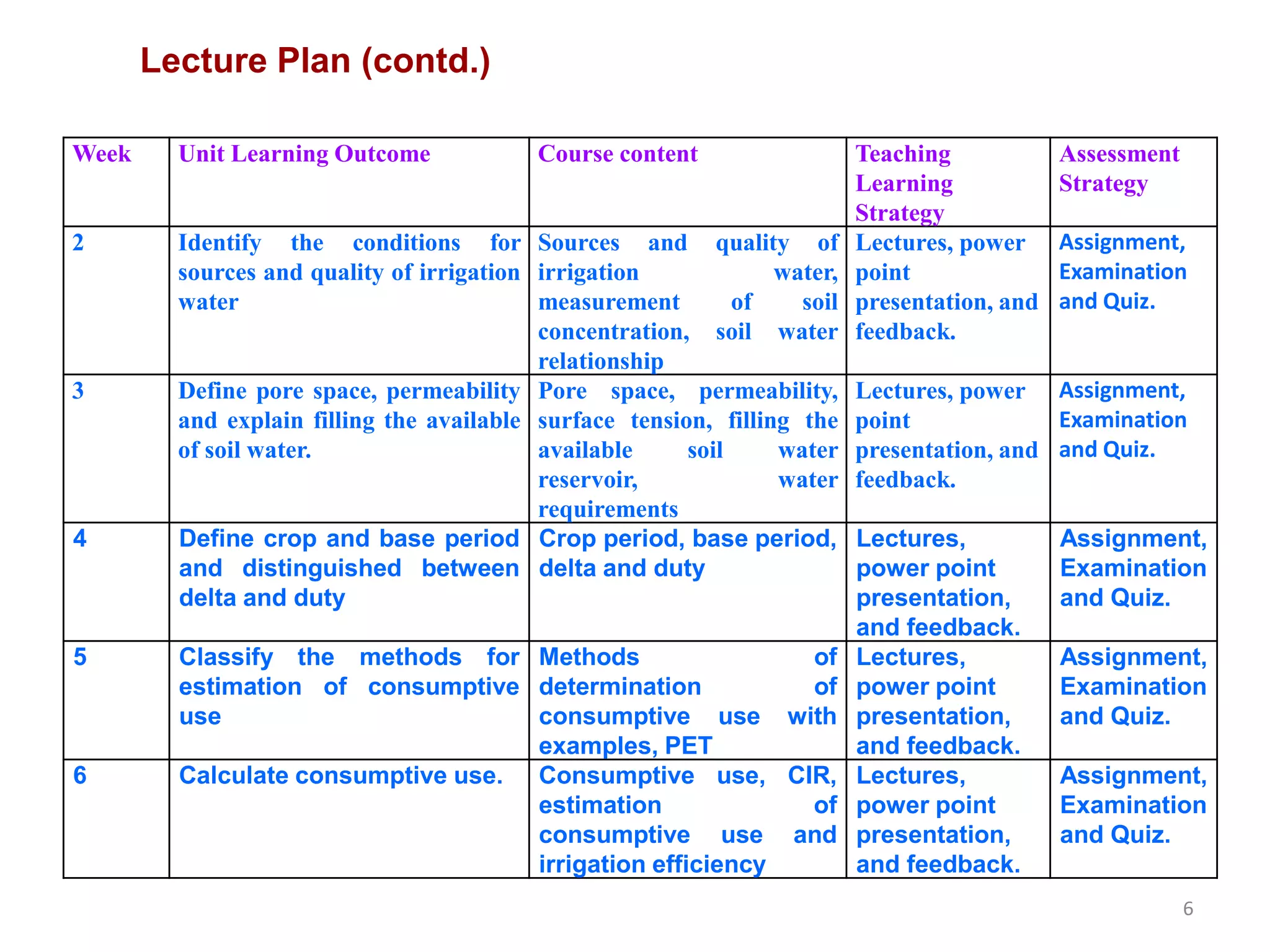
The document outlines a course on Irrigation and Flood Control (CE 1005) at the World University of Bangladesh, focusing on essential irrigation concepts, methods, design of irrigation structures, and flood control. The university's mission is to provide quality education for academic and personal growth while producing leaders in civil engineering for national development. Course outcomes include understanding various irrigation methods, crop water requirements, and designing relevant structures to enhance agricultural practices in the context of Bangladesh.