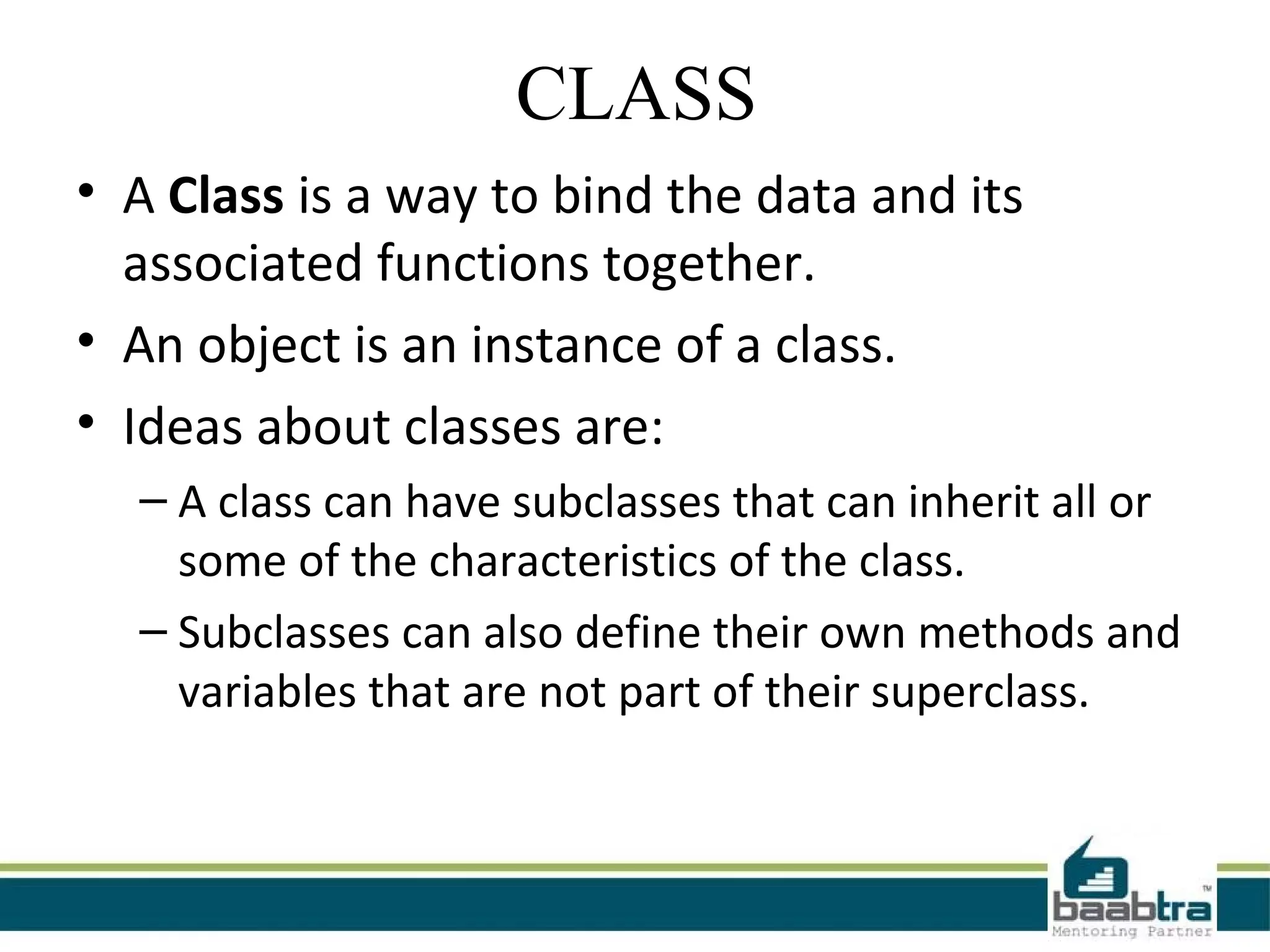
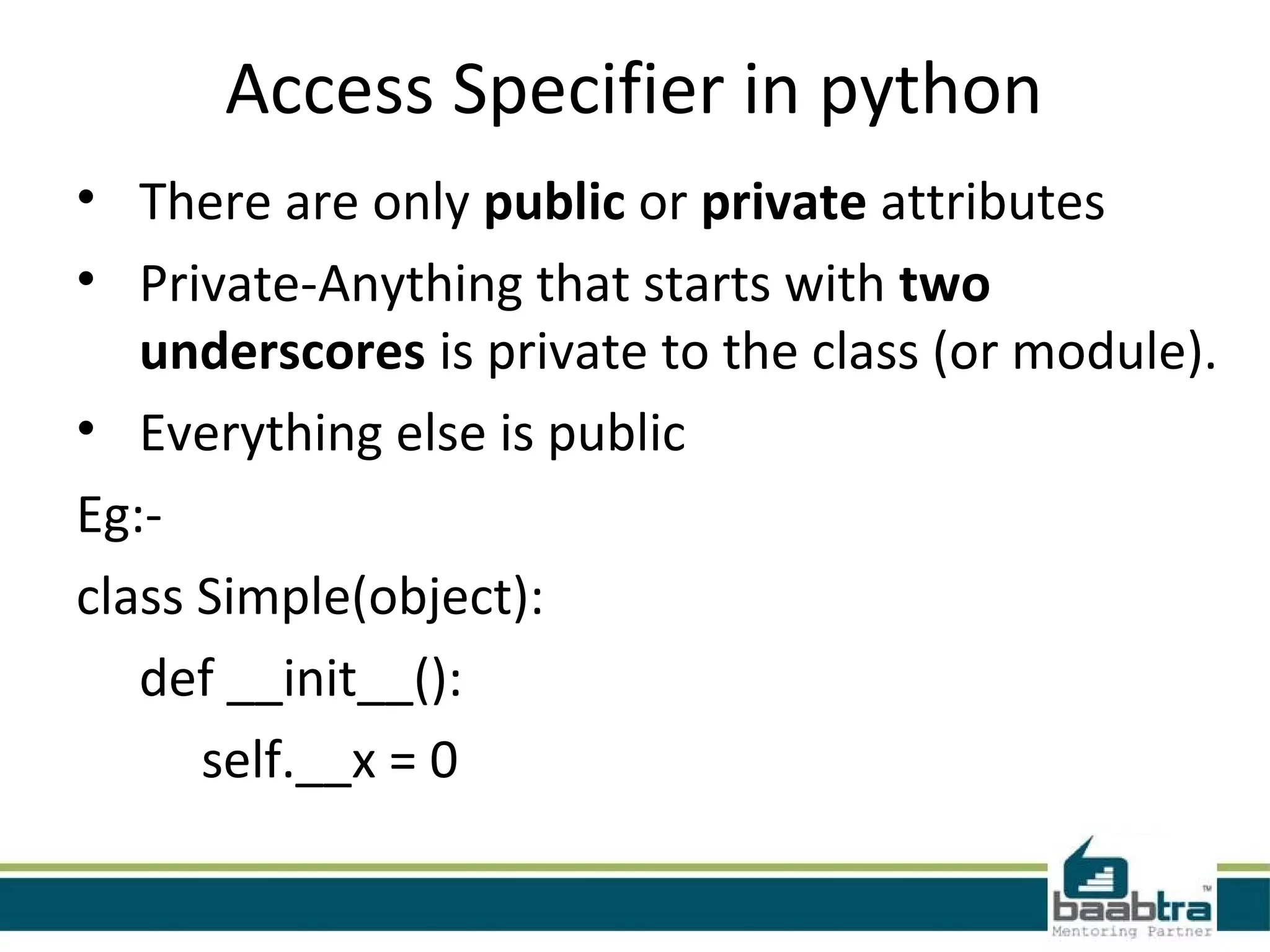
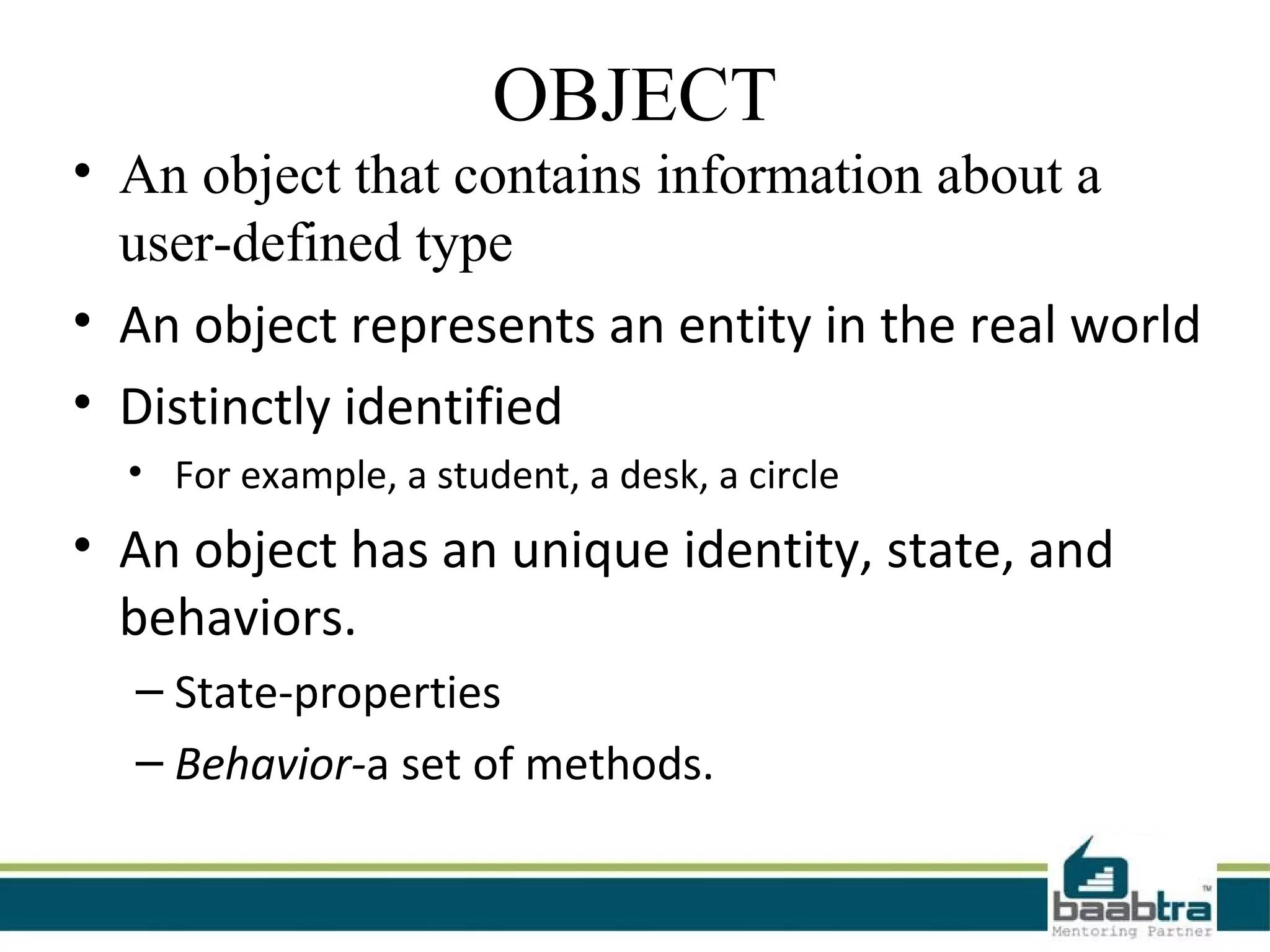
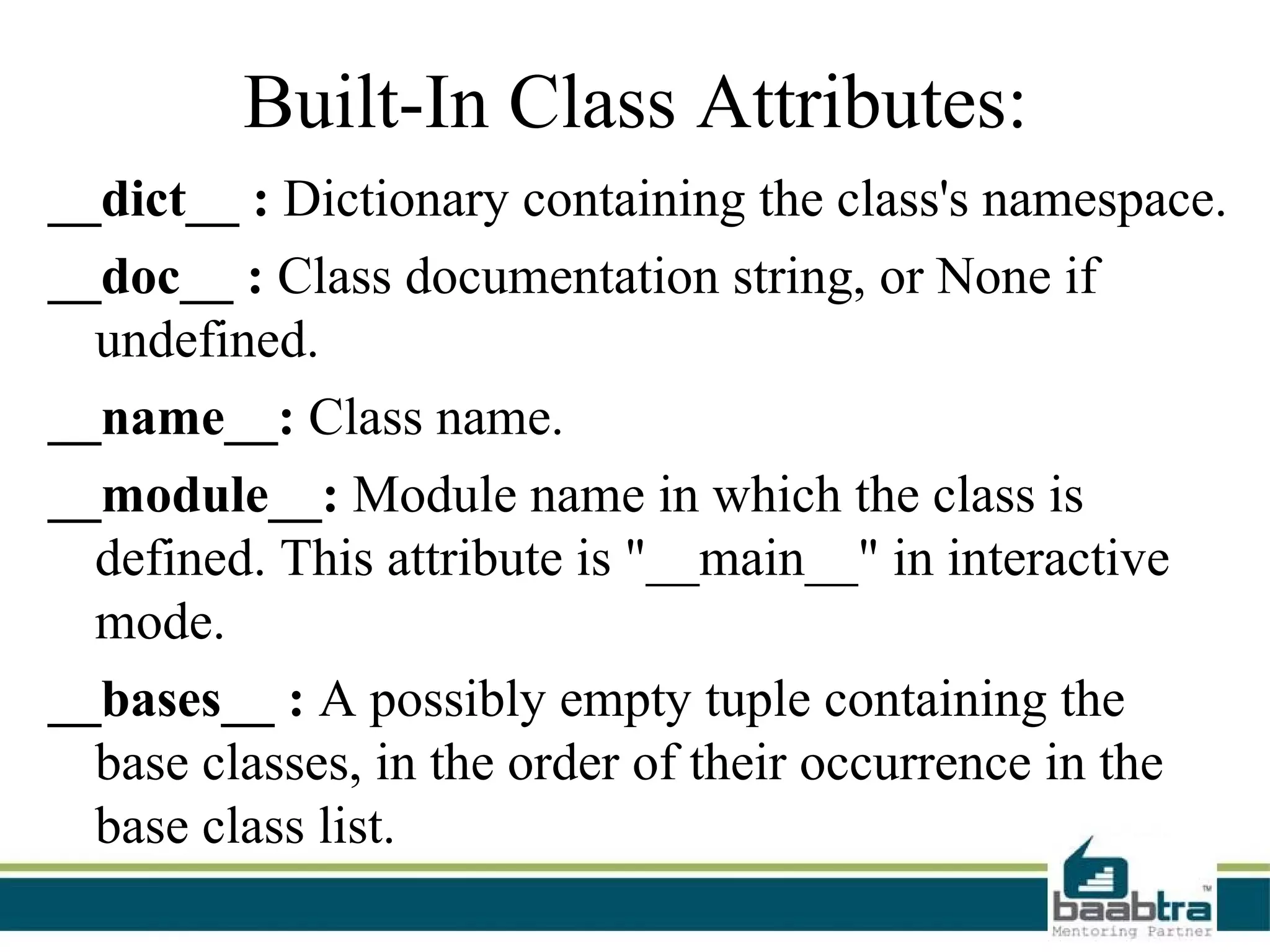
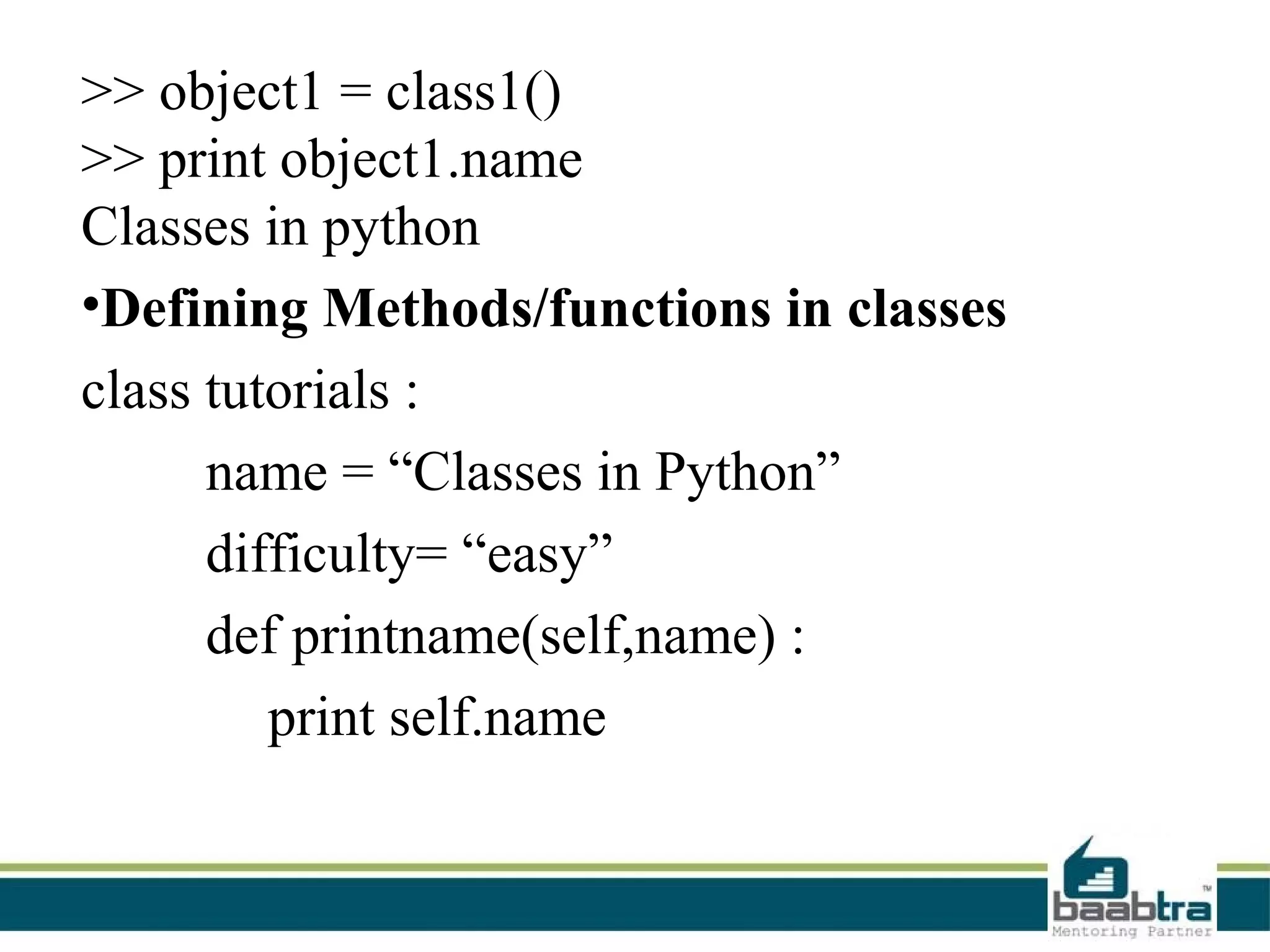
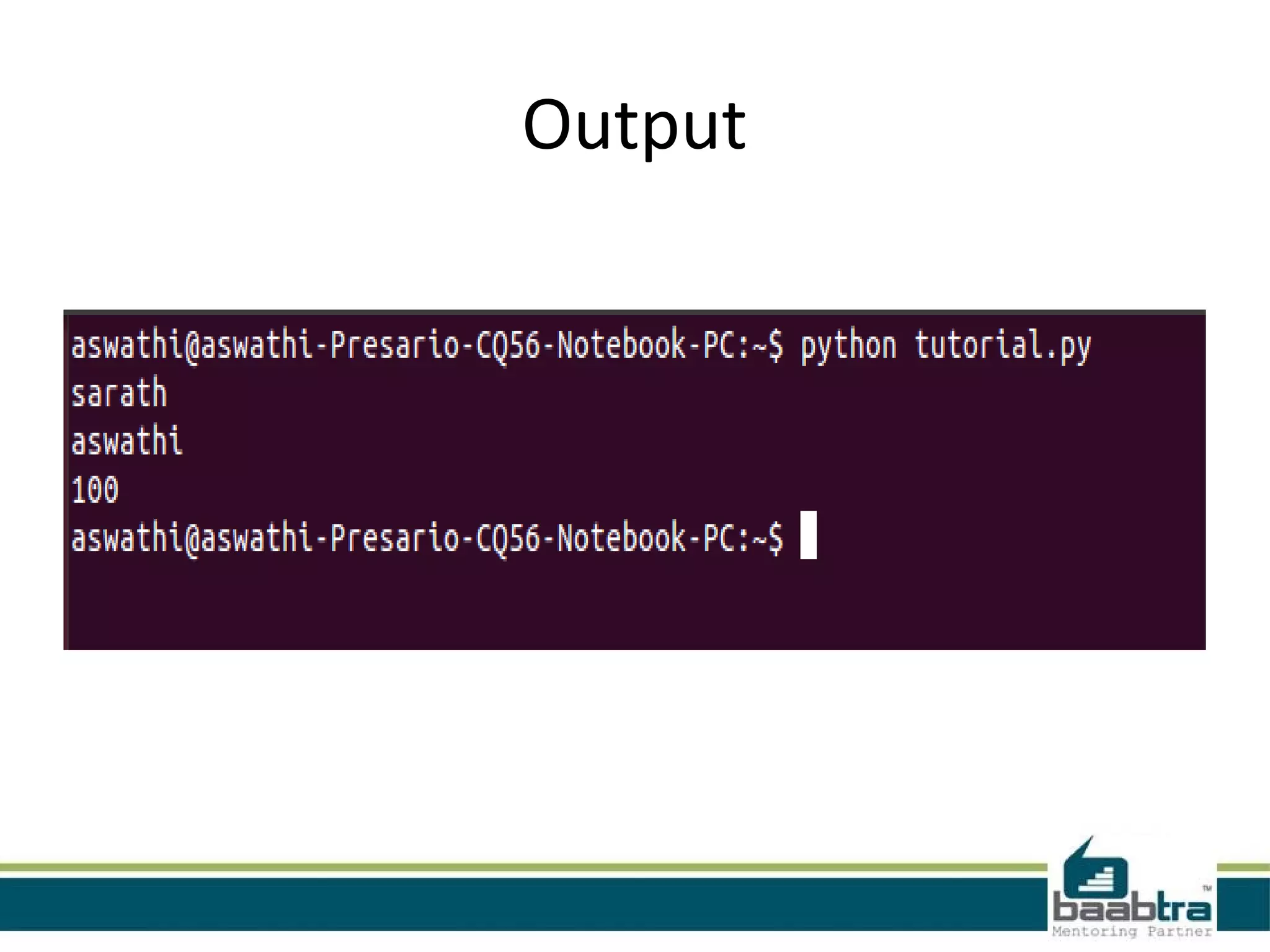
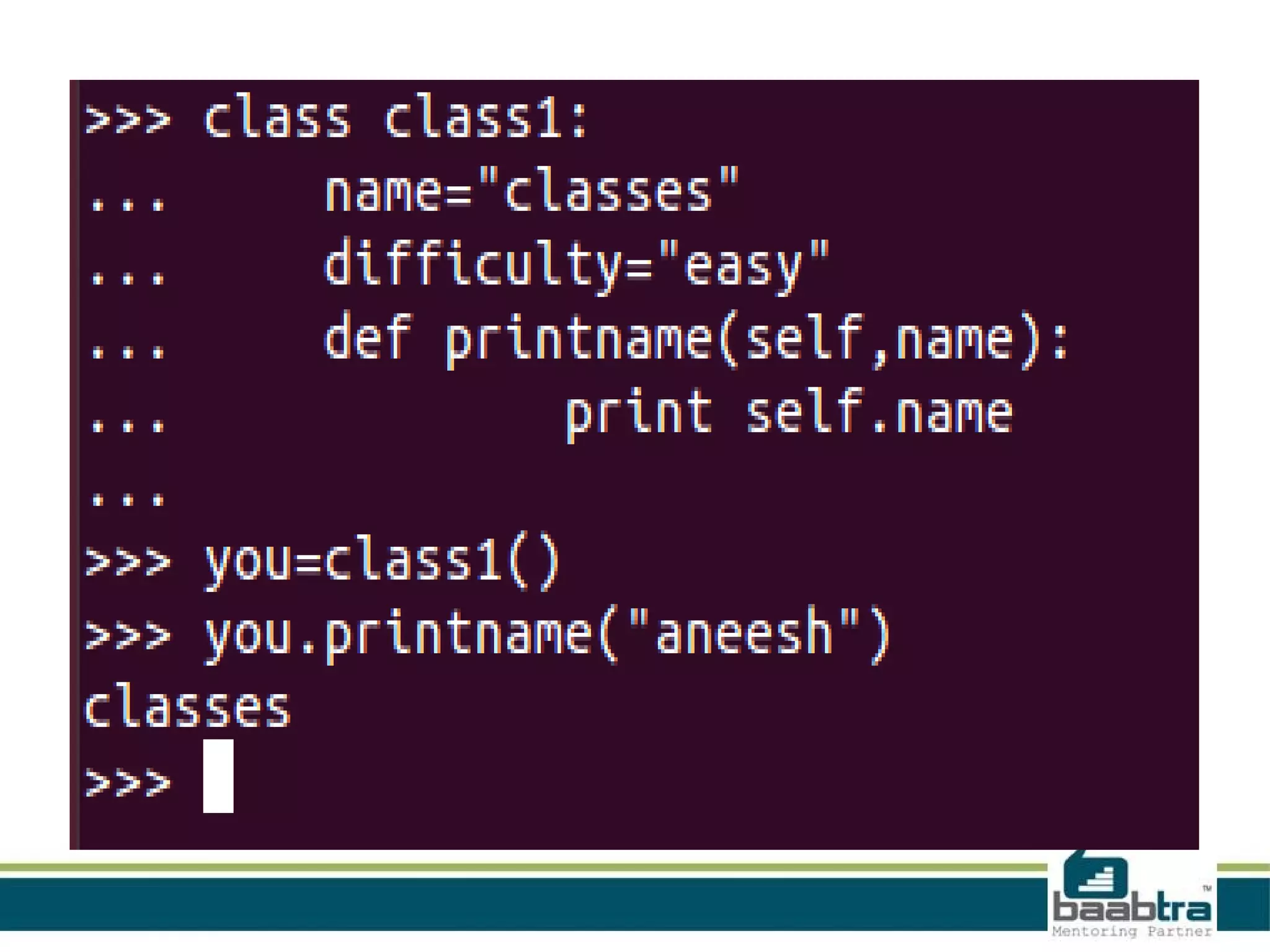
This document provides an overview of classes and objects in Python. It defines a class as a way to bind data and functions together. An object is an instance of a class and represents real-world entities with unique identities and behaviors. The document discusses class attributes like __dict__, __doc__, and __name__. It also covers access specifiers like private, protected, and public and provides examples of declaring classes and creating class objects in Python.